Adaptive nonparametric regression
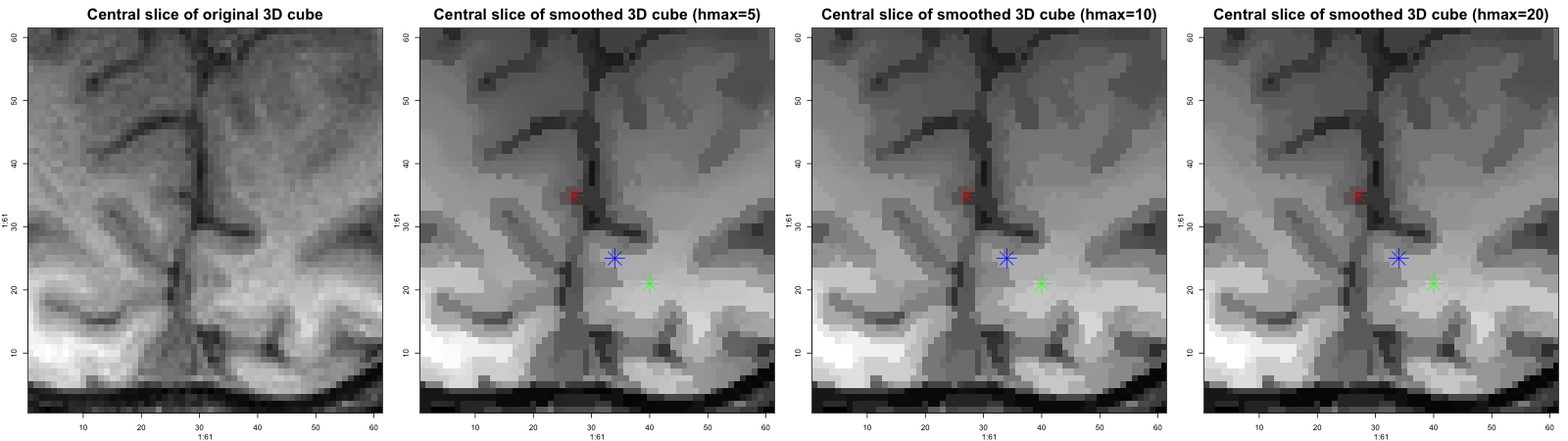
Successful statistical modeling and data analysis often requires the use of smoothing procedures that can adapt to the unknown underlying structure. This includes an intrinsic detection of edges or discontinuities in imaging or signal processing as well as non-stationarities in time series. Established parametric and nonparametric methods often provide results that do not sufficiently meet demands from applications. The general principle of structural adaptation forms the basis of most of the new smoothing algorithms developed at WIAS. This approach enables an efficient description and analysis of complex discontinuous models. Within the recent years a series of innovative approaches and algorithms has been developed. Examples are adaptive weights smoothing (AWS) (Polzehl & Spokoiny 2000), , propagation separation methods (PS), (Polzehl & Spokoiny 2006, Becker & Mathé 2013), Pointwise Adaptive Methods (PA), (Spokoiny 1998, Polzehl & Spokoiny 2003, Spokoiny & Vial 2009), local model selection (LMS), stagewise aggregation (SA) and (Belomestny & Spokoiny 2007) local change point detection (LCP) (Mercurio & Spokoiny 2004, Spokoiny 2009). All these procedures are based on a new local parametric approach and have been justified within a series of publications on theoretical results. In this context important problems and questions in the field of modern parametric and nonparametric statistics have been solved. This includes the problem of automatic selection of smoothing parameters in case of qualitative structural assumptions. Structural adaptive methods have been developed and investigated for several classes of statistical models.Apart from regression this especially includes nonstationary time series and volatility models but also adaptive classification methods and models for extremes. Strong methodological connections exist to adaptive methods for dimension reduction and to multiscale methods. Several algorithms have been implemented as contributed packages ( adaptive weights smoothing aws, adaptive image processing adimpro, functional magnetic resonance imaging fmri and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging dti) (Image processing/Neuroimaging Packages) of the R Environment for Statistical Computing .
Software Adaptive weights clustering
Software description can be found at a separate page.Dimension reduction
The problem of dimension reduction arises in various forms with modeling or analysis of complex, usually high-dimensional data structures. Examples are relations between variables in regression models where single- or multi-index models (Hristache et al. 2001, Dalalyan et al. 2008) allow for a more efficient description and methods that infer on linear or nonlinear subspaces that contain most of the relevant information on underlying structures. Such models and corresponding procedures are often a prerequisite for an efficient statistical modeling and data analysis. Classical procedures like principal component analysis (PCA) or independent component analysis (ICA) are based on strict assumptions and are of limited use in this context. Based on the principle of structural adaptation novel methods and procedures for dimension reduction have been developed at WIAS. The proposed dimension reduction methods for regression can be interpreted as nonlinear PCA. These methods allow to efficiently estimate a dimension reduction space after a finite number of iterations. Non-Gaussian componet analysis (NGCA) (Blanchard et al. 2006 , Diederichs et al. 2013) provides a new promising approach to the analysis of high-dimensional data structures. It is based on the assumption that structure lives in low-dimensional subspaces and projections onto these subspaces are characterized by non-Gaussianity. This assumption is then used to identify these informative subspaces.Simultaneous Statistical Inference
The more questions you ask, the more wrong answers you are expected to receive - even if every single source of your information is quite trustworthy. We consider cases in which the sources of information are data, and the questions are formalized by statistical hypothesis-alternative pairs. From the mathematical point of view, this leads to multiple test problems. Criteria and methods (multiple tests) are developed which ensure that with high probability not too many wrong decisions are made, even if many hypotheses are of interest under the scope of one and the same statistical model, i. e., regarding one and the same dataset.
High-throughput technologies in different fields of modern life sciences have led to massive multiplicity and given rise to multiple test problems with more hypotheses than observations. Driven by these developments, also new statistical paradigms have arisen. In particular, it is fair to say that a new era of multiple testing began when Yoav Benjamini and Yosef Hochberg formally introduced the false discovery rate (FDR) and the linear step-up test for FDR control in 1995.
At WIAS, FDR methodology and multivariate multiple tests are developed for temporally, spatially, or spatio-temporally dependent data. Furthermore, multiple test theory can also be used in related fields of simultaneous statistical inference and statistical learning, for example in the context of binary classification and model selection. Our contributions to simultaneous statistical inference are made with particular emphasis on life science applications in (behavioral) genetics, epigenetics, brain-computer interfacing, functional magnetic resonance imaging, and neuroeconomics. Main publications: Blanchard & Roquain 2009, Blanchard et al. 2010, Dickhaus 2013, Dickhaus et al 2013, Bodnar & Dickhaus 2017, Schildknecht et al. 2015, Schildknecht et al. 2016.
Publications
 Monographs
Monographs
-
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Magnetic Resonance Brain Imaging: Modeling and Data Analysis using R, 2nd Revised Edition, Series: Use R!, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2023, 258 pages, (Monograph Published), DOI 10.1007/978-3-031-38949-8 .
Abstract
This book discusses the modeling and analysis of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data acquired from the human brain. The data processing pipelines described rely on R. The book is intended for readers from two communities: Statisticians who are interested in neuroimaging and looking for an introduction to the acquired data and typical scientific problems in the field; and neuroimaging students wanting to learn about the statistical modeling and analysis of MRI data. Offering a practical introduction to the field, the book focuses on those problems in data analysis for which implementations within R are available. It also includes fully worked examples and as such serves as a tutorial on MRI analysis with R, from which the readers can derive their own data processing scripts. The book starts with a short introduction to MRI and then examines the process of reading and writing common neuroimaging data formats to and from the R session. The main chapters cover three common MR imaging modalities and their data modeling and analysis problems: functional MRI, diffusion MRI, and Multi-Parameter Mapping. The book concludes with extended appendices providing details of the non-parametric statistics used and the resources for R and MRI data.The book also addresses the issues of reproducibility and topics like data organization and description, as well as open data and open science. It relies solely on a dynamic report generation with knitr and uses neuroimaging data publicly available in data repositories. The PDF was created executing the R code in the chunks and then running LaTeX, which means that almost all figures, numbers, and results were generated while producing the PDF from the sources. -
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Magnetic Resonance Brain Imaging: Modeling and Data Analysis using R, Series: Use R!, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2019, 231 pages, (Monograph Published), DOI 10.1007/978-3-030-29184-6 .
Abstract
This book discusses the modeling and analysis of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data acquired from the human brain. The data processing pipelines described rely on R. The book is intended for readers from two communities: Statisticians who are interested in neuroimaging and looking for an introduction to the acquired data and typical scientific problems in the field; and neuroimaging students wanting to learn about the statistical modeling and analysis of MRI data. Offering a practical introduction to the field, the book focuses on those problems in data analysis for which implementations within R are available. It also includes fully worked examples and as such serves as a tutorial on MRI analysis with R, from which the readers can derive their own data processing scripts. The book starts with a short introduction to MRI and then examines the process of reading and writing common neuroimaging data formats to and from the R session. The main chapters cover three common MR imaging modalities and their data modeling and analysis problems: functional MRI, diffusion MRI, and Multi-Parameter Mapping. The book concludes with extended appendices providing details of the non-parametric statistics used and the resources for R and MRI data.The book also addresses the issues of reproducibility and topics like data organization and description, as well as open data and open science. It relies solely on a dynamic report generation with knitr and uses neuroimaging data publicly available in data repositories. The PDF was created executing the R code in the chunks and then running LaTeX, which means that almost all figures, numbers, and results were generated while producing the PDF from the sources. -
H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, Chapter 2: Incomparability/Inequality Measures and Clustering, in: Partial Order Concepts in Applied Sciences, M. Fattore, R. Brüggemann, eds., Springer International Publishing, New York, 2017, pp. 21--34, (Chapter Published).
-
V. Spokoiny, Th. Dickhaus, Basics of Modern Mathematical Statistics, 18 of Springer Texts in Statistics, Springer, Berlin et al., 2015, 296 pages, (Monograph Published).
-
H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, Chapter 3: Measures of Incomparability and of Inequality and Their Applications, in: Multi-indicator Systems and Modelling in Partial Order, R. Brüggemann, L. Carlsen, J. Wittmann, eds., Springer, New York et al., 2014, pp. 47--67, (Chapter Published).
-
TH. Dickhaus, Simultaneous Statistical Inference, Springer, Berlin et al., 2014, 180 pages, (Monograph Published).
-
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Chapter 4: Structural Adaptive Smoothing: Principles and Applications in Imaging, in: Mathematical Methods for Signal and Image Analysis and Representation, L. Florack, R. Duits, G. Jongbloed, M.-C. VAN Lieshout, L. Davies, eds., 41 of Computational Imaging and Vision, Springer, London et al., 2012, pp. 65--81, (Chapter Published).
 Articles in Refereed Journals
Articles in Refereed Journals
-
N. Puchkin, F. Noskov, V. Spokoiny, Sharper dimension-free bounds on the Frobenius distance between sample covariance and its expectation, Bernoulli. Official Journal of the Bernoulli Society for Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 31 (2025), pp. 1664--1691, DOI 10.3150/24-BEJ1787 .
-
L. Schmitz, N. Tapia, Free generators and Hoffman's isomorphism for the two-parameter shuffle algebra, Communications in Algebra, (2025), published online: 01.11.2025, DOI 10.1080/00927872.2025.2569445 .
Abstract
Signature transforms have recently been extended to data indexed by two and more parameters. With free Lyndon generators, ideas from B∞-algebras and a novel two-parameter Hoffman exponential, we provide three classes of isomorphisms between the underlying two-parameter shuffle and quasi-shuffle algebras. In particular, we provide a Hopf algebraic connection to the (classical, one-parameter) shuffle algebra over the extended alphabet of connected matrix compositions. -
L. Mertenskötter, M. Kantner, Frequency noise characterization of narrow-linewidth lasers: A Bayesian approach, IEEE Photonics Journal, 16 (2024), pp. 0601407/1--0601407/7, DOI 10.1109/JPHOT.2024.3385184 .
Abstract
We describe a Bayesian estimation approach to infer on the frequency noise characteristics of narrow-linewidth semiconductor lasers from delayed self-heterodyne beat note measurements. Our technique is grounded in a statistical model of the measurement process that accounts for both the impact of the interferometer and the detector noise. The approach yields accurate results, even in scenarios where the intrinsic linewidth plateau is obscured by detector noise. The analysis is carried out using a Markov-chain Monte Carlo method in the frequency domain and exploits prior knowledge about the statistical distribution of the data. The method is validated using simulated time series data from a stochastic laser rate equation model incorporating 1/f -type non-Markovian noise. -
G. Dong, M. Flaschel, M. Hintermüller, K. Papafitsoros, C. Sirotenko, K. Tabelow, Data--driven methods for quantitative imaging, GAMM-Mitteilungen, 48 (2025), pp. e202470014/1-- e202470014/35 (published online on 06.11.2024), DOI 10.1002/gamm.202470014 .
Abstract
In the field of quantitative imaging, the image information at a pixel or voxel in an underlying domain entails crucial information about the imaged matter. This is particularly important in medical imaging applications, such as quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (qMRI), where quantitative maps of biophysical parameters can characterize the imaged tissue and thus lead to more accurate diagnoses. Such quantitative values can also be useful in subsequent, automatized classification tasks in order to discriminate normal from abnormal tissue, for instance. The accurate reconstruction of these quantitative maps is typically achieved by solving two coupled inverse problems which involve a (forward) measurement operator, typically ill-posed, and a physical process that links the wanted quantitative parameters to the reconstructed qualitative image, given some underlying measurement data. In this review, by considering qMRI as a prototypical application, we provide a mathematically-oriented overview on how data-driven approaches can be employed in these inverse problems eventually improving the reconstruction of the associated quantitative maps. -
C. Kiss, L. Németh, B. Vető , Modelling the age distribution of longevity leaders, Scientific Reports, 14 (2024), pp. 20592/1--20592/13, DOI 10.1038/s41598-024-71444-w .
Abstract
Human longevity leaders with remarkably long lifespan play a crucial role in the advancement of longevity research. In this paper, we propose a stochastic model to describe the evolution of the age of the oldest person in the world by a Markov process, in which we assume that the births of the individuals follow a Poisson process with increasing intensity, lifespans of individuals are independent and can be characterized by a gamma?Gompertz distribution with time-dependent parameters. We utilize a dataset of the world?s oldest person title holders since 1955, and we compute the maximum likelihood estimate for the parameters iteratively by numerical integration. Based on our preliminary estimates, the model provides a good fit to the data and shows that the age of the oldest person alive increases over time in the future. The estimated parameters enable us to describe the distribution of the age of the record holder process at a future time point. -
R.A. Vandermeulen, R. Saitenmacher, Generalized identifiability bounds for mixture models with grouped samples, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 70 (2024), pp. 2746--2758, DOI 10.1109/TIT.2024.3367433 .
-
M. Kantner, L. Mertenskötter, Accurate evaluation of self-heterodyne laser linewidth measurements using Wiener filters, Optics Express, 31 (2023), pp. 15994--16009, DOI 10.1364/OE.485866 .
Abstract
Self-heterodyne beat note measurements are widely used for the experimental characterization of the frequency noise power spectral density (FN-PSD) and the spectral linewidth of lasers. The measured data, however, must be corrected for the transfer function of the experimental setup in a post-processing routine. The standard approach disregards the detector noise and thereby induces reconstruction artifacts, i.e., spurious spikes, in the reconstructed FN-PSD. We introduce an improved post-processing routine based on a parametric Wiener filter that is free from reconstruction artifacts, provided a good estimate of the signal-to-noise ratio is supplied. Building on this potentially exact reconstruction, we develop a new method for intrinsic laser linewidth estimation that is aimed at deliberate suppression of unphysical reconstruction artifacts. Our method yields excellent results even in the presence of strong detector noise, where the intrinsic linewidth plateau is not even visible using the standard method. The approach is demonstrated for simulated time series from a stochastic laser model including 1 / f-type noise. -
O. Klein, On forward and inverse uncertainty quantification for a model for a magneto mechanical device involving a hysteresis operator, Applications of Mathematics, 68 (2023), pp. 795--828, DOI 10.21136/AM.2023.0080-23 .
Abstract
Modeling real world objects and processes one may has to deal with hysteresis effects but also with uncertainties. Following D. Davino, P. Krejčí, and C. Visone: Fully coupled modeling of magneto-mechanical hysteresis through `thermodynamic' compatibility. Smart Mater. Struct., 22(9), (2013) 0950099, a model for a magnetostrictive material involving a generalized Prandtl- Ishlinskiĭ-operator is considered here. Using results of measurements, some parameters in the model are determined and inverse Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) is used to determine random densities to describe the remaining parameters and their uncertainties. Afterwards, the results are used do perform forward UQ and to compare the results with measured data. This extends some of the results from O. Klein, D. Davino, and C. Visone. On forward and inverse uncertainty quantification for models involving hysteresis operators. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 15 (2020) 53. -
V. Spokoiny, Dimension free non-asymptotic bounds on the accuracy of high dimensional Laplace approximation, SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, 11 (2023), pp. 1044--1068, DOI 10.1137/22M1495688 .
Abstract
This note attempts to revisit the classical results on Laplace approximation in a modern non-asymptotic and dimension free form. Such an extension is motivated by applications to high dimensional statistical and optimization problems. The established results provide explicit non-asymptotic bounds on the quality of a Gaussian approximation of the posterior distribution in total variation distance in terms of the so called empheffective dimension ( dimL ). This value is defined as interplay between information contained in the data and in the prior distribution. In the contrary to prominent Bernstein - von Mises results, the impact of the prior is not negligible and it allows to keep the effective dimension small or moderate even if the true parameter dimension is huge or infinite. We also address the issue of using a Gaussian approximation with inexact parameters with the focus on replacing the Maximum a Posteriori (MAP) value by the posterior mean and design the algorithm of Bayesian optimization based on Laplace iterations. The results are specified to the case of nonlinear regression. -
N. Puchkin, V. Spokoiny, Structure-adaptive manifold estimation, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., 23 (2022), pp. 1--62.
Abstract
We consider a problem of manifold estimation from noisy observations. Many manifold learning procedures locally approximate a manifold by a weighted average over a small neighborhood. However, in the presence of large noise, the assigned weights become so corrupted that the averaged estimate shows very poor performance. We suggest a novel computationally efficient structure-adaptive procedure, which simultaneously reconstructs a smooth manifold and estimates projections of the point cloud onto this manifold. The proposed approach iteratively refines the weights on each step, using the structural information obtained at previous steps. After several iterations, we obtain nearly öracle" weights, so that the final estimates are nearly efficient even in the presence of relatively large noise. In our theoretical study we establish tight lower and upper bounds proving asymptotic optimality of the method for manifold estimation under the Hausdorff loss. Our finite sample study confirms a very reasonable performance of the procedure in comparison with the other methods of manifold estimation. -
A. Kroshnin, V. Spokoiny, A. Suvorikova, Statistical inference for Bures--Wasserstein barycenters, The Annals of Applied Probability, 31 (2021), pp. 1264--1298, DOI 10.1214/20-AAP1618 .
-
L. Antoine, P. Pigato, Maximum likelihood drift estimation for a threshold diffusion, , published online on 23.10.2019, urlhttps://doi.org/10.1111/sjos.12417, DOI 10.1111/sjos.12417 .
Abstract
We study the maximum likelihood estimator of the drift parameters of a stochastic differential equation, with both drift and diffusion coefficients constant on the positive and negative axis, yet discontinuous at zero. This threshold diffusion is called the drifted Oscillating Brownian motion. The asymptotic behaviors of the positive and negative occupation times rule the ones of the estimators. Differently from most known results in the literature, we do not restrict ourselves to the ergodic framework: indeed, depending on the signs of the drift, the process may be ergodic, transient or null recurrent. For each regime, we establish whether or not the estimators are consistent; if they are, we prove the convergence in long time of the properly rescaled difference of the estimators towards a normal or mixed normal distribution. These theoretical results are backed by numerical simulations. -
N. Alia, V. John, S. Ollila, Re-visiting the single-phase flow model for liquid steel ladle stirred by gas, Applied Mathematical Modelling. Simulation and Computation for Engineering and Environmental Systems. Elsevier Science Inc., New York, NY. English, English abstracts., 67 (2019), pp. 549--556 (published online on 21.11.2018), DOI 10.1016/j.apm.2018.11.005 .
-
A. Lejay, P. Pigato, Statistical estimation of the oscillating Brownian motion, Bernoulli. Official Journal of the Bernoulli Society for Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 24 (2018), pp. 3568--3602, DOI 10.3150/17-BEJ969 .
Abstract
We study the asymptotic behavior of estimators of a two-valued, discontinuous diffusion coefficient in a Stochastic Differential Equation, called an Oscillating Brownian Motion. Using the relation of the latter process with the Skew Brownian Motion, we propose two natural consistent estimators, which are variants of the integrated volatility estimator and take the occupation times into account. We show the stable convergence of the renormalized errors? estimations toward some Gaussian mixture, possibly corrected by a term that depends on the local time. These limits stem from the lack of ergodicity as well as the behavior of the local time at zero of the process. We test both estimators on simulated processes, finding a complete agreement with the theoretical predictions. -
D. Belomestny, H. Mai, J.G.M. Schoenmakers, Generalized Post--Widder inversion formula with application to statistics, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 455 (2017), pp. 89--104.
Abstract
In this work we derive an inversion formula for the Laplace transform of a density observed on a curve in the complex domain, which generalizes the well known Post-Widder formula. We establish convergence of our inversion method and derive the corresponding convergence rates for the case of a Laplace transform of a smooth density. As an application we consider the problem of statistical inference for variance-mean mixture models. We construct a nonparametric estimator for the mixing density based on the generalized Post-Widder formula, derive bounds for its root mean square error and give a brief numerical example. -
Y. Nesterov, V. Spokoiny, Random gradient-free minimization of convex functions, Foundations of Computational Mathematics. The Journal of the Society for the Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 17 (2017), pp. 527--566.
Abstract
Summary: In this paper, we prove new complexity bounds for methods of convex optimization based only on computation of the function value. The search directions of our schemes are normally distributed random Gaussian vectors. It appears that such methods usually need at most nn times more iterations than the standard gradient methods, where nn is the dimension of the space of variables. This conclusion is true for both nonsmooth and smooth problems. For the latter class, we present also an accelerated scheme with the expected rate of convergence O(n2k2)O(n2k2), where kk is the iteration counter. For stochastic optimization, we propose a zero-order scheme and justify its expected rate of convergence O(nk1/2)O(nk1/2). We give also some bounds for the rate of convergence of the random gradient-free methods to stationary points of nonconvex functions, for both smooth and nonsmooth cases. Our theoretical results are supported by preliminary computational experiments. -
H.-J. Mucha, Assessment of stability in partitional clustering using resampling techniques, Archives of Data Science Series A, 1 (2017), pp. 21--35, DOI 10.5445/KSP/1000058747/02 .
-
V. Spokoiny, Penalized maximum likelihood estimation and effective dimension, Annales de l'Institut Henri Poincare. Probabilites et Statistiques, 53 (2017), pp. 389--429, DOI 10.1214/15-AIHP720 .
-
A. Kalinina, A. Suvorikova, V. Spokoiny, M. Gelfand, Detection of homologous recombination in closely related strains, Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 14 (2016), pp. 1641001/1--1641001/12.
-
A. Andresen, V. Spokoiny, Convergence for an alternation maximization procedure, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., 17 (2016), pp. 1--53.
-
D. Belomestny, J.G.M. Schoenmakers, Statistical inference for time-changed Lévy processes via Mellin transform approach, Stochastic Processes and their Applications, 126 (2016), pp. 2092--2122.
-
A. Gasnikov, P. Dvurechensky, V. Spokoiny, P. Stetsyuk, A. Suvorikova, Superposition of the balancing algorithm and the universal gradient method for search of the regularized Wasserstein barycenter and equilibria in multistage transport models, Proceedings of Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, 8 (2016), pp. 5--24.
-
K. Schildknecht, K. Tabelow, Th. Dickhaus, More specific signal detection in functional magnetic resonance imaging by false discovery rate control for hierarchically structured systems of hypotheses, PLOS ONE, 11 (2016), pp. e0149016/1--e0149016/21, DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0149016 .
-
CH. Bayer, A. Moraes, R. Tempone, P. Villanova, An efficient forward-reverse expectation-maximization algorithm for statistical inference in stochastic reaction networks, Stochastic Analysis and Applications, 34 (2016), pp. 193--231.
-
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Low SNR in diffusion MRI models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 111 (2016), pp. 1480--1490, DOI 10.1080/01621459.2016.1222284 .
Abstract
Noise is a common issue for all magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques such as diffusion MRI and obviously leads to variability of the estimates in any model describing the data. Increasing spatial resolution in MR experiments further diminish the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). However, with low SNR the expected signal deviates from the true value. Common modeling approaches therefore lead to a bias in estimated model parameters. Adjustments require an analysis of the data generating process and a characterization of the resulting distribution of the imaging data. We provide an adequate quasi-likelihood approach that employs these characteristics. We elaborate on the effects of typical data preprocessing and analyze the bias effects related to low SNR for the example of the diffusion tensor model in diffusion MRI. We then demonstrate the relevance of the problem using data from the Human Connectome Project. -
R. Hildebrand, Centro-affine hypersurface immersions with parallel cubic form, Beitrage zur Algebra und Geometrie. Contributions to Algebra and Geometry, 56 (2015), pp. 593--640.
Abstract
We consider non-degenerate centro-affine hypersurface immersions in Rn whose cubic form is parallel with respect to the Levi-Civita connection of the affine metric. There exists a bijective correspondence between homothetic families of proper affine hyperspheres with center in the origin and with parallel cubic form, and Köchers conic ? -domains, which are the maximal connected sets consisting of invertible elements in a real semi-simple Jordan algebra. Every level surface of the ? function in an ? -domain is an affine complete, Euclidean complete proper affine hypersphere with parallel cubic form and with center in the origin. On the other hand, every proper affine hypersphere with parallel cubic form and with center in the origin can be represented as such a level surface. We provide a complete classification of proper affine hyperspheres with parallel cubic form based on the classification of semi-simple real Jordan algebras. Centro-affine hypersurface immersions with parallel cubic form are related to the wider class of real unital Jordan algebras. Every such immersion can be extended to an affine complete one, whose conic hull is the connected component of the unit element in the set of invertible elements in a real unital Jordan algebra. Our approach can be used to study also other classes of hypersurfaces with parallel cubic form. -
K. Schildknecht, S. Olek, Th. Dickhaus, Simultaneous statistical inference for epigenetic data, PLOS ONE, 10 (2015), pp. e0125587/1--e0125587/15.
Abstract
Epigenetic research leads to complex data structures. Since parametric model assumptions for the distribution of epigenetic data are hard to verify we introduce in the present work a nonparametric statistical framework for two-group comparisons. Furthermore, epigenetic analyses are often performed at various genetic loci simultaneously. Hence, in order to be able to draw valid conclusions for specific loci, an appropriate multiple testing correction is necessary. Finally, with technologies available for the simultaneous assessment of many interrelated biological parameters (such as gene arrays), statistical approaches also need to deal with a possibly unknown dependency structure in the data. Our statistical approach to the nonparametric comparison of two samples with independent multivariate observables is based on recently developed multivariate multiple permutation tests. We adapt their theory in order to cope with families of hypotheses regarding relative effects. Our results indicate that the multivariate multiple permutation test keeps the pre-assigned type I error level for the global null hypothesis. In combination with the closure principle, the family-wise error rate for the simultaneous test of the corresponding locus/parameter-specific null hypotheses can be controlled. In applications we demonstrate that group differences in epigenetic data can be detected reliably with our methodology. -
K. Tabelow, S. Mohammadi, N. Weiskopf, J. Polzehl, POAS4SPM --- A toolbox for SPM to denoise diffusion MRI data, Neuroinformatics, 13 (2015), pp. 19--29.
Abstract
We present an implementation of a recently developed noise reduction algorithm for dMRI data, called multi-shell position orientation adaptive smoothing (msPOAS), as a toolbox for SPM. The method intrinsically adapts to the structures of different size and shape in dMRI and hence avoids blurring typically observed in non-adaptive smoothing. We give examples for the usage of the toolbox and explain the determination of experiment-dependent parameters for an optimal performance of msPOAS. -
K. Tabelow, H.U. Voss, J. Polzehl, Local estimation of the noise level in MRI using structural adaptation, Medical Image Analysis, 20 (2015), pp. 76--86.
Abstract
We present a method for local estimation of the signal-dependent noise level in magnetic resonance images. The procedure uses a multi-scale approach to adaptively infer on local neighborhoods with similar data distribution. It exploits a maximum-likelihood estimator for the local noise level. The validity of the method was evaluated on repeated diffusion data of a phantom and simulated data using T1-data corrupted with artificial noise. Simulation results are compared with a recently proposed estimate. The method was applied to a high-resolution diffusion dataset to obtain improved diffusion model estimation results and to demonstrate its usefulness in methods for enhancing diffusion data. -
Y. Chen, V. Spokoiny, Modeling nonstationary and leptokurtic financial time series, Econometric Theory, (2015), pp. 703--728.
-
T. Bodnar, Th. Dickhaus, On the Simes inequality in elliptical models, Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, (published online on Sept. 4, 2015), pp. 1--16, DOI 10.1007/s10463-015-0539-4 .
Abstract
We provide necessary and sufficient conditions for the validity of the inequality of Simes (1986) in models with elliptical dependencies. Necessary conditions are presented in terms of sufficient conditions for the reverse Simes inequality. One application of our main results concerns the problem of model misspecification, in particular the case that the assumption of Gaussianity of test statistics is violated. Since our sufficient conditions require non-negativity of correlation coefficients between test statistics, we also develop exact tests for vectors of correlation coefficients. -
A. Gasnikov, Y. Nesterov, V. Spokoiny, On the efficiency of a randomized mirror descent algorithm in online optimization problems, Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 55 (2015), pp. 580--596.
-
V.G. Gitis, A.B. Derendyaev, S.A. Pirogov, V. Spokoiny, E.F. Yurkov, Adaptive estimation of seismic parameter fields from earthquakes catalogs, Journal of Communications Technology and Electronics, 60 (2015), pp. 1459--1465.
-
S. Mohammadi, K. Tabelow, L. Ruthotto, Th. Feiweier, J. Polzehl, N. Weiskopf, High-resolution diffusion kurtosis imaging at 3T enabled by advanced post-processing, Frontiers in Neuroscience, 8 (2015), pp. 427/1--427/14.
-
TH. Dickhaus, Th. Royen, On multivariate chi-square distributions and their applications in testing multiple hypotheses, Statistics. A Journal of Theoretical and Applied Statistics, (2015), pp. 427--454.
Abstract
We are considered with three different types of multivariate chi-square distributions. Their members play important roles as limiting distributions of vectors of test statistics in several applications of multiple hypotheses testing. We explain these applications and provide formulas for computing multiplicity-adjusted $p$-values under the respective global hypothesis. -
V. Spokoiny, M. Zhilova, Bootstrap confidence sets under a model misspecification, The Annals of Statistics, 43 (2015), pp. 2653--2675.
Abstract
A multiplier bootstrap procedure for construction of likelihood-based confidence sets is considered for finite samples and possible model misspecification. Theoretical results justify the bootstrap consistency for small or moderate sample size and allow to control the impact of the parameter dimension: the bootstrap approximation works if the ratio of cube of the parameter dimension to the sample size is small. The main result about bootstrap consistency continues to apply even if the underlying parametric model is misspecified under the so called Small Modeling Bias condition. In the case when the true model deviates significantly from the considered parametric family, the bootstrap procedure is still applicable but it becomes a bit conservative: the size of the constructed confidence sets is increased by the modeling bias. We illustrate the results with numerical examples of misspecified constant and logistic regressions. -
A. Andresen, V. Spokoiny, Critical dimension in profile semiparametric estimation, Electronic Journal of Statistics, 8 (2014), pp. 3077--3125.
-
S. Becker, K. Tabelow, S. Mohammadi, N. Weiskopf, J. Polzehl, Adaptive smoothing of multi-shell diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance data by msPOAS, NeuroImage, 95 (2014), pp. 90--105.
Abstract
In this article we present a noise reduction method (msPOAS) for multi-shell diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance data. To our knowledge, this is the first smoothing method which allows simultaneous smoothing of all q-shells. It is applied directly to the diffusion weighted data and consequently allows subsequent analysis by any model. Due to its adaptivity, the procedure avoids blurring of the inherent structures and preserves discontinuities. MsPOAS extends the recently developed position-orientation adaptive smoothing (POAS) procedure to multi-shell experiments. At the same time it considerably simplifies and accelerates the calculations. The behavior of the algorithm msPOAS is evaluated on diffusion-weighted data measured on a single shell and on multiple shells. -
D. Belomestny, V. Spokoiny, Concentration inequalities for smooth random fields, Theory of Probability and its Applications, 58 (2014), pp. 314--323.
Abstract
In this note we derive a sharp concentration inequality for the supremum of a smooth random field over a finite dimensional set. It is shown that this supremum can be bounded with high probability by the value of the field at some deterministic point plus an intrinsic dimension of the optimisation problem. As an application we prove the exponential inequality for a function of the maximal eigenvalue of a random matrix is proved. -
G. Blanchard, Th. Dickhaus, E. Roquain, F. Villers, On least favorable configurations for step-up-down tests, Statistica Sinica, 24 (2014), pp. 1--23.
-
T. Bodnar, Th. Dickhaus, False discovery rate control under Archimedean copula, Electronic Journal of Statistics, 8 (2014), pp. 2207--2241.
-
S. Becker, P. Mathé, A different perspective on the Propagation-Separation approach, Electronic Journal of Statistics, 7 (2013), pp. 2702--2736.
Abstract
The Propagation-Separation approach is an iterative procedure for pointwise estimation of local constant and local polynomial functions. The estimator is defined as a weighted mean of the observations with data-driven weights. Within homogeneous regions it ensures a similar behavior as non-adaptive smoothing (propagation), while avoiding smoothing among distinct regions (separation). In order to enable a proof of stability of estimates, the authors of the original study introduced an additional memory step aggregating the estimators of the successive iteration steps. Here, we study theoretical properties of the simplified algorithm, where the memory step is omitted. In particular, we introduce a new strategy for the choice of the adaptation parameter yielding propagation and stability for local constant functions with sharp discontinuities. -
M. Zhilova, V. Spokoiny, Uniform properties of the local maximum likelihood estimate, Automation and Remote Control, 74 (2013), pp. 1656--1669.
-
M. Welvaert, K. Tabelow, R. Seurinck, Y. Rosseel, Adaptive smoothing as inference strategy: More specificity for unequally sized or neighboring regions, Neuroinformatics, 11 (2013), pp. 435--445.
Abstract
Although spatial smoothing of fMRI data can serve multiple purposes, increasing the sensitivity of activation detection is probably its greatest benefit. However, this increased detection power comes with a loss of specificity when non-adaptive smoothing (i.e. the standard in most software packages) is used. Simulation studies and analysis of experimental data was performed using the R packages neuRosim and fmri. In these studies, we systematically investigated the effect of spatial smoothing on the power and number of false positives in two particular cases that are often encountered in fMRI research: (1) Single condition activation detection for regions that differ in size, and (2) multiple condition activation detection for neighbouring regions. Our results demonstrate that adaptive smoothing is superior in both cases because less false positives are introduced by the spatial smoothing process compared to standard Gaussian smoothing or FDR inference of unsmoothed data. -
D. Belomestny, V. Spokoiny, Concentration inequalities for smooth random fields, Theory of Probability and its Applications, (2013), pp. 401--410.
-
R. Bruggemann, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Ranking of polluted regions in south west Germany based on a multi-indicator system, MATCH. Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry, 69 (2013), pp. 433--462.
-
E. Diederichs, A. Juditsky, A. Nemirovski, V. Spokoiny, Sparse non Gaussian component analysis by semidefinite programming, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., (2013), pp. 1--28.
-
F. Gach, R. Nickl, V. Spokoiny, Spatially adaptive density estimation by localised Haar projections, Annales de l'Institut Henri Poincare. Probabilites et Statistiques, 49 (2013), pp. 900--914.
-
TH. Dickhaus, B. Blankertz, F.C. Meinecke, Binary classification with pFDR-pFNR losses, Biometrical Journal, 55 (2013), pp. 463--477.
-
TH. Dickhaus, J. Stange, Multiple point hypothesis test problems and effective numbers of tests for control of the family-wise error rate, Calcutta Statistical Association Bulletin, 65 (2013), pp. 123--144.
-
TH. Dickhaus, Randomized p-values for multiple testing of composite null hypotheses, Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 143 (2013), pp. 1968--1979.
-
V. Spokoiny, M. Zhilova, Sharp deviation bounds for quadratic forms, Mathematical Methods of Statistics, 22 (2013), pp. 100--113.
-
V. Spokoiny, W. Wang, W. Härdle, Local quantile regression (with rejoinder), Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 143 (2013), pp. 1109--1129.
-
S. Becker, K. Tabelow, H.U. Voss, A. Anwander, R.M. Heidemann, J. Polzehl, Position-orientation adaptive smoothing of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance data (POAS), Medical Image Analysis, 16 (2012), pp. 1142--1155.
Abstract
We introduce an algorithm for diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging data enhancement based on structural adaptive smoothing in both space and diffusion direction. The method, called POAS, does not refer to a specific model for the data, like the diffusion tensor or higher order models. It works by embedding the measurement space into a space with defined metric and group operations, in this case the Lie group of three-dimensional Euclidean motion SE(3). Subsequently, pairwise comparisons of the values of the diffusion weighted signal are used for adaptation. The position-orientation adaptive smoothing preserves the edges of the observed fine and anisotropic structures. The POAS-algorithm is designed to reduce noise directly in the diffusion weighted images and consequently also to reduce bias and variability of quantities derived from the data for specific models. We evaluate the algorithm on simulated and experimental data and demonstrate that it can be used to reduce the number of applied diffusion gradients and hence acquisition time while achieving similar quality of data, or to improve the quality of data acquired in a clinically feasible scan time setting. -
K. Tabelow, H.U. Voss, J. Polzehl, Modeling the orientation distribution function by mixtures of angular central Gaussian distributions, Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 203 (2012), pp. 200--211.
Abstract
In this paper we develop a tensor mixture model for diffusion weighted imaging data using an automatic model selection criterion for the order of tensor components in a voxel. We show that the weighted orientation distribution function for this model can be expanded into a mixture of angular central Gaussian distributions. We show properties of this model in extensive simulations and in a high angular resolution experimental data set. The results suggest that the model may improve imaging of cerebral fiber tracts. We demonstrate how inference on canonical model parameters may give rise to new clinical applications. -
H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, Finding incomparable pairs of subsets by using formal concept analysis, Statistica & Applicazioni, Special Issue (2011), pp. 61--79.
-
S. Arlot, G. Blanchard, E. Roquain, Some non-asymptotic results on resampling in high dimension, I: Confidence regions, The Annals of Statistics, 38 (2010), pp. 51--82.
-
S. Arlot, G. Blanchard, E. Roquain, Some non-asymptotic results on resampling in high dimension, II: Multiple tests, The Annals of Statistics, 38 (2010), pp. 83--99.
-
Y. Chen, W. Härdle, V. Spokoiny, GHICA --- Risk analysis with GH distributions and independent components, Journal of Empirical Finance, 17 (2010), pp. 255--269.
-
D. Belomestny, Spectral estimation of the fractional order of a Lévy process, The Annals of Statistics, 38 (2010), pp. 317--351.
-
G. Blanchard, G. Lee, C. Scott, Semi-supervised novelty detection, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., 11 (2010), pp. 2973--3009.
Abstract
A common setting for novelty detection assumes that labeled examples from the nominal class are available, but that labeled examples of novelties are unavailable. The standard (inductive) approach is to declare novelties where the nominal density is low, which reduces the problem to density level set estimation. In this paper, we consider the setting where an unlabeled and possibly contaminated sample is also available at learning time. We argue that novelty detection in this semi-supervised setting is naturally solved by a general reduction to a binary classification problem. In particular, a detector with a desired false positive rate can be achieved through a reduction to Neyman-Pearson classification. Unlike the inductive approach, semi-supervised novelty detection (SSND) yields detectors that are optimal (e.g., statistically consistent) regardless of the distribution on novelties. Therefore, in novelty detection, unlabeled data have a substantial impact on the theoretical properties of the decision rule. We validate the practical utility of SSND with an extensive experimental study. We also show that SSND provides distribution-free, learning-theoretic solutions to two well known problems in hypothesis testing. First, our results provide a general solution to the general two-sample problem, that is, the problem of determining whether two random samples arise from the same distribution. Second, a specialization of SSND coincides with the standard $p$-value approach to multiple testing under the so-called random effects model. Unlike standard rejection regions based on thresholded $p$-values, the general SSND framework allows for adaptation to arbitrary alternative distributions. -
G. Blanchard, P. Mathé, Conjugate gradient regularization under general smoothness and noise assumptions, Journal of Inverse and Ill-Posed Problems, 18 (2010), pp. 701--726.
-
G. Blanchard, Adaptive FDR control under independence and dependence, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., 10 (2010), pp. 2837--2871.
-
E. Diederichs, A. Juditsky, V. Spokoiny, Ch. Schütte, Sparse non-Gaussian component analysis, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 56 (2010), pp. 3033--3047.
-
J. Polzehl, H.U. Voss, K. Tabelow, Structural adaptive segmentation for statistical parametric mapping, NeuroImage, 52 (2010), pp. 515--523.
Abstract
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging inherently involves noisy measurements and a severe multiple test problem. Smoothing is usually used to reduce the effective number of multiple comparisons and to locally integrate the signal and hence increase the signal-to-noise ratio. Here, we provide a new structural adaptive segmentation algorithm (AS) that naturally combines the signal detection with noise reduction in one procedure. Moreover, the new method is closely related to a recently proposed structural adaptive smoothing algorithm and preserves shape and spatial extent of activation areas without blurring the borders. -
N. Serdyukova, Dependence on the dimension for complexity of approximation of random fields, Theory of Probability and its Applications, 54 (2010), pp. 272--284.
-
K. Tabelow, V. Piëch, J. Polzehl, H.U. Voss, High-resolution fMRI: Overcoming the signal-to-noise problem, Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 178 (2009), pp. 357--365.
Abstract
Increasing the spatial resolution in functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) inherently lowers the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In order to still detect functionally significant activations in high-resolution images, spatial smoothing of the data is required. However, conventional non-adaptive smoothing comes with a reduced effective resolution, foiling the benefit of the higher acquisition resolution. We show how our recently proposed structural adaptive smoothing procedure for functional MRI data can improve signal detection of high-resolution fMRI experiments regardless of the lower SNR. The procedure is evaluated on human visual and sensory-motor mapping experiments. In these applications, the higher resolution could be fully utilized and high-resolution experiments were outperforming normal resolution experiments by means of both statistical significance and information content. -
H.-G. Bartel, J. Dolata, H.-J. Mucha, Klassifikation von 613 Proben als Referenzen für die Herstellungsprovenienzen römischer Baukeramik im nördlichen Obergermanien, Mainzer Archäologische Zeitschrift, 8 (2009), pp. 51--76.
-
P. Čížek, W. Härdle, V. Spokoiny, Adaptive pointwise estimation in time-inhomogeneous conditional heteroscedasticity models, The Econometrics Journal, 12 (2009), pp. 248--271.
-
E. Giacomini, W. Härdle, V. Krätschmer, Dynamic semiparametric factor models in risk neutral density estimation, AStA. Advances in Statistical Analysis. A Journal of the German Statistical Society, 93 (2009), pp. 387--402.
-
E. Giacomini, W. Härdle, V. Spokoiny, Inhomogeneous dependency modelling with time varying copulae, Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 27 (2009), pp. 224--234.
Abstract
Measuring dependence in a multivariate time series is tantamount to modelling its dynamic structure in space and time. In the context of a multivariate normally distributed time series, the evolution of the covariance (or correlation) matrix over time describes this dynamic. A wide variety of applications, though, requires a modelling framework different from the multivariate normal. In risk management the non-normal behaviour of most financial time series calls for nonlinear dependency. The correct modelling of non-gaussian dependencies is therefore a key issue in the analysis of multivariate time series. In this paper we use copulae functions with adaptively estimated time varying parameters for modelling the distribution of returns, free from the usual normality assumptions. Further, we apply copulae to estimation of Value-at-Risk (VaR) of a portfolio and show its better performance over the RiskMetrics approach, a widely used methodology for VaR estimation -
Y. Golubev, V. Spokoiny, Exponential bounds for minimum contrast estimators, Electronic Journal of Statistics, 3 (2009), pp. 712--746.
-
A. Schwaighöfer, T. Schröter, S. Mika, G. Blanchard, How wrong can we get? A review of machine learning approaches and error bars, Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening, 12 (2009), pp. 453--468.
-
D. Belomestny, G.N. Milstein, V. Spokoiny, Regression methods in pricing American and Bermudan options using consumption processes, Quantitative Finance, 9 (2009), pp. 315--327.
Abstract
Here we develop methods for efficient pricing multidimensional discrete-time American and Bermudan options by using regression based algorithms together with a new approach towards constructing upper bounds for the price of the option. Applying sample space with payoffs at the optimal stopping times, we propose sequential estimates for continuation values, values of the consumption process, and stopping times on the sample paths. The approach admits constructing both low and upper bounds for the price by Monte Carlo simulations. The methods are illustrated by pricing Bermudan swaptions and snowballs in the Libor market model. -
J. Polzehl, S. Sperlich, A note on structural adaptive dimension reduction, Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 79 (2009), pp. 805--818.
-
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Structural adaptive smoothing in diffusion tensor imaging: The R package dti, Journal of Statistical Software, 31 (2009), pp. 1--24.
Abstract
Diffusion Weighted Imaging has become and will certainly continue to be an important tool in medical research and diagnostics. Data obtained with Diffusion Weighted Imaging are characterized by a high noise level. Thus, estimation of quantities like anisotropy indices or the main diffusion direction may be significantly compromised by noise in clinical or neuroscience applications. Here, we present a new package dti for R, which provides functions for the analysis of diffusion weighted data within the diffusion tensor model. This includes smoothing by a recently proposed structural adaptive smoothing procedure based on the Propagation-Separation approach in the context of the widely used Diffusion Tensor Model. We extend the procedure and show, how a correction for Rician bias can be incorporated. We use a heteroscedastic nonlinear regression model to estimate the diffusion tensor. The smoothing procedure naturally adapts to different structures of different size and thus avoids oversmoothing edges and fine structures. We illustrate the usage and capabilities of the package through some examples. -
V. Spokoiny, C. Vial, Parameter tuning in pointwise adaptation using a propagation approach, The Annals of Statistics, 37 (2009), pp. 2783--2807.
Abstract
This paper discusses the problem of adaptive estimating a univariate object like the value of a regression function at a given point or a linear functional in a linear inverse problem. We consider an adaptive procedure originated from Lepski (1990) which selects in a data-driven way one estimate out of a given class of estimates ordered by their variability. A serious problem with using this and similar procedures is the choice of some tuning parameters like thresholds. Numerical results show that the theoretically recommended proposals appear to be too conservative and lead to a strong oversmoothing effects. A careful choice of the parameters of the procedure is extremely important for getting the reasonable quality of estimation. The main contribution of this paper is the new approach for choosing the parameters of the procedure by providing the prescribed behavior of the resulting estimate in the simple parametric situation. We establish a non-asymptotical “oracle” bound which shows that the estimation risk is, up to a logarithmic multiplier, equal to the risk of the “oracle” estimate which is optimally selected from the given family. A numerical study demonstrates the nice performance of the resulting procedure in a number of simulated examples. -
V. Spokoiny, Multiscale local change point detection with applications to Value-at-Risk, The Annals of Statistics, 37 (2009), pp. 1405--1436.
Abstract
This paper offers a new procedure for nonparametric estimation and forecasting of time series with applications to volatility modeling for financial data. The approach is based on the assumption of local homogeneity: for every time point there exists a historical emphinterval of homogeneity, in which the volatility parameter can be well approximated by a constant. The procedure recovers this interval from the data using the local change point (LCP) analysis. Afterwards the estimate of the volatility can be simply obtained by local averaging. The approach carefully addresses the question of choosing the tuning parameters of the procedure using the so called “propagation” condition. The main result claims a new “oracle” inequality in terms of the modeling bias which measures the quality of the local constant approximation. This result yields the optimal rate of estimation for smooth and piecewise constant volatility functions. Then the new procedure is applied to some data sets and a comparison with a standard GARCH model is also provided. Finally we discuss applications of the new method to the Value at Risk problem. The numerical results demonstrate a very reasonable performance of the new method. -
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, A.M. Uluğ, J.P. Dyke, R. Watts, L.A. Heier, H.U. Voss, Accurate localization of brain activity in presurgical fMRI by structure adaptive smoothing, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 27 (2008), pp. 531--537.
Abstract
An important problem of the analysis of fMRI experiments is to achieve some noise reduction of the data without blurring the shape of the activation areas. As a novel solution to this problem, the Propagation-Separation approach (PS), a structure adaptive smoothing method, has been proposed recently. PS adapts to different shapes of activation areas by generating a spatial structure corresponding to similarities and differences between time series in adjacent locations. In this paper we demonstrate how this method results in more accurate localization of brain activity. First, it is shown in numerical simulations that PS is superior over Gaussian smoothing with respect to the accurate description of the shape of activation clusters and and results in less false detections. Second, in a study of 37 presurgical planning cases we found that PS and Gaussian smoothing often yield different results, and we present examples showing aspects of the superiority of PS as applied to presurgical planning. -
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, V. Spokoiny, H.U. Voss, Diffusion tensor imaging: Structural adaptive smoothing, NeuroImage, 39 (2008), pp. 1763--1773.
Abstract
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) data is characterized by a high noise level. Thus, estimation errors of quantities like anisotropy indices or the main diffusion direction used for fiber tracking are relatively large and may significantly confound the accuracy of DTI in clinical or neuroscience applications. Besides pulse sequence optimization, noise reduction by smoothing the data can be pursued as a complementary approach to increase the accuracy of DTI. Here, we suggest an anisotropic structural adaptive smoothing procedure, which is based on the Propagation-Separation method and preserves the structures seen in DTI and their different sizes and shapes. It is applied to artificial phantom data and a brain scan. We show that this method significantly improves the quality of the estimate of the diffusion tensor and hence enables one either to reduce the number of scans or to enhance the input for subsequent analysis such as fiber tracking. -
H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, J. Dolata, Über Identifikationsmethoden, dargestellt am Beispiel römischer Baukeramik, Berliner Beiträge zur Archäometrie, 21 (2008), pp. 115--132.
-
A. Dalalyan, A. Juditsky, V. Spokoiny, A new algorithm for estimating the effective dimension-reduction subspace, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., 9 (2008), pp. 1647--1678.
-
D. Divine, J. Polzehl, F. Godtliebsen, A propagation-separation approach to estimate the autocorrelation in a time-series, Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 15 (2008), pp. 591--599.
-
I.G. Grama, V. Spokoiny, Statistics of extremes by oracle estimation, The Annals of Statistics, 36 (2008), pp. 1619--1648.
Abstract
We use the fitted Pareto law to construct an accompanying approximation of the excess distribution function. A selection rule of the location of the excess distribution function is proposed based on a stagewise lack-of-fit testing procedure. Our main result is an oracle type inequality for the Kullback-Leibler loss of the obtained adaptive estimator. -
V. Katkovnik, V. Spokoiny, Spatially adaptive estimation via fitted local likelihood techniques, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56 (2008), pp. 873--886.
Abstract
This paper offers a new technique for spatially adaptive estimation. The local likelihood is exploited for nonparametric modelling of observations and estimated signals. The approach is based on the assumption of a local homogeneity of the signal: for every point there exists a neighborhood in which the signal can be well approximated by a constant. The fitted local likelihood statistics is used for selection of an adaptive size of this neighborhood. The algorithm is developed for quite a general class of observations subject to the exponential distribution. The estimated signal can be uni- and multivariable. We demonstrate a good performance of the new algorithm for Poissonian image denoising and compare of the new method versus the intersection of confidence interval (ICI) technique that also exploits a selection of an adaptive neighborhood for estimation. -
Y. Chen, W. Härdle, V. Spokoiny, Portfolio value at risk based on independent components analysis, Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 205 (2007), pp. 594--607.
Abstract
Risk management technology applied to high-dimensional portfolios needs simple and fast methods for calculation of value at risk (VaR). The multivariate normal framework provides a simple off-the-shelf methodology but lacks the heavy-tailed distributional properties that are observed in data. A principle component-based method (tied closely to the elliptical structure of the distribution) is therefore expected to be unsatisfactory. Here, we propose and analyze a technology that is based on independent component analysis (ICA). We study the proposed ICVaR methodology in an extensive simulation study and apply it to a high-dimensional portfolio situation. Our analysis yields very accurate VaRs. -
H.U. Voss, K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, O. Tchernichovski, K. Maul, D. Salgado-Commissariat, D. Ballon, S.A. Helekar, Functional MRI of the zebra finch brain during song stimulation suggests a lateralized response topography, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104 (2007), pp. 10667--10672.
Abstract
Electrophysiological and activity-dependent gene expression studies of birdsong have contributed to the understanding of the neural representation of natural sounds. However, we have limited knowledge about the overall spatial topography of song representation in the avian brain. Here, we adapt the noninvasive functional MRI method in mildly sedated zebra finches (Taeniopygia guttata) to localize and characterize song driven brain activation. Based on the blood oxygenation level-dependent signal, we observed a differential topographic responsiveness to playback of bird's own song, tutor song, conspecific song, and a pure tone as a nonsong stimulus. The bird's own song caused a stronger response than the tutor song or tone in higher auditory areas. This effect was more pronounced in the medial parts of the forebrain. We found left-right hemispheric asymmetry in sensory responses to songs, with significant discrimination between stimuli observed only in the right hemisphere. This finding suggests that perceptual responses might be lateralized in zebra finches. In addition to establishing the feasibility of functional MRI in sedated songbirds, our results demonstrate spatial coding of song in the zebra finch forebrain, based on developmental familiarity and experience. -
D. Belomestny, V. Spokoiny, Spatial aggregation of local likelihood estimates with applications to classification, The Annals of Statistics, 35 (2007), pp. 2287--2311.
Abstract
This paper presents a new method for spatially adaptive local (constant) likelihood estimation which applies to a broad class of nonparametric models, including the Gaussian, Poisson and binary response models. The main idea of the method is given a sequence of local likelihood estimates (”weak” estimates), to construct a new aggregated estimate whose pointwise risk is of order of the smallest risk among all “weak” estimates. We also propose a new approach towards selecting the parameters of the procedure by providing the prescribed behavior of the resulting estimate in the simple parametric situation. We establish a number of important theoretical results concerning the optimality of the aggregated estimate. In particular, our “oracle” results claims that its risk is up to some logarithmic multiplier equal to the smallest risk for the given family of estimates. The performance of the procedure is illustrated by application to the classification problem. A numerical study demonstrates its nice performance in simulated and real life examples. -
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Adaptive smoothing of digital images: The R package adimpro, Journal of Statistical Software, 19 (2007), pp. 1--17.
Abstract
Digital imaging has become omnipresent in the past years with a bulk of applications ranging from medical imaging to photography. When pushing the limits of resolution and sensitivity noise has ever been a major issue. However, commonly used non-adaptive filters can do noise reduction at the cost of a reduced effective spatial resolution only. Here we present a new package adimpro for R, which implements the Propagation-Separation approach by Polzehl and Spokoiny (2006) for smoothing digital images. This method naturally adapts to different structures of different size in the image and thus avoids oversmoothing edges and fine structures. We extend the method for imaging data with spatial correlation. Furthermore we show how the estimation of the dependence between variance and mean value can be included. We illustrate the use of the package through some examples. -
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, fmri: A package for analyzing fmri data, Newsletter of the R Project for Statistical Computing, 7 (2007), pp. 13--17.
-
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, H.U. Voss, V. Spokoiny, Analyzing fMRI experiments with structural adaptive smoothing procedures, NeuroImage, 33 (2006), pp. 55--62.
Abstract
Data from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) consists of time series of brain images which are characterized by a low signal-to-noise ratio. In order to reduce noise and to improve signal detection the fMRI data is spatially smoothed. However, the common application of a Gaussian filter does this at the cost of loss of information on spatial extent and shape of the activation area. We suggest to use the propagation-separation procedures introduced by Polzehl and Spokoiny (2006) instead. We show that this significantly improves the information on the spatial extent and shape of the activation region with similar results for the noise reduction. To complete the statistical analysis, signal detection is based on thresholds defined by random field theory. Effects of ad aptive and non-adaptive smoothing are illustrated by artificial examples and an analysis of experimental data. -
G. Blanchard, M. Kawanabe, M. Sugiyama, V. Spokoiny, K.-R. Müller, In search of non-Gaussian components of a high-dimensional distribution, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. English, English abstracts., 7 (2006), pp. 247--282.
Abstract
Finding non-Gaussian components of high-dimensional data is an important preprocessing step for efficient information processing. This article proposes a new em linear method to identify the “non-Gaussian subspace” within a very general semi-parametric framework. Our proposed method, called NGCA (Non-Gaussian Component Analysis), is essentially based on the fact that we can construct a linear operator which, to any arbitrary nonlinear (smooth) function, associates a vector which belongs to the low dimensional non-Gaussian target subspace up to an estimation error. By applying this operator to a family of different nonlinear functions, one obtains a family of different vectors lying in a vicinity of the target space. As a final step, the target space itself is estimated by applying PCA to this family of vectors. We show that this procedure is consistent in the sense that the estimaton error tends to zero at a parametric rate, uniformly over the family. Numerical examples demonstrate the usefulness of our method. -
A. Goldenshluger, V. Spokoiny, Recovering convex edges of image from noisy tomographic data, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52 (2006), pp. 1322--1334.
-
J. Polzehl, V. Spokoiny, Propagation-separation approach for local likelihood estimation, Probability Theory and Related Fields, 135 (2006), pp. 335--362.
Abstract
The paper presents a unified approach to local likelihood estimation for a broad class of nonparametric models, including, e.g., regression, density, Poisson and binary response models. The method extends the adaptive weights smoothing (AWS) procedure introduced by the authors [Adaptive weights smoothing with applications to image sequentation. J. R. Stat. Soc., Ser. B 62, 335-354 (2000)] in the context of image denoising. The main idea of the method is to describe a greatest possible local neighborhood of every design point in which the local parametric assumption is justified by the data. The method is especially powerful for model functions having large homogeneous regions and sharp discontinuities. The performance of the proposed procedure is illustrated by numerical examples for density estimation and classification. We also establish some remarkable theoretical non-asymptotic results on properties of the new algorithm. This includes the “propagation” property which particularly yields the root-$n$ consistency of the resulting estimate in the homogeneous case. We also state an “oracle” result which implies rate optimality of the estimate under usual smoothness conditions and a “separation” result which explains the sensitivity of the method to structural changes. -
A. Samarov, V. Spokoiny, C. Vial, Component identification and estimation in nonlinear high-dimensional regression models by structural adaptation, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 100 (2005), pp. 429--445.
-
M. Giurcanu, V. Spokoiny, Confidence estimation of the covariance function of stationary and locally stationary processes, Statistics & Decisions. International Journal for Statistical Theory and Related Fields, 22 (2004), pp. 283--300.
-
A. Goldenshluger, V. Spokoiny, On the shape-from-moments problem and recovering edges from noisy Radon data, Probability Theory and Related Fields, 128 (2004), pp. 123--140.
-
G.N. Milstein, J.G.M. Schoenmakers, V. Spokoiny, Transition density estimation for stochastic differential equations via forward-reverse representations, Bernoulli. Official Journal of the Bernoulli Society for Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 10 (2004), pp. 281--312.
Abstract
The general reverse diffusion equations are derived and applied to the problem of transition density estimation of diffusion processes between two fixed states. For this problem we propose density estimation based on forward?reverse representations and show that this method allows essentially better results to be achieved than the usual kernel or projection estimation based on forward representations only. -
J. Polzehl, S. Zwanzig, On a symmetrized simulation extrapolation estimator in linear errors-in-variables models, Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 47 (2004), pp. 675-688.
Abstract
Application of naive regression estimates in errors-in-variables models suffers from a severe bias. The simulation extrapolation estimator (SIMEX) was introduced by Cook and Stefanski as a correction method modeling the dependence of error variance in the regressors and bias of the regression method. Our symmetrized simulation extrapolation estimator (SYMEX), a generalization of SIMEX, allows to employ the symmetric structure of errors-in-variables models. Relations of both SIMEX and SYMEX to total least squares are investigated. -
V. Spokoiny, D. Mercurio, Statistical inference for time-inhomogeneous volatility models, The Annals of Statistics, 32 (2004), pp. 577--602.
-
W. Härdle, H. Herwatz, V. Spokoiny, Time inhomogeneous multiple volatility modelling, Journal of Financial Econometrics, 1 (2003), pp. 55-95.
-
D. Belomestny, V. Jentsch, M. Schreckenberg, Completion and continuation of nonlinear traffic time series: A probabilistic approach, Journal of Physics. A. Mathematical and General, 36 (2003), pp. 11369-11383.
Abstract
When dealing with nonlinear time series of car traffic on highways, one of the outstanding problems to be solved is completion and continuation of data in space and time. To this end, the underlying process is decomposed into stochastic and deterministic components. The former is approximated by Gaussian white noise, while the latter refers, apart from always existing trends, to the space- and time-dependent jam propagation process. Jams are modelled in terms of dynamical Bayesian networks with radial basis functions involved. The models developed are used to tackle travel time estimation and prediction. Results are obtained for one of the most crowded traffic areas of Europe, namely the ring-like highway around Cologne. -
J. Polzehl, V. Spokoiny, Image denoising: Pointwise adaptive approach, The Annals of Statistics, 31 (2003), pp. 30--57.
Abstract
A new method of pointwise adaptation has been proposed and studied in Spokoiny (1998) in context of estimation of piecewise smooth univariate functions. The present paper extends that method to estimation of bivariate grey-scale images composed of large homogeneous regions with smooth edges and observed with noise on a gridded design. The proposed estimator $, hatf(x) ,$ at a point $, x ,$ is simply the average of observations over a window $, hatU(x) ,$ selected in a data-driven way. The theoretical properties of the procedure are studied for the case of piecewise constant images. We present a nonasymptotic bound for the accuracy of estimation at a specific grid point $, x ,$ as a function of the number of pixel $n$, of the distance from the point of estimation to the closest boundary and of smoothness properties and orientation of this boundary. It is also shown that the proposed method provides a near optimal rate of estimation near edges and inside homogeneous regions. We briefly discuss algorithmic aspects and the complexity of the procedure. The numerical examples demonstrate a reasonable performance of the method and they are in agreement with the theoretical issues. An example from satellite (SAR) imaging illustrates the applicability of the method. -
J.L. Horowitz, V. Spokoiny, An adaptive, rate-optimal test of linearity for median regression models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 97 (2002), pp. 822--835.
-
R. Liptser, A.Y. Veretennikov, V. Spokoiny, Freidlin-Wentzell type moderate deviations for smooth processes, Markov Processes and Related Fields, 8 (2002), pp. 611-636.
-
V. Spokoiny, Variance estimation for high-dimensional regression models, Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 82 (2002), pp. 111--133.
-
L. Dümbgen, V. Spokoiny, Multiscale testing of qualitative hypotheses, The Annals of Statistics, 29 (2001), pp. 124--152.
-
W. Härdle, S. Sperlich, V. Spokoiny, Structural tests for additive regression, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 96 (2001), pp. 1333--1347.
-
J.L. Horowitz, V. Spokoiny, An adaptive, rate-optimal test of a parametric mean-regression model against a nonparametric alternative, Econometrica. Journal of the Econometric Society, 69 (2001), pp. 599--631.
-
M. Hristache, A. Juditsky, J. Polzehl, V. Spokoiny, Structure adaptive approach for dimension reduction, The Annals of Statistics, 29 (2001), pp. 1537--1566.
Abstract
We propose a new method of effective dimension reduction for a multi-index model which is based on iterative improvement of the family of average derivative estimates. The procedure is computationally straightforward and does not require any prior information about the structure of the underlying model. We show that in the case when the effective dimension $m$ of the index space does not exceed $3$, this space can be estimated with the rate $n^-1/2$ under rather mild assumptions on the model. -
M. Hristache, A. Juditsky, V. Spokoiny, Direct estimation of the index coefficient in a single-index model, The Annals of Statistics, 29 (2001), pp. 595--623.
-
S. Jaschke, U. Küchler, Coherent risk measures and good-deal bounds, Statistics & Probability Letters, 5 (2001), pp. 181--200.
-
J. Polzehl, B. Grund, Semiparametric lack-of-fit tests in an additive hazard regression model, Statistics and Computing, 11 (2001), pp. 323-335.
Abstract
In the semiparametric additive hazard regression model of McKeague and Sasieni (Biometrika 81: 501-514), the hazard contributions of some covariates are allowed to change over time, without parametric restrictions (Aalen model), while the contributions of other covariates are assumed to be constant. In this paper, we develop tests that help to decide which of the covariate contributions indeed change over time. The remaining covariates may be modelled with constant hazard coefficients, thus reducing the number of curves that have to be estimated nonparametrically. Several bootstrap tests are proposed. The behavior of the tests is investigated in a simulation study. In a practical example, the tests consistently identify covariates with constant and with changing hazard contributions. -
J. Polzehl, V. Spokoiny, Functional and dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging using vector adaptive weights smoothing, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series C. Applied Statistics, 50 (2001), pp. 485--501.
Abstract
We consider the problem of statistical inference for functional and dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). A new approach is proposed which extends the adaptive weights smoothing (AWS) procedure from Polzehl and Spokoiny (2000) originally designed for image denoising. We demonstrate how the AWS method can be applied for time series of images, which typically occur in functional and dynamic MRI. It is shown how signal detection in functional MRI and analysis of dynamic MRI can benefit from spatially adaptive smoothing. The performance of the procedure is illustrated using real and simulated data. -
V. Spokoiny, Data driven testing the fit of linear models, Mathematical Methods of Statistics, 10 (2001), pp. 465--497.
-
R. Liptser, V. Spokoiny, Deviation probability bound for martingales with applications to statistical estimation, Statistics & Probability Letters, 46 (2000), pp. 347--357.
-
R. Liptser, V. Spokoiny, On estimating a dynamic function of a stochastic system with averaging, Statistical Inference for Stochastic Processes. An International Journal Devoted to Time Series Analysis and the Statistics of Continuous Time Processes and Dynamical Systems, 3 (2000), pp. 225--249.
-
J. Polzehl, V. Spokoiny, Adaptive Weights Smoothing with applications to image restoration, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B. Statistical Methodology, 62 (2000), pp. 335--354.
Abstract
We propose a new method of nonparametric estimation which is based on locally constant smoothing with an adaptive choice of weights for every pair of data-points. Some theoretical properties of the procedure are investigated. Then we demonstrate the performance of the method on some simulated univariate and bivariate examples and compare it with other nonparametric methods. Finally we discuss applications of this procedure to magnetic resonance and satellite imaging. -
V. Spokoiny, Adaptive drift estimation for nonparametric diffusion model, The Annals of Statistics, 28 (2000), pp. 815--836.
 Contributions to Collected Editions
Contributions to Collected Editions
-
L. Mertenskötter, M. Kantner, Bayesian estimation of laser linewidth from delayed self-heterodyne measurements, Conference on Structural Nonlinear Dynamics and Diagnosis (CSNDD 2023), Marrakesh, Morocco, May 15 - 17, 2024, M. Belhaq, ed., 301 of Springer Proceedings in Physics, Springer, Singapur, 2024, pp. 269--279, DOI 10.1007/978-981-99-7958-5_21 .
Abstract
We present a statistical inference approach to estimate the frequency noise characteristics of ultra-narrow linewidth lasers from delayed self-heterodyne beat note measurements using Bayesian inference. Particular emphasis is on estimation of the intrinsic (Lorentzian) laser linewidth. The approach is based on a statistical model of the measurement process, taking into account the effects of the interferometer as well as the detector noise. Our method therefore yields accurate results even when the intrinsic linewidth plateau is obscured by detector noise. The regression is performed on periodogram data in the frequency domain using a Markov-chain Monte Carlo method. By using explicit knowledge about the statistical distribution of the observed data, the method yields good results already from a single time series and does not rely on averaging over many realizations, since the information in the available data is evaluated very thoroughly. The approach is demonstrated for simulated time series data from a stochastic laser rate equation model with 1 / f-type non-Markovian noise. -
O. Klein, On forward and inverse uncertainty quantification for a model for a magneto mechanical device involving a hysteresis operator, in: Proceedings of the Murphys 2022 Conference, V. Dolejší, ed., 6 of Applications of Mathematics (Special Issue), Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, 2023, pp. 795--828, DOI 10.21136/AM.2023.0080-23 .
Abstract
Modeling real world objects and processes one may has to deal with hysteresis effects but also with uncertainties. Following D. Davino, P. Krejčí, and C. Visone: Fully coupled modeling of magneto-mechanical hysteresis through `thermodynamic' compatibility. Smart Mater. Struct., 22(9), (2013) 0950099, a model for a magnetostrictive material involving a generalized Prandtl- Ishlinskiĭ-operator is considered here. Using results of measurements, some parameters in the model are determined and inverse Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) is used to determine random densities to describe the remaining parameters and their uncertainties. Afterwards, the results are used do perform forward UQ and to compare the results with measured data. This extends some of the results from O. Klein, D. Davino, and C. Visone. On forward and inverse uncertainty quantification for models involving hysteresis operators. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 15 (2020) 53. -
H. Kremer, J.-J. Zhu, K. Muandet, B. Schölkopf, Functional generalized empirical likelihood estimation for conditional moment restrictions, in: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, K. Chaudhuri, S. Jegelka, L. Song, C. Szepesvari, G. Niu, S. Sabato, eds., 162 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 2022, pp. 11665--11682.
Abstract
Important problems in causal inference, economics, and, more generally, robust machine learning can be expressed as conditional moment restrictions, but estimation becomes challenging as it requires solving a continuum of unconditional moment restrictions. Previous works addressed this problem by extending the generalized method of moments (GMM) to continuum moment restrictions. In contrast, generalized empirical likelihood (GEL) provides a more general framework and has been shown to enjoy favorable small-sample properties compared to GMM-based estimators. To benefit from recent developments in machine learning, we provide a functional reformulation of GEL in which arbitrary models can be leveraged. Motivated by a dual formulation of the resulting infinite dimensional optimization problem, we devise a practical method and explore its asymptotic properties. Finally, we provide kernel- and neural network-based implementations of the estimator, which achieve state-of-the-art empirical performance on two conditional moment restriction problems. -
Y. Nemmour, H. Kremer, B. Schölkopf, J.-J. Zhu, Maximum mean discrepancy distributionally robust nonlinear chance-constrained optimization with finite-sample guarantee, in: 2022 IEEE 61st Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Cancun, Mexico, 2022, pp. 5660--5667, DOI 10.1109/CDC51059.2022.9993212 .
-
M. Kantner, L. Mertenskötter, Data-driven modeling of non-Markovian noise in semiconductor lasers, in: 22nd International Conference on Numerical Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices (NUSOD), Turin, Italy, 2022, J. Piprek, P. Bardella, eds., IEEE, 2022, pp. 57--58, DOI 10.1109/NUSOD54938.2022.9894788 .
Abstract
Non-Markovian noise degrades the coherence properties of semiconductor lasers and contributes significantly to broadening of the linewidth. Since modeling of such colored noise systems from first principles is not accessible, we aim for a data-driven modeling approach in which a system of stochastic rate equations shall be reconstructed from time series data. -
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Distance and data transformation, in: The Encyclopedia of Archaeological Sciences, S.L. López Varela, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. published online on 26.11.2018, urlhttps://doi.org/10.1002/9781119188230.saseas0194, DOI 10.1002/9781119188230.saseas0194 .
-
H.-J. Mucha, T.M. Gluhak, Finding groups in compositional data -- Some experiments, in: Big data clustering: Data preprocessing, variable selection, and dimension reduction, H.-J. Mucha, ed., WIAS Reports, 2017, pp. 97--105.
Abstract
The talk is concerned with finding groups (clusters) in compositional data, that is nonnegative data with row sums (or column sums, respectively) equal to a constant, usually 1 in case of proportions or 100 in case of percentages. Without loss of generality, the cluster analysis of observations (row points) of compositional data is considered here, where the row profiles contains parts of some whole. Special distance functions between the profiles are proposed. Finally, applications to archaeometry are presented. -
N. Buzun, A. Suvorikova, V. Spokoiny, Multiscale parametric approach for change point detection, in: Proceedings of Information Technology and Systems 2016 -- The 40th Interdisciplinary Conference & School, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, pp. 979--996.
-
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, SHOWCASE 21 -- Towards in-vivo histology, in: MATHEON -- Mathematics for Key Technologies, M. Grötschel, D. Hömberg, J. Sprekels, V. Mehrmann ET AL., eds., 1 of EMS Series in Industrial and Applied Mathematics, European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Zurich, 2014, pp. 378--379.
-
H. Lamecker, H.-Ch. Hege, K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, F2 -- Image processing, in: MATHEON -- Mathematics for Key Technologies, M. Grötschel, D. Hömberg, J. Sprekels, V. Mehrmann ET AL., eds., 1 of EMS Series in Industrial and Applied Mathematics, European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Zurich, 2014, pp. 359--376.
-
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, J. Dolata, Dual scaling classification and its application to archaeometry, in: Data Analysis, Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery, M. Spiliopoulou, L. Schmidt-Thieme, R. Janning, eds., 48 of Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Heidelberg et al., 2014, pp. 105--113.
-
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Soft bootstrapping in cluster analysis and its comparison with other resampling methods, in: Data Analysis, Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery, M. Spiliopoulou, L. Schmidt-Thieme, R. Janning, eds., 48 of Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Heidelberg et al., 2014, pp. 97--104.
Abstract
The bootstrap approach is resampling taken with replacement from the original data. Here we consider sampling from the empirical distribution of a given data set in order to investigate the stability of results of cluster analysis. Concretely, the original bootstrap technique can be formulated by choosing the following weights of observations: m i = n, if the corresponding object i is drawn n times, and m i = 0, otherwise. We call the weights of observations masses. In this paper, we present another bootstrap method, called soft bootstrapping, that consists of random change of the ?bootstrap masses? to some degree. Soft bootstrapping can be applied to any cluster analysis method that makes (directly or indirectly) use of weights of observations. This resampling scheme is especially appropriate for small sample sizes because no object is totally excluded from the soft bootstrap sample. At the end we compare different resampling techniques with respect to cluster analysis. -
B. Maldonado, C. Morales-Merino, H.-J. Mucha, Ancient technology, modern science: Archaeometallurgy in northern Chile, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2013, A. Hauptmann, O. Mecking, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 6, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2013, pp. 70--74.
-
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, C. Morales-Merino, Visualisation of cluster analysis results, in: Classification and Data Mining, A. Giusti, G. Ritter, M. Vichi, eds., Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Berlin, 2013, pp. 261--270.
-
TH. Dickhaus, J. Gierl, Simultaneous test procedures in terms of p-value copulae, in: Proceedings of the 2nd Annual International Conference on Computational Mathematics, Computational Geometry & Statistics (CMCGS 2013), K. Chen, C. Raju, eds., Global Science and Technology Forum, Singapore, 2013, pp. 75--80.
-
H.-J. Mucha, J. Dolata, H.-G. Bartel, Classification of Roman tiles with stamp PARDALIVS, in: Algorithms from & for Nature and Life, B. Lausen, D. VAN DEN Poel, A. Ultsch, eds., Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Heidelberg, 2013, pp. 309--317.
-
H.-J. Mucha, R. Naumann, G. Schneider, H.-G. Bartel, M. Daszkiewicz, Diskriminanzanalytische Überprüfung einer Klassifikation von Keramikfunden aus Uruk, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2013, A. Hauptmann, O. Mecking, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 6, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2013, pp. 159--163.
-
S. Behrendt, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, D.P. Mielke, Zur Problematik der multivariaten statistischen Analyse umfangreicher P-RFA-Datenmengen phönizischer Keramik, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2012, F. Schlütter, S. Greif, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 5, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2012, pp. 157--159.
-
J. Dolata, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Eine neue Referenzgruppe für die römische Ziegelproduktion der I. Thrakerkohorte am Mittelrhein, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2012, F. Schlütter, S. Greif, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 5, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2012, pp. 171--173.
-
C. Morales-Merino, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Multivariate statistical analysis of clay and ceramic-data for provenance of Bronze Age pottery from Troia, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2012, F. Schlütter, S. Greif, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 5, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2012, pp. 174--176.
-
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, An accelerated K-means algorithm based on adaptive distances, in: Challenges at the Interface of Data Analysis, Computer Science, and Optimization --- Proceedings of the 34th Annual Conference of the Gesellschaft für Klassifikation e. V., Karlsruhe, July 21--23, 2010, W. Gaul, A. Geyer-Schulz, L. Schmidt-Thieme, J. Kunze, eds., Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Heidelberg, 2012, pp. 37--47.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Method selection in cluster analysis followed by built-in validation, in: Data Analysis Methods and its Applications, J. Pociecha, R. Decker, eds., Wydawnictwo C. H. Beck, Warszawa, 2012, pp. 125--142.
-
H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, J. Dolata, Geochemical and statistical investigation of Roman stamped tiles of the Legio XXI Rapax, in: Classification as a Tool for Research. 11th IFCS Biennial Conference and 33rd Annual Conference of the Gesellschaft für Klassifikation e. V., Dresden, March 13--18, 2009, H. Locarek-Junge, C. Weihs, eds., Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 2010, pp. 427--434.
-
J. Dolata, D. Lück, H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, C. Wenzel, Analysen römischer Ziegel aus dem Kastellbad von Groß-Gerau: ihre statistische Auswertung und archäologische Bewertung, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2010, O. Hahn, A. Hauptmann, D. Modarressi-Tehrani, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 3, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2010, pp. 129--131.
-
J. Dolata, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Mathematisch-archäometrische Auswertung der GIS-gestützten Fundkartierung römischer Ziegel aus Mainz, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2010, O. Hahn, A. Hauptmann, D. Modarressi--Tehrani, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 3, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2010, pp. 119--121.
-
J. Dolata, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Mapping findspots of Roman military brickstamps in em Mogontiacum (Mainz) and archaeometrical analysis, in: Advances in Data Analysis, Data Handling and Business Intelligence, A. Fink, B. Lausen, W. Seidel, A. Ultsch, eds., Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Heidelberg, 2010, pp. 595--603.
-
E. Haimerl, H.-J. Mucha, Comparing the stability of clustering results of dialect data based on several distance matrices, in: Classification as a Tool for Research. Proceedings of the 11th IFCS Biennial Conference and 33rd Annual Conference of the Gesellschaft für Klassifikation e. V., Dresden, March 13--18, 2009, H. Locarek-Junge, C. Weihs, eds., Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization, Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 2010, pp. 665--672.
-
C. Morales-Merino, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, E. Pernicka, Clay sediments analysis in the Troad and its segmentation, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2010, O. Hahn, A. Hauptmann, D. Modarressi--Tehrani, M. Prange, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 3, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2010, pp. 122--124.
-
G. Blanchard, N. Krämer, Kernel partial least squares is universally consistent, in: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS 2010), Y.W. Teh, M. Titterington, eds., 9 of JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, Journal of Machine Learning Research, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010, pp. 57--64.
-
P. Čížek, V. Spokoiny, Varying coefficient GARCH models, in: Handbook of Financial Time Series, T.G. Andersen, R.A. Davis, J.--P. Kreiss, T. Mikosch, eds., Springer, Berlin, 2009, pp. 169--185.
-
J. Dolata, H.-G. Bartel, H.-J. Mucha, Geochemische und statistische Erkundung der Herstellungsorte von Ziegeln der em Legio XXI Rapax, in: Oedenburg Fouilles Françaises, Allemandes et Suisses à Biesheim et Kunheim, Haut-Rhin, France. Volume 1: Les Camps Militaires Julio-Claudiens, M. Reddé, ed., 79 of Monographien des Römisch-Germanischen Zentralmuseums, Verlag des Römisch-Germanischen Zentralmuseums, Mainz, 2009, pp. 355-364.
-
C. Scott, G. Blanchard, Novelty detection: Unlabeled data definitely help, in: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, April 16--18, 2009, Clearwater Beach, Florida, USA, D. VAN Dyke, M. Welling, eds., 5 of JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, JMLR, 2009, pp. 464--471.
-
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, J. Dolata, Finding Roman brickyards in Germania Superior by model-based cluster analysis of archaeometric data, in: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology (CAA 2007), A. Posluschny, K. Lambers, I. Herzog, eds., 10 of Kolloquien zur Vor- und Frühgeschichte, Habelt Verlag, Bonn, 2009, pp. 360--365.
-
H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, J. Dolata, Zur Klassifikation römischer Ziegel von Fundorten im südlichen Obergermanien. I. Multivariate statistische Analyse der archäometrischen Daten, in: Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2009, Jahrestagung in der Pinakothek der Moderne, München, 25.--28. März 2009, A. Hauptmann, H. Stege, eds., Metalla, Sonderheft 2, Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum, 2009, pp. 144--146.
-
M. Elagin, V. Spokoiny, Locally time homogeneous time series modelling, in: Applied Quantitative Finance (2nd edition), W. Härdle, N. Hautsch, L. Overbeck, eds., Springer, Berlin, 2008, pp. 345--362.
 Preprints, Reports, Technical Reports
Preprints, Reports, Technical Reports
-
F. Besold, V. Spokoiny, Adaptive weights community detection, Preprint no. 2951, WIAS, Berlin, 2022, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2951 .
Abstract, PDF (628 kByte)
Due to the technological progress of the last decades, Community Detection has become a major topic in machine learning. However, there is still a huge gap between practical and theoretical results, as theoretically optimal procedures often lack a feasible implementation and vice versa. This paper aims to close this gap and presents a novel algorithm that is both numerically and statistically efficient. Our procedure uses a test of homogeneity to compute adaptive weights describing local communities. The approach was inspired by the Adaptive Weights Community Detection (AWCD) algorithm by [2]. This algorithm delivered some promising results on artificial and real-life data, but our theoretical analysis reveals its performance to be suboptimal on a stochastic block model. In particular, the involved estimators are biased and the procedure does not work for sparse graphs. We propose significant modifications, addressing both shortcomings and achieving a nearly optimal rate of strong consistency on the stochastic block model. Our theoretical results are illustrated and validated by numerical experiments. -
H.-J. Mucha, Big data clustering: Data preprocessing, variable selection, and dimension reduction, Report no. 29, WIAS, Berlin, 2017, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.REPORT.29 .
PDF (20 MByte) -
V. Avanesov, Nonparametric change point detection in regression, Preprint no. 2687, WIAS, Berlin, 2020, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2687 .
Abstract, PDF (329 kByte)
This paper considers the prominent problem of change-point detection in regression. The study suggests a novel testing procedure featuring a fully data-driven calibration scheme. The method is essentially a black box, requiring no tuning from the practitioner. The approach is investigated from both theoretical and practical points of view. The theoretical study demonstrates proper control of first-type error rate under H0 and power approaching 1 under H1. The experiments conducted on synthetic data fully support the theoretical claims. In conclusion, the method is applied to financial data, where it detects sensible change-points. Techniques for change-point localization are also suggested and investigated -
V. Avanesov, How to gamble with non-stationary X-armed bandits and have no regrets, Preprint no. 2686, WIAS, Berlin, 2020, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2686 .
Abstract, PDF (287 kByte)
In X-armed bandit problem an agent sequentially interacts with environment which yields a reward based on the vector input the agent provides. The agent's goal is to maximise the sum of these rewards across some number of time steps. The problem and its variations have been a subject of numerous studies, suggesting sub-linear and sometimes optimal strategies. The given paper introduces a new variation of the problem. We consider an environment, which can abruptly change its behaviour an unknown number of times. To that end we propose a novel strategy and prove it attains sub-linear cumulative regret. Moreover, the obtained regret bound matches the best known bound for GP-UCB for a stationary case, and approaches the minimax lower bound in case of highly smooth relation between an action and the corresponding reward. The theoretical result is supported by experimental study. -
H.-J. Mucha, G. Ritter, Classification and clustering: Models, software and applications, Report no. 26, WIAS, Berlin, 2009, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.REPORT.26 .
Abstract, Postscript (92 MByte), PDF (24 MByte)
We are pleased to present the report on the 30th Fall Meeting of the working group “Data Analysis and Numerical Classification” (AG-DANK) of the German Classification Society. The meeting took place at the Weierstrass Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics (WIAS), Berlin, from Friday Nov. 14 till Saturday Nov. 15, 2008. Already 12 years ago, WIAS had hosted a traditional Fall Meeting with special focus on classification and multivariate graphics (Mucha and Bock, 1996). This time, the special topics were stability of clustering and classification, mixture decomposition, visualization, and statistical software.The working group AG-DANK of the German Classification Society (“Gesellschaft für Klassifikation,” GfKl) deals with all statistical, mathematical, and computational aspects of data analysis and classification problems (clustering, discriminant analysis, supervised/unsupervised classification, pattern recognition, data mining) and with their applications in the sciences, the economy, engineering, archaeometry, and the administration. The GfKl, founded in the year 1977, is a transdisciplinary scientific society that aims at promoting methods of classification and data analysis in theory and application.
The editors and the working group AG-DANK would like to thank all who have contributed to this report. Our special thanks go to the head of WIAS for their active support and thorough preparation of the event.
MUCHA, H.-J. and BOCK, H.-H. (Eds.) (1996): Classification and multivariate graphics: models, software and applications. Report no. 10, WIAS, Berlin.
-
S. Mohammadi, Ch. D'alonzo, L. Ruthotto, J. Polzehl, I. Ellerbrock, M.F. Callaghan, N. Weiskopf, K. Tabelow, Simultaneous adaptive smoothing of relaxometry and quantitative magnetization transfer mapping, Preprint no. 2432, WIAS, Berlin, 2017, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2432 .
Abstract, PDF (3888 kByte)
Attempts for in-vivo histology require a high spatial resolution that comes with the price of a decreased signal-to-noise ratio. We present a novel iterative and multi-scale smoothing method for quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) data that yield proton density, apparent transverse and longitudinal relaxation, and magnetization transfer maps. The method is based on the propagation-separation approach. The adaptivity of the procedure avoids the inherent bias from blurring subtle features in the calculated maps that is common for non-adaptive smoothing approaches. The characteristics of the methods were evaluated on a high-resolution data set (500 μ isotropic) from a single subject and quantified on data from a multi-subject study. The results show that the adaptive method is able to increase the signal-to-noise ratio in the calculated quantitative maps while largely avoiding the bias that is otherwise introduced by spatially blurring values across tissue borders. As a consequence, it preserves the intensity contrast between white and gray matter and the thin cortical ribbon. -
V. Avanesov, J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Consistency results and confidence intervals for adaptive l1-penalized estimators of the high-dimensional sparse precision matrix, Preprint no. 2229, WIAS, Berlin, 2016, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2229 .
Abstract, PDF (522 kByte)
In this paper we consider the adaptive l1-penalized estimators for the precision matrix in a finite-sample setting. We show consistency results and construct confidence intervals for the elements of the true precision matrix. Additionally, we analyze the bias of these confidence intervals. We apply the estimator to the estimation of functional connectivity networks in functional Magnetic Resonance data and elaborate the theoretical results in extensive simulation experiments. -
S. Becker, The Propagation-Separation Approach: Consequences of model misspecification, Preprint no. 1877, WIAS, Berlin, 2013, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1877 .
Abstract, PDF (1952 kByte)
The article presents new results on the Propagation-Separation Approach by Polzehl and Spokoiny (2006). This iterative procedure provides a unified approach for nonparametric estimation, supposing a local parametric model. The adaptivity of the estimator ensures sensitivity to structural changes. Originally, an additional memory step was included into the algorithm, where most of the theoretical properties were based on. However, in practice, a simplified version of the algorithm is used, where the memory step is omitted. Hence, we aim to justify this simplified procedure by means of a theoretical study and numerical simulations. In our previous study, we analyzed the simplified Propagation-Separation Approach, supposing piecewise constant parameter functions with sharp discontinuities. Here, we consider the case of a misspecified model. -
V.A. Panov, Estimation of the signal subspace without estimation of the inverse covariance matrix, Preprint no. 1546, WIAS, Berlin, 2010, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1546 .
Abstract, Postscript (1278 kByte), PDF (120 kByte)
Let a high-dimensional random vector $vecX$ can be represented as a sum of two components - a signal $vecS$, which belongs to some low-dimensional subspace $mathcalS$, and a noise component $vecN$. This paper presents a new approach for estimating the subspace $mathcalS$ based on the ideas of the Non-Gaussian Component Analysis. Our approach avoids the technical difficulties that usually exist in similar methods - it doesn't require neither the estimation of the inverse covariance matrix of $vecX$ nor the estimation of the covariance matrix of $vecN$. -
T. Krueger, N. Krämer, K. Rieck, ASAP: Automatic semantics-aware analysis of network payloads, Preprint no. 1502, WIAS, Berlin, 2010, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1502 .
Abstract, Postscript (888 kByte), PDF (370 kByte)
Automatic inspection of network payloads is a prerequisite for effective analysis of network communication. Security research has largely focused on network analysis using protocol specifications, for example for intrusion detection, fuzz testing and forensic analysis. The specification of a protocol alone, however, is often not sufficient for accurate analysis of communication, as it fails to reflect individual semantics of network applications. We propose a framework for semantics-aware analysis of network payloads which automaticylly extracts semantic components from recorded network traffic. Our method proceeds by mapping network payloads to a vector space and identifying semantic templates corresponding to base directions in the vector space. We demonstrate the efficacy of semantics-aware analysis in different security applications: automatic discovery of patterns in honeypot data, analysis of malware communication and network intrusion detection. -
V.A. Panov, Non-Gaussian component analysis: New ideas, new proofs, new applications, Preprint no. 1501, WIAS, Berlin, 2010, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1501 .
Abstract, Postscript (1829 kByte), PDF (328 kByte)
In this article, we present new ideas concerning Non-Gaussian Component Analysis (NGCA). We use the structural assumption that a high-dimensional random vector $vX$ can be represented as a sum of two components - a low-dimensional signal $vS$ and a noise component $vN$. We show that this assumption enables us for a special representation for the density function of $vX$. Similar facts are proven in original papers about NGCA, but our representation differs from the previous versions. The new form helps us to provide a strong theoretical support for the algorithm; moreover, it gives some ideas about new approaches in multidimensional statistical analysis. In this paper, we establish important results for the NGCA procedure using the new representation, and show benefits of our method. -
N. Krämer, M. Sugiyama, The degrees of freedom of partial least squares regression, Preprint no. 1487, WIAS, Berlin, 2010, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1487 .
Abstract, Postscript (1128 kByte), PDF (415 kByte)
The derivation of statistical properties for Partial Least Squares regression can be a challenging task. The reason is that the construction of latent components from the predictor variables also depends on the response variable. While this typically leads to good performance and interpretable models in practice, it makes the statistical analysis more involved. In this work, we study the intrinsic complexity of Partial Least Squares Regression. Our contribution is an unbiased estimate of its Degrees of Freedom. It is defined as the trace of the first derivative of the fitted values, seen as a function of the response. We establish two equivalent representations that rely on the close connection of Partial Least Squares to matrix decompositions and Krylov subspace techniques. We show that the Degrees of Freedom depend on the collinearity of the predictor variables: The lower the collinearity is, the higher the Degrees of Freedom are. In particular, they are typically higher than the naive approach that defines the Degrees of Freedom as the number of components. Further, we illustrate that the Degrees of Freedom are useful for model selection. Our experiments indicate that the model complexity based on the Degrees of Freedom estimate is lower than the model complexity of the naive approach. In terms of prediction accuracy, both methods obtain the same accuracy as cross-validation. -
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, H. Wu, Elastoplastic Timoshenko beams, Preprint no. 1430, WIAS, Berlin, 2009, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1430 .
Abstract, Postscript (1427 kByte), PDF (335 kByte)
A Timoshenko type elastoplastic beam equation is derived by dimensional reduction from a general 3D system with von Mises plasticity law. It consists of two second-order hyperbolic equations with an anisotropic vectorial Prandtl--Ishlinskii hysteresis operator. Existence and uniqueness of a strong solution for an initial-boundary value problem is proven via standard energy and monotonicity methods. -
V. Spokoiny, Parameter estimation in time series analysis, Preprint no. 1404, WIAS, Berlin, 2009, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1404 .
Abstract, Postscript (587 kByte), PDF (326 kByte)
The paper offers a novel unified approach to studying the accuracy of parameter estimation for a time series. Important features of the approach are: (1) The underlying model is not assumed to be parametric. (2) The imposed conditions on the model are very mild and can be easily checked in specific applications. (3) The considered time series need not to be ergodic or stationary. The approach is equally applicable to ergodic, unit root and explosive cases. (4) The parameter set can be unbounded and non-compact. (5) No conditions on parameter identifiability are required. (6) The established risk bounds are nonasymptotic and valid for large, moderate and small samples. (7) The results describe confidence and concentration sets rather than the accuracy of point estimation. The whole approach can be viewed as complementary to the classical one based on the asymptotic expansion of the log-likelihood. In particular, it claims a consistency of the considered estimate in a rather general sense, which usually is assumed to be fulfilled in the asymptotic analysis. In standard situations under ergodicity conditions, the usual rate results can be easily obtained as corollaries from the established risk bounds. The approach and the results are illustrated on a number of popular time series models including autoregressive, Generalized Linear time series, ARCH and GARCH models and meadian/quantile regression. -
M. Elagin, Locally adaptive estimation methods with application to univariate time series, Preprint no. 1383, WIAS, Berlin, 2008, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1383 .
Abstract, Postscript (1800 kByte), PDF (414 kByte)
The paper offers a unified approach to the study of three locally adaptive estimation methods in the context of univariate time series from both theoretical and empirical points of view. A general procedure for the computation of critical values is given. The underlying model encompasses all distributions from the exponential family providing for great flexibility. The procedures are applied to simulated and real financial data distributed according to the Gaussian, volatility, Poisson, exponential and Bernoulli models. Numerical results exhibit a very reasonable performance of the methods. -
M. Elagin, V. Spokoiny, Locally time homogeneous time series modelling, Preprint no. 1379, WIAS, Berlin, 2008, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1379 .
Abstract, Postscript (937 kByte), PDF (380 kByte)
In this paper three locally adaptive estimation methods are applied to the problems of variance forecasting, value-at-risk analysis and volatility estimation within the context of nonstationary financial time series. A general procedure for the computation of critical values is given. Numerical results exhibit a very reasonable performance of the methods. -
D. Hoffmann, K. Tabelow, Structural adaptive smoothing for single-subject analysis in SPM: The aws4SPM-toolbox, Technical Report no. 11, WIAS, Berlin, 2008, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.TECHREPORT.11 .
Abstract
There exists a variety of software tools for analyzing functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging data. A very popular one is the freely available SPM package by the Functional Imaging Laboratory at the Wellcome Department of Imaging Neuroscience. In order to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio it provides the possibility to smooth the data in a pre-processing step by a Gaussian filter. However, this comes at the cost of reducing the effective resolution. In a series of recent papers it has been shown, that using a structural adaptive smoothing algorithm based on the Propagation-Separation method allows for enhanced signal detection while preserving the shape and spatial extent of the activation areas. Here, we describe our implementation of this algorithm as a toolbox for SPM.
 Talks, Poster
Talks, Poster
-
L. Kuen, Numerical study of time dependent dynamical simulations of PCSELs, Nonlinear Dynamics in Semiconductor Lasers 2025, Berlin, June 16 - 18, 2025.
-
J.-J. Zhu, Gradient flows in the (marginal) entropy-regularized transport geometry for sampling and inference, Workshop on Bayesian Analysis and Artificial Intelligence, September 10 - 12, 2025, Peking University, Center for Statistical Science, China, September 11, 2025.
-
L. Mertenskötter, M. Kantner, Narrow-linewidth lasers, CLEO Conference, North Carolina, USA, May 5 - 10, 2024.
-
V. Spokoiny, Inference for nonlinear problems, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UEST), School of Mathematical Sciences, Chengdu, China, May 14, 2024.
-
A. Suvorikova, Bernstein type inequality for unbounded martingales, Workshop ``Statistics and Learning Theory in the Era of Artificial Intelligence'', June 23 - 28, 2024, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach (MFO), June 28, 2024.
-
O. Klein, A model for a magneto mechanical device: Forward and inverse uncertainty quantization, Leibniz MMS Days 2024, Kaiserslautern, April 10 - 12, 2024.
-
O. Klein, On a model for a magneto mechanical device: Forward and inverse uncertainty quantification, 2nd Workshop of the MATH+ Thematic Einstein Semester ``Mathematics of Small Data Analysis'', Berlin, January 17 - 19, 2024.
-
V. Spokoiny, Gaussian variational inference in high dimension, Mohamed Bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI), Department of Machine Learning, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, March 12, 2024.
-
V. Spokoiny, Inference for nonlinear inverse problems, The Mathematics of Data: Workshop on Optimal Transport and PDEs, January 21 - 26, 2024, National University of Singapore, Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Singapore, January 23, 2024.
-
J.-J. Zhu, Gradient flows and kernelization in the Hellinger--Kantorovich (a.k.a. Wasserstein--Fisher--Rao) space, EUROPT 2024, 21st Conference on Advances in Continuous Optimization, June 26 - 28, 2024, Lund University, Department of Automatic Control, Sweden, June 28, 2024.
-
J.-J. Zhu, Transport and flow: The modern mathematics of distributional learning and optimization, Universität des Saarlandes, Saarland Informatics Campus, Saarbrücken, July 5, 2024.
-
L. Schmeller, Gel models for phase separation at finite strains, 93rd Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM), May 29 - June 2, 2023, Technische Universität Dresden, June 2, 2023.
-
L. Mertenskötter, Kalman filtering of stochastic laser dynamics: Parameter and state space estimation from time-delayed measurements, International Conference on Structural Nonlinear Dynamics and Diagnosis, May 15 - 17, 2023, Marrakech, Morocco, May 17, 2023.
-
J. Polzehl, Smoothing techniques for quantitative MR, colloquium, Marquette University, Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, Milwaukee, USA, November 3, 2023.
-
A. Selahi, Recovering battery ageing dynamics with invertible neuronal networks, 10th International Congress on Industrial and Applied Mathematics (ICIAM 2023), August 20 - 25, 2023, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan, August 23, 2023.
-
A. Selahi, Recovery of battery ageing dynamics using Bayesian inference, 93rd Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM), May 29 - June 2, 2023, Technische Universität Dresden, June 1, 2023.
-
M. Kantner, Wiener filter enhanced estimation of the intrinsic laser linewidth from delayed self-heterodyne beat note measurements, 2023 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics/Europe-European Quantum Electronics Virtual Conferences, Munich, June 26 - 30, 2023.
-
O. Klein, On a model for a magneto mechanical device: Forward and inverse uncertainty quantification, 13th International Symposium on Hysteresis Modeling and Micromagnetics (HMM 2023), June 5 - 7, 2023, Technische Universität Wien, Austria, June 6, 2023.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bayesian inference for complex models, MIA 2023 -- Mathematics and Image Analysis, February 1 - 3, 2023, Berlin, February 3, 2023.
-
V. Spokoiny, Estimation and inference for error-in-operator model, Lecture Series Trends in Statistics, National University of Singapore, Department of Mathematics, Singapore, August 25, 2023.
-
L. Mertenskötter, M. Kantner, U. Bandelow, H. Wenzel, Non-Markovian noise in semiconductor lasers, MATH+ Day 2022, Technische Universität Berlin, November 18, 2022.
-
L. Mertenskötter, M. Kantner, U. Bandelow, H. Wenzel, Non-Markovian noise in semiconductor lasers, Nonlinear Dynamics in Semiconductor Lasers 2025, Berlin, June 16 - 18, 2025.
-
L. Mertenskötter, Data-Driven modeling of Non-Markovian noise in semiconductor laser, 22nd International Conference on Numerical Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices (NUSOD), September 12 - 16, 2022, Politecnico di Torino, Italy.
-
H. Kremer, J.-J. Zhu, K. Muandet, B. Schölkopf, Functional generalized empirical likelihood estimation for conditional moment restrictions (spotlight, online talk), ICML 2022: 39th International Conference on Machine Learning (Online Event), July 18 - 23, 2022, Baltimore, USA, July 19, 2022.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bayesian inference for nonlinear inverse problems, SFB 1294 Annual Meeting 2022, September 13 - 14, 2022, Universität Potsdam, Institut für Mathematik, September 13, 2022.
-
V. Spokoiny, Laplace approximation in high dimension, Workshop ``Re-thinking High-dimensional Mathematical Statistics'', May 16 - 20, 2022, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, May 17, 2022.
-
J.-J. Zhu, F. Nüske, Data-Driven Modeling and Optimization of Dynamical Systems under Uncertainty (Ph.D. 16-hour minicourse), IRTG 2544 Stochastic Analysis in Interaction, July 11 - 14, 2022, Technische Universität Berlin.
-
J.-J. Zhu, Distributionally robust learning and optimization in MMD geometry, KU Leuven, STADIUS Center for Dynamical Systems, Signal Processing, and Data, Belgium, September 9, 2022.
-
J.-J. Zhu, Kernel methods for distributionally robust machine learning and optimization, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Department of Operations Analytics, Netherlands, July 28, 2022.
-
A. Maltsi, Model-based geometry reconstruction of TEM images, MATH+ Day 2021 (Online Event), Technische Universität Berlin, November 5, 2021.
-
A. Suvorikova, Optimal transport in machine learning (onlne talk), Seminar of the International Laboratory of Stochastic Algorithms and High-dimensional Inference (HDI Lab), National Research University -- Higher School of Economics (HSE), Faculty of Computer Science (Online Event), Moscow, Russian Federation, April 29, 2021.
-
A. Suvorikova, Statistics for non-statisticians (online talk), ITaS Interdisciplinary Conference 2021 (Online Event), November 15 - 17, 2021, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems, Moscow, Russian Federation, November 16, 2021.
-
A. Suvorikova, Survey of methods of k-means clustering with optimal transport (online talk), Third HSE-Yandex Autumn School on Generative Models (Hybrid Event), November 23 - 26, 2021, National Research University -- Higher School of Economics (HSE), Yandex SDA Campus, Moscow, Russian Federation, November 26, 2021.
-
J.-J. Zhu, Learning and approximation in multi-stage optimization under distribution shift, Universität Freiburg, SysCOp Lab, November 16, 2021.
-
V. Avanesov, Data-driven confidence bands for distributed nonparametric regression (online talk), The 33rd Annual Conference on Learning Theory (COLT 2020) (Online Event), July 9 - 12, 2020, Graz, Austria, July 10, 2020.
-
A. Suvorikova, Change point detection in high-dimensional data (online talk), Joint Aramco-HSE Reserach Seminar, Higher School of Economics, Faculty of Computer Science, Moscow, Russian Federation, April 15, 2020.
-
P. Dvurechensky, Distributed optimization for Wasserstein barycenters (online talk), 15th INFORMS Telecommunication and Network Analytics Conference 2020 (Online Event), October 20 - 21, 2020, INFORMS Telecommunications & Networks Analytics, Catonsville, USA, October 21, 2020.
-
TH. Koprucki, K. Tabelow, T. Streckenbach, T. Niermann, A. Maltsi, Model-based geometry reconstruction of TEM images, MATH+ Day 2020 (Online Event), Berlin, November 6, 2020.
-
F. Besold, Manifold clustering with adaptive weights, Structural Inference in High-Dimensional Models 2, National Research University Higher School of Economics, HDILab, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation, August 26 - 30, 2019.
-
F. Besold, Manifold clustering with adaptive weights, Joint Workshop of BBDC, BZML and RIKEN AIP, Fraunhofer Institute HHI, September 9 - 10, 2019.
-
D. Dvinskikh, Decentralized and parallelized primal and dual accelerated methods, Structural Inference in High-Dimensional Models 2, National Research University Higher School of Economics, HDILab, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation, August 26 - 30, 2019.
-
TH. Koprucki, On a database of simulated TEM images for In(Ga)As/GaAs quantum dots with various shapes, 19th International Conference on Numerical Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices (NUSOD 2019) , Session ``Nano-structures", July 8 - 12, 2019, University of Ottawa, Canada, July 8, 2019.
-
V. Spokoiny, Advanced statistical methods, April 9 - 11, 2019, Higher School of Economics, National Research University, Moscow, Russian Federation.
-
V. Spokoiny, Optimal stopping and control via reinforced regression, Optimization and Statistical Learning, March 25 - 28, 2019, Les Houches School of Physics, France, March 26, 2019.
-
A. Suvorikova, Statistical inference with optimal transport, Spring School ``Structural Inference 2018'' and Closing Workshop, FOR 1735 ``Structural Inference in Statistics'', Lübbenau, March 4 - 9, 2018.
-
P. Pigato, Estimation of piecewise-constant coefficients in a stochastic differential equation, The 40th Conference on Stochastic Processes and their Applications (SPA 2018), University of Gothenburg, Göteborg, Sweden, June 13, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Adaptive nonparametric clustering, Multiscale Problems in Materials Science and Biology: Analysis and Computation, January 8 - 12, 2018, Tsinghua University, Yau Mathematical Sciences Center, Sanya, Hainan, China, January 10, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bootstrap confidence sets for spectral projectors of sample covariance, 12th International Vilnius Conference on Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics and 2018 IMS Annual Meeting on Probability and Statistics, July 2 - 6, 2018, Vilnius University, Lithuanian Mathematical Society and the Institute of Mathematical Statistics, Lithuania, July 5, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Gaussian process forecast with multidimensional distributional input, 4th Conference of the International Society for Nonparametric Statistics, June 11 - 15, 2018, University of Salerno, Italy, June 15, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Inference for spectral projectors, Workshop ``Statistical Inference for Structured High-dimensional Models'', March 11 - 16, 2018, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, March 14, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Large ball probability with applications in statistics, Mathematical Workshop of the School of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Dolgoprudny, Russian Federation, November 30, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Large ball probability with applications to statistical inference, 6th Princeton Day of Statistics, Princeton University, Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering, USA, November 9, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Prior impact in Bayesian inference, International Seminar & Workshop: ``Stochastic Dynamics on Large Networks: Prediction and Inference'', October 15 - 16, 2018, Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme, Dresden, October 15, 2018.
-
V. Spokoiny, Structured nonparametric and high-dimensional statistics, 2018 Joint Meeting of the Korean Mathematical Society and the German Mathematical Society, October 3 - 6, 2018, Korean Mathematical Society, Seoul, Korea (Republic of), October 5, 2018.
-
A. Suvorikova, Construction of confidence sets in 2-Wasserstein space, Haindorf Seminar 2017, January 24 - 28, 2017, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Fakultät, Hejnice, Czech Republic, January 26, 2017.
-
A. Suvorikova, Construction of confidence sets in 2-Wasserstein space, Machine Learning Seminar, Université Paul-Sabatier, Institut de Mathématiques de Toulouse, France, December 1, 2017.
-
A. Suvorikova, Construction of non-asymptotic confidence sets in 2-Wasserstein space, Spring School ``Structural Inference'' 2017, Bad Malente, March 5 - 10, 2017.
-
P. Pigato, Estimation of the parameters of a diffusion with discontinuous coefficients, 7th Annual ERC Berlin-Oxford Young Researchers Meeting on Applied Stochastic Analysis, May 18 - 20, 2017, WIAS-Berlin, May 20, 2017.
-
A. Koziuk, Bootstrap for the regression problem with instrumental variables, Haindorf Seminar 2017, January 24 - 28, 2017, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Fakultät, Hejnice, Czech Republic, January 26, 2017.
-
H.-J. Mucha, About the influence of multiple points of bootstrapping on the validation of clustering results, European Classification and Data Analysis Conference 2017 (ECDA2017), September 27 - 29, 2017, Wrocław University of Economics, Poland, September 27, 2017.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Big data clustering: Comparison of the performance of a new fast pre-clustering and subsampling, German Polish Seminar on Data Analysis and Applications 2017, September 25 - 26, 2017, Wrocław University of Economics, Poland, September 26, 2017.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Hierarchical clustering of big data using a special bootstrapping version, AG DANK Herbsttagung, November 17 - 18, 2017, Gesellschaft für KlassifikationGesellschaft für Klassifikation, Data Science Society, November 18, 2017.
-
A. Suvorikova, Bootstrap confidence sets for Wasserstein barycenters, Meeting in Mathematical Statistics 2016 ``Advances in Nonparametric and High-dimensional Statistics'', December 12 - 16, 2016, Fréjus, France, December 16, 2016.
-
A. Suvorikova, Bootstrap procedure in the space of Gaussian measures, Information Technology and Systems 2016, September 25 - 30, 2016, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems, St. Petersburg.
-
A. Suvorikova, Multiscale change point detection, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Institut für Mathematische Stochastik, November 9, 2016.
-
CH. Bayer, The forward-reverse method for conditional Markov processes, Bayes in Paris, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Administration Économique, Paris, France, January 28, 2016.
-
V. Spokoiny, Adaptive weights clustering, Mathematisches Kolloquium, Universität Ulm, Institut für Analysis, November 18, 2016.
-
V. Spokoiny, Clustering using adaptive weights, Yandex, Moscow, Russian Federation, October 28, 2016.
-
V. Spokoiny, Inference for Structural Nonparametrics, Open Access: urlhttp://www.mathnet.ru/php/conference.phtml?option_lang=eng&eventID=25&confid=872, February 15 - March 1, 2016, Independent University of Moscow (IUM), Russian Federation.
-
V. Spokoiny, Inference for structured regression, Meeting in Mathematical Statistics 2016 ``Advances in Nonparametric and High-dimensional Statistics'', December 12 - 16, 2016, Fréjus, France, December 15, 2016.
-
N. Buzun, Multiplier bootstrap with misspecified models, Statistics Mathematics and Applications, August 31 - September 4, 2015, La Villa Clythia, Fréjus, France, September 1, 2015.
-
N. Buzun, Multiscale parametric approach for change point detection, Information Technologies and Systems 2015, September 6 - 11, 2015, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems, Sochi, Russian Federation, September 9, 2015.
-
K. Schildknecht, Simultaneous statistical inference for epigenetic data, 61. Biometrischen Kolloquium in Dortmund, March 16 - 18, 2015, Technische Universität Dortmund, Fakultät Statistik, March 18, 2015.
-
J. Stange, On the correlation structure of test statistics in genetic case-control association studies, 61. Biometrischen Kolloquium in Dortmund, March 16 - 18, 2015, Technische Universität Dortmund, Fakultät Statistik, March 17, 2015.
-
CH. Bayer, The forward-reverse method for conditional Markov processes, MInisymposium ``Multilevel Monte Carlo Methods and Applications'' of the 8th International Congress on Industrial and Applied Mathematics (ICIAM2015), August 10 - 14, 2015, International Council for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Beijing, China, August 10, 2015.
-
CH. Bayer, The forward-reverse method for conditional diffusion processes, Advances in Uncertainty Quantification Methods, Algorithms and Applications (UQAW 2015), January 6 - 9, 2015, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, January 6, 2015.
-
CH. Bayer, The forward-reverse method for conditional diffusion processes, Oberseminar Finanz- und Versicherungsmathematik, Technische Universität München, Fakultät für Mathematik, January 19, 2015.
-
CH. Bayer , The forward-reverse method for conditional Markov processes, International Conference on Scientific Computation and Differential Equations, Universität Potsdam, Institut für Mathematik, September 16, 2015.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bootstrap tuning in model selection, Lomonosov State University, Faculty of Computer Sciences, Moscow, Russian Federation, September 18, 2015.
-
V. Spokoiny, Predictive modeling: Methods and applications, Skolkov Institute of Science and Technology, Moscow, Russian Federation, August 27, 2015.
-
M. Zhilova, Non-asymptotic confidence bounds via multiplier bootstrap, CRC 649 "Economic Risk" Conference, July 10 - 12, 2014, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Sonderforschungsbereich 649: Ökonomisches Risiko, July 11, 2014.
-
M. Zhilova, Parametric confidence sets using multiplier bootstrap, Premoday, February 21, 2014, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, Russian Federation, February 21, 2014.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform confidence bands for generalized regression via multiplier bootstrap, International Symposium on Financial Engineering and Risk Management 2014, June 27 - 28, 2014, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing, China, June 27, 2014.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform confidence bands in generalized regression via multiplier bootstrap, The 3rd Institute of Mathematical Statistics Asia Pacific Rim Meeting, June 29 - July 3, 2014, Taipei, Taiwan, Province Of China, July 1, 2014.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform confidence sets via multiplier bootstrap, New Horizons in Statistical Decision Theory, September 7 - 13, 2014, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, September 9, 2014.
-
A. Andresen, Finite sample analysis of M-estimators, International Workshop ``Advances in Optimization and Statistics'', May 15 - 16, 2014, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 16, 2014.
-
A. Andresen, Finite sample analysis of maximum likelihood estimators, Kolloquium über Mathematische Statistik und Stochastische Prozesse, Universität Hamburg, April 22, 2014.
-
R. Hildebrand, Spectrahedral cones generated by rank 1 matrices, Workshop ``Real Algebraic Geometry With A View Toward Systems Control and Free Positivity'', April 6 - 12, 2014, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, April 11, 2014.
-
K. Schildknecht, A two-stage hierarchical multiple test procedure based on the asymptotically optimal rejection curve, 60. Biometrisches Kolloquium, Bremen, March 10 - 13, 2014.
-
K. Schildknecht, A two-stage hierarchical multiple test procedure based on the asymptotically optimal rejection curve, Workshop Adaptive Designs and Multiple Testing Procedures, Internationalen Biometrischen Gesellschaft, Basel, Switzerland, June 5, 2014.
-
J. Stange, Computation of an effective number of simultaneous $chi^2$ tests, International Workshop ``Advances in Optimization and Statistics'', May 15 - 16, 2014, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 15, 2014.
-
J. Stange, Multiple testing adjustments with copula models, 27th International Biometric Conference (IBC 2014), Florence, Italy, July 6 - 11, 2014.
-
J. Stange , Multiple testing adjustments with copula models, Haindorf Seminar 2014, February 6 - 8, 2014, Humboldt-Universitát zu Berlin, Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Fakultät, Hejnice, Czech Republic, February 6, 2014.
-
N. Willrich, Model selection by Lepski's method for penalized likelihood, International Workshop ``Advances in Optimization and Statistics'', May 15 - 16, 2014, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 16, 2014.
-
S. Mohammadi, L. Ruthotto, K. Tabelow, T. Feiweier, J. Polzehl, N. Weiskopf, ACID -- A post-processing toolbox for advanced diffusion MRI, 20th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Hamburg, June 8 - 12, 2014.
-
TH. Dickhaus, T. Bodnar, False discovery rate control under Archimedean copula, 27th International Biometric Conference (IBC 2014), July 6 - 11, 2014, International Biometric Society, Florence, Italy, July 7, 2014.
-
TH. Dickhaus, Randomized p-values for multiple testing of composite null hypotheses, 60. Biometrisches Kolloquium, March 11 - 13, 2014, Universität Bremen, March 12, 2014.
-
TH. Dickhaus, Simultaneous Bayesian analysis of contingency tables in genetic association studies, Bayesian Biostatistics 2014, July 2 - 5, 2014, University of Zurich, Switzerland, July 2, 2014.
-
TH. Dickhaus, Simultaneous Bayesian analysis of contingency tables in genetic association studies, International Workshop ``Advances in Optimization and Statistics'', May 15 - 16, 2014, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 15, 2014.
-
P. Friz, Implied, local and stochastic volatility: Analytical results in Heston and Stein Stein, Thematic Cycle on Robust Management in Finance, Workshop ``Model Approximation and Numerical Methods'' (February -- March 2014), Institut Louis Bachelier, Paris, France, March 14, 2014.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Bottom-up variable selection in cluster analysis using bootstrapping: A proposal, European Conference on Data Analysis (ECDA 2014), July 2 - 4, 2014, Jacobs University Bremen gGmbH, July 4, 2014.
-
H.-J. Mucha, From univariate to multivariate clustering with application to P-ED-XRF data, Workshop ``Application of Portable Energy-dispersive X-ray Fluorescence to the Analysis of Archaeological Ceramics'', June 20 - 21, 2014, Excellence Cluster TOPOI, Berlin, June 21, 2014.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Variable selection in cluster analysis by means of bootstrapping, International Workshop ``Advances in Optimization and Statistics'', May 15 - 16, 2014, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 16, 2014.
-
J. Polzehl, Estimation of sparse precision matrices, MMS-Workshop ``large p small n'', WIAS-Berlin, April 15, 2014.
-
J. Polzehl, Quantification of noise in MR experiments, Statistical Challenges in Neuroscience, September 3 - 5, 2014, University of Warwick, Centre for Research in Statistical Methodology, UK, September 4, 2014.
-
J. Polzehl, Statistical problems in diffusion weighted MR, CoSy Seminar, University of Uppsala, Department of Mathematics, Sweden, November 11, 2014.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bernstein--von Mises theorem for a quasi-posterior, International Symposium on Financial Engineering and Risk Management 2014, June 27 - 28, 2014, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing, China, June 27, 2014.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bootstrap confidence sets under a model misspecification, Workshop ``New Horizons in Statistical Decision Theory'', September 7 - 13, 2014, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, September 8, 2014.
-
V. Spokoiny, Construction of the sharp confidence bands using multiplier bootstrap, Advances in Stochastic Analysis, September 3 - 5, 2014, National Research University -- Higher School of Economics, Laboratory of Stochastic Analysis and its Applications, Moscow, Russian Federation, September 5, 2014.
-
V. Spokoiny, Modern Parametric Statistics, February 10 - 25, 2014, Independent University of Moscow, Russian Federation.
-
K. Tabelow, S. Mohammadi, N. Weiskopf, J. Polzehl, Adaptive noise reduction in multi-shell dMRI data with SPM by POAS4SPM, 20th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Hamburg, June 8 - 12, 2014.
-
K. Tabelow, H.U. Voss, J. Polzehl, Local estimation of noise standard deviation in MRI images using propagation separation, 20th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Hamburg, June 8 - 12, 2014.
-
K. Tabelow, H.U. Voss, J. Polzehl, Local estimation of the noise level in MRI images using structural adaptation, 5th Ultra-Highfield MRI Scientific Symposium, Max Delbrück Center, Berlin, June 20, 2014.
-
K. Tabelow, High-resolution diffusion MRI by msPOAS, Statistical Challenges in Neuroscience, September 3 - 5, 2014, University of Warwick, Centre for Research in Statistical Methodology, UK, September 4, 2014.
-
S. Becker, The propagation-separation approach: Choice of the adaptation bandwidth and its (in-)dependence of the unknown parameter, PreMoLab Workshop on: Advances in predictive modeling and optimization, May 16 - 17, 2013, WIAS-Berlin, May 17, 2013.
-
M. Zhilova, Resampling based uniform confidence bands in quantile regression, Tagung des SFB 649 "Ökonomisches Risiko" in Motzen, June 20 - 22, 2013, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, School of Business and Economics, June 22, 2013.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform confidence bands in local estimation, 29th European Meeting of Statisticians (EMS), July 20 - 25, 2013, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary, July 20, 2013.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform confidence bands in local estimation, Premoday February 2013, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology State University, Russian Federation, February 22, 2013.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform confidence bands in local parametric estimation, Haindorf-Seminar 2013, February 7 - 9, 2013, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Czech Republic, February 9, 2013.
-
R. Hildebrand, Convex projective programming, International Conference on Continuous Optimization (ICCOPT2013), July 29 - August 1, 2013, Universidade Nove de Lisboa, Portugal, July 31, 2013.
-
R. Hildebrand, Scaling relationships between the copositive cone and the cone of sum of squares polynomials, International Conference on Continuous Optimization (ICCOPT2013), July 29 - August 1, 2013, Universidade Nove de Lisboa, Portugal, July 30, 2013.
-
K. Tabelow, S. Becker, S. Mohammadi, N. Weiskopf, J. Polzehl, Multi-shell position-orientation adaptive smoothing (msPOAS), 19th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Seattle, USA, June 16 - 20, 2013.
-
M. Welvaert, K. Tabelow, R. Seurinck, Y. Rosseel, Defining ROIs based on localizer studies: More specific localization using adaptive smoothing, 19th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Seattle, USA, June 16 - 20, 2013.
-
TH. Dickhaus, Bootstrap methods for simultaneous statistical inference in dynamic factor models, Princeton-Humboldt Conference 2013, November 1 - 2, 2013, Princeton University, Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering, USA, November 1, 2013.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Assessment of stability in partitional clustering using resampling techniques, Third Bilateral German-Polish Symposium on Data Analysis and Its Applications (GPSDAA 2013), September 26 - 28, 2013, Technische Universität Dresden, September 27, 2013.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Resampling techniques in cluster analysis: Is subsampling better than bootstrapping?, European Conference on Data Analysis, July 10 - 12, 2013, University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg, July 11, 2013.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Selection of variables in cluster analysis using resampling techniques: A proposal, Conference of the International Federation of Classification Societies (IFCS), July 14 - 17, 2013, Tilburg University, Netherlands, July 16, 2013.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Variables election in cluster analysis using resampling techniques, British Classification Society Meeting 2013, November 8 - 9, 2013, University College London, Department of Statistical Science, UK, November 8, 2013.
-
V. Spokoiny, Identification and critical dimension in semiparametric estimation, Workshop ``Mathematical Statistics of Partially Identified Objects'', April 21 - 27, 2013, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, April 21, 2013.
-
V. Spokoiny, Robust clustering using adaptive weights, International Workshop on Statistical Learning, June 26 - 28, 2013, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, PreMoLab, Russian Federation, June 27, 2013.
-
S. Becker, Diffusion weighted imaging: Modeling and analysis beyond the diffusion tensor, Methodological Workshop: Structural Brain Connectivity: Diffusion Imaging---State of the Art and Beyond, October 30 - November 2, 2012, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, November 2, 2012.
-
S. Becker, Image processing via orientation scores, Workshop ``Computational Inverse Problems'', October 23 - 26, 2012, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, October 25, 2012.
-
S. Becker, Revisiting: Propagation-separation approach for local likelihood estimation, PreMoLab: Moscow-Berlin-Stochastic and Predictive Modeling, May 29 - June 1, 2012, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 31, 2012.
-
M. Zhilova, Uniform properties of local maximum likelihood estimate, 55-th Scientific conference of Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, November 19 - 24, 2012, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Dolgoprudny, Russian Federation, November 24, 2012.
-
M. Becker, CP-detection, outlook, ECONS Projekttreffen, PIK Potsdam, December 12, 2012.
-
M. Becker, Change point detection via universal compressors, PreMoLab: Moscow-Berlin Stochastic and Predictive Modeling, May 30 - June 2, 2012, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, May 31, 2012.
-
M. Becker, Changepoint detection via universal compressors, ECONS - Projekttreffen, WIAS - Berlin, June 7, 2012.
-
K. Tabelow, Position-orientation adaptive smoothing (POAS) diffusion weighted imaging data, Workshop on Neurogeometry, November 15 - 17, 2012, Masaryk University, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Brno, Czech Republic, November 16, 2012.
-
J. Dolata, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Eine neue Referenzgruppe für die römische Ziegelproduktion der I. Thrakerkohorte am Mittelrhein, Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2012, Tübingen, March 27 - 31, 2012.
-
C. Morales-Merino, H.-J. Mucha, H.-G. Bartel, Multivariate statistical analysis of clay and ceramic-data for provenance of Bronze age pottery from Troia, Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2012, Tübingen, March 27 - 31, 2012.
-
M. Zhilova, Quasi MLE in Instrumental variable model, PreMoDay II, March 16, 2012, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Russian Federation, March 16, 2012.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Clustering and visualisation based on dual scaling, 4th Japanese-German Symposium on Classification (JGSC2012), March 8 - 10, 2012, Doshisha University, Kyoto, Japan, March 9, 2012.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Dual scaling classification and its application to archaeometry, 36th Annual Conference of the German Classification Society, August 1 - 3, 2012, Universität Hildesheim, Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL), August 2, 2012.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Measures of incomparability and of inequality and their application, 10th Workshop on Partial Order, Theory and Application: Multi-Indicator Systems and Modelling in Partial Order, September 27 - 28, 2012, Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin, September 28, 2012.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Soft bootstrapping and its comparison with other resampling methods, 36th Annual Conference of the German Classification Society, August 1 - 3, 2012, Universität Hildesheim, Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL), August 2, 2012.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Visualisation and cluster analysis, Herbsttagung der AG Datenanalyse und numerische Klassifikation, October 5 - 6, 2012, Landschaftsverband Rheinland, LVR-Amt für Bodendenkmalpflege im Rheinland, Bonn, October 6, 2012.
-
J. Polzehl, Adaptive methods for noise reduction in diffusion weighted MR, BRIC Seminar Series, University of North Carolina, School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, July 10, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Basics of modern parametric statistics, February 13 - 28, 2012, Independent University of Moscow, Center for Continuous Mathematical Education, Russian Federation.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bernstein--von Mises theorem for quasi posteriors, International Workshop on Recent Advances in Time Series Analysis (RATS 2012), June 8 - 12, 2012, University of Cyprus, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Protaras, June 9, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bernstein--von Mises theorem for quasi posteriors, Workshop ``Frontiers in Nonparametric Statistics'', March 11 - 17, 2012, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, March 12, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bernstein--von Mises theorem for quasi posteriors, Workshop II on Financial Time Series Analysis: High-dimensionality, Non-stationarity and the Financial Crisis, June 19 - 22, 2012, National University of Singapore, Institute for Mathematical Sciences, June 21, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bernstein--von Mises theorem for quasi posteriors, Workshop on Recent Developments in Statistical Multiscale Methods, July 16 - 18, 2012, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Institut für Mathematische Stochastik, July 17, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Bernstein--von Mises theorem for quasi posteriors, PreMoLab Seminar, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, March 15, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Parametric estimation: Modern view, PreMoDay I, February 24, 2012, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, February 24, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Some methods of modern statistics, Information Technology and Systems 2, August 19 - 25, 2012, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Petrozavodsk, August 20, 2012.
-
M. Becker, Change point detection via universal compressors, ECONS (Evolving Complex Networks) Spring School and Workshop, March 28 - 31, 2011, Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung, Wandlitz, March 29, 2011.
-
S. Becker, Structural adaptive smoothing in R3xS2 with application to diffusion weighted imaging, Statistics Mathematics and Applications (StatMathAppli 2011), August 29 - September 2, 2011, Fréjus, France, September 1, 2011.
-
S. Becker, Structural adaptive smoothing in R3xS2 with application to diffusion weighted imaging, Chemnitz Symposium on Inverse Problems 2011, September 22 - 23, 2011, Technische Universität, Fakultät für Mathematik, September 22, 2011.
-
E. Diederichs, Modellselektion durch Semidefinite Relaxation, Jahrestagung der Deutschen Mathematiker-Vereinigung (DMV) 2011, September 19 - 22, 2011, Universität zu Köln, Mathematisches Institut, September 21, 2011.
-
E. Diederichs, Recent trends in large scale optimization, ECONS (Evolving Complex Networks) Spring School and Workshop, March 28 - 31, 2011, Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung, Wandlitz, March 31, 2011.
-
V. Panov, Non-Gaussian component analysis, ECONS Spring School and Workshop, March 28 - 31, 2011, Potsdam Institut für Klimaforschung, March 31, 2011.
-
S. Becker, Model-free structural adaptive smoothing of diffusion weighted images, Workshop on Statistics and Neuroimaging 2011, November 23 - 25, 2011, WIAS, November 24, 2011.
-
M. Becker, Current state of research on SILT and CP-detection, ECONS-projekt-meeting, November 21, 2011, Leibniz-Institut für Gewässerökologie und Binnenfischerei (IGB), November 21, 2011.
-
E. Diederichs, Sparse non-Gaussian component analysis, Structural Methods of Data Analysis and Optimization, December 15 - 17, 2011, Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute for Information Transmission Problems (Kharkevich Institute), Moscow, December 16, 2011.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Geochemical and statistical investigation of clay deposits in the troad and its implication for provenance of bronze age fine pottery from Troia, Joint Conference of the German Classification Society (GfKl), German Association for Pattern Recognition (DAGM), Symposium of the International Federation of Classification Societies (IFCS), August 30 - September 2, 2011, Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main, September 1, 2011.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Method selection in cluster analysis followed by built-in validation, Second Bilateral German-Polish Symposium on Data Analysis and Its Applications (GPSDAA 2011), April 14 - 16, 2011, Cracow University of Economics, Poland, April 16, 2011.
-
J. Polzehl, Statistical issues in modeling diffusion weighted magnetic resonance data, 3rd International Conference on Statistics and Probability 2011 (IMS-China), July 8 - 11, 2011, Institute of Mathematical Statistics, Xian, China, July 10, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Alternating and semiparametric efficiency, Conference in Honour of Joel Horowitz, June 23 - 24, 2011, Centre for Microdata Methods and Practice, London, UK, June 24, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Alternating and semiparametric efficiency, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Analyse de l'Information (ENSAI), Rennes, France, September 16, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Methods of dimension reduction, ECONS (Evolving Complex Networks) Spring School and Workshop, March 28 - 30, 2011, Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung, March 29, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Modern parametric theory, September 13 - 16, 2011, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Analyse de l'Information (ENSAI), Rennes, France.
-
V. Spokoiny, Non-Gaussian component analysis using semi-definite relaxation, MASCOT NUM (Méthodes d'Analyse Stochastique pour les COdes et Traitements NUMériques) 2011 Workshop, March 23 - 25, 2011, Villard de Lans, France, March 25, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Parametric inference. Revisited, 5èmes Journées Statistiques du Sud, June 14 - 16, 2011, Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, Faculté des Sciences, June 15, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Structure adaptive estimation by alternating, Workshop ``Stuctural Inference Day'', April 18, 2011, Universität Hamburg, April 18, 2011.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Classification based on dual scaling, Herbsttagung der AG DA-NK der GfKl, November 11 - 12, 2011, Heinrich Heine Universität Düsseldorf, November 11, 2011.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Classification of roman tiles with stamp Pardalis, Joint Conference of the German Classification Society (GfKl), German Association for Pattern Recognition (DAGM), Symposium of the International Federation of Classification Societies (IFCS), August 30 - September 2, 2011, Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main, September 1, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Alternating and semiparametric efficiency, Workshop ``Very High Dimensional Semiparametric Models'', October 3 - 7, 2011, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, October 4, 2011.
-
V. Spokoiny, Semiparametric estimation alternating and efficiency, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Administration Économique (ENSAE), Paris, France, December 12, 2011.
-
A. Beinrucker, An application of Gaussian processes to Bayesian statistics, Seminar ``Gaussian Processe'', Universität Potsdam, Fachbereich Mathematik, November 25, 2010.
-
A. Beinrucker, Classification using FISTA, MASH Meeting, November 8 - 9, 2010, EU-Projekt MASH, Prag, Czech Republic, November 9, 2010.
-
A. Beinrucker, MASH --- Massive sets of heuristics, Machine Learning Summer School, Canberra, Australia, September 27 - October 6, 2010.
-
N. Krämer, Conjugate gradient regularization --- A statistical framework for partial least squares regression, 4th Workshop on Partial Least Squares and Related Methods for Cutting-edge Research in Experimental Sciences, May 10 - 11, 2010, École Supérieure d'Électricité, Department of Information Systems and Decision Sciences, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, May 11, 2010.
-
N. Krämer, The degrees of freedom of partial least squares regression, DAGStat 2010, March 23 - 26, 2010, Technische Universität Dortmund, Fakultät Statistik, March 23, 2010.
-
V. Panov, Non-Gaussian component classification with applications to American Option Pricing, Haindorf Seminar 2010 (Klausurtagung des SFB 649), February 11 - 14, 2010, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Fakultät, Hejnice, Czech Republic, February 13, 2010.
-
K. Tabelow, J.D. Clayden, P. Lafaye DE Micheaux, J. Polzehl, V.J. Schmid, B. Whitcher, Image analysis and statistical inference in NeuroImaging with R., Human Brain Mapping 2010, Barcelona, Spain, June 6 - 10, 2010.
-
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, S. Mohammadi, M. Deppe, Impact of smoothing on the interpretation of FA maps, Human Brain Mapping 2010, Barcelona, Spain, June 6 - 10, 2010.
-
G. Blanchard, N. Krämer, Kernel partial least squares is universally consistent, AI & Statistics 2010, Sardinia, Italy, May 13 - 15, 2010.
-
G. Blanchard, N. Krämer, Optimal rates for conjugate gradient regularization, AI & Statistics 2010, Sardinia, Italy, May 13 - 15, 2010.
-
G. Blanchard, On optimal rates for kernel conjugate gradient regularization under random design and noise, Mini Special Semester on Inverse Problems, Part II: ``Inverse Problems in Data Driven Modelling'', July 19 - 22, 2010, Johann Radon Institute for Computational and Applied Mathematics (RICAM), Linz, Austria, July 20, 2010.
-
G. Blanchard, Optimal rate for kernel conjugate gradient regularization, Workshop "Modern Nonparametric Statistics: Going Beyond Asymptotic Minimax", March 29 - April 2, 2010, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, March 30, 2010.
-
N. Krämer, Modeling of high-dimensional data with partial least squares, University of Leeds, Faculty of Medicine and Health, Leeds Institute of Genetics, Health and Therapeutics, UK, September 2, 2010.
-
N. Krämer, Regularized estimation of large-scale gene associaton networks, 55. GMDS-Jahrestagung: Effiziente und wirtschaftliche Gesundheitsversorgung von heute und morgen --- nur mit Medizinischer Dokumentation, Medizinischer Informatik, Medizinischer Biometrie und Epidemiologie, September 6 - 7, 2010, Hochschule Mannheim, Institut für Medizinische Informatik, September 6, 2010.
-
N. Krämer, The consistency of partial least spuares and conjugate gradient regularization, 73rd Annual Meeting of the Institute of Mathematical Statistics, August 9 - 13, 2010, Institute of Mathematical Statistics (IMS), Sweden, August 13, 2010.
-
P. Mathé, The Lepskii balancing principle for conjugate gradient regularization, Workshop on Inverse Problems: Developments in Theory and Applications (IP-TA 2010), February 8 - 12, 2010, Stefan Banach International Mathematical Center, Warsaw, Poland, February 9, 2010.
-
H.-J. Mucha, An accelerated K-means algorithm based on adaptive distances, 34th Annual Conference of the German Classification Society (GfKl) and International Symposium on the Data Analysis Interface, July 21 - 23, 2010, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), July 22, 2010.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Automatische Klassifikation (Clusteranalyse), IBM SPSS Kundentag 2010, June 8, 2010, SPSS GmbH Software, München, June 8, 2010.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Pairwise data clustering accompanied by validation and visualisation, 3rd German-Japanese Workshop ``Advances in Data Analysis and Related New Techniques and Applications'', July 20 - 21, 2010, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), July 20, 2010.
-
J. Polzehl, K. Tabelow, Image and signal processing in the biomedical sciences: Diffusion-weighted imaging modeling and beyond, 1st Annual Scientific Symposium ``Ultrahigh Field Magnetic Resonance'', Max Delbrück Center, Berlin, April 16, 2010.
-
J. Polzehl, Statistical problems in functional and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance, Uppsala University, Dept. of Mathematics, Graduate School in Mathematics and Computing, Sweden, May 27, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Local parametric estimation, October 18 - 22, 2010, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Analyse de l'Information (ENSAI), Rennes, France.
-
V. Spokoiny, Semidefinite non-Gaussian component analysis, Bivariate Penalty Choice in Model Selection, Deutsches Diabetes Zentrum Düsseldorf, June 17, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Semidefinite optimization in instrumental variable estimation with shape constraints, Conference on ``Shape Restrictions in Non- and Semiparametric Estimation of Econometric Models'', November 1 - 7, 2010, Northwestern University, Department of Statisics, Chicago, USA, November 6, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Sparse non-Gaussian component analysis, Journées STAR 2010, October 21 - 22, 2010, Université Rennes II, France, October 22, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Sparse non-Gaussian component analysis, School of Mathematics Colloquium, November 19, 2010, University of Edinburgh, School of Mathematics, UK, November 19, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Sparse non-Gaussian component analysis, University of Cambridge, Faculty of Mathematics, Statistical Laboratory, UK, May 7, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Statistical estimation: Modern view, Rencontres de Statistiques Mathématiques 10, December 13 - 17, 2010, Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (CIRM), Luminy, France, December 16, 2010.
-
V. Spokoiny, Statistical estimation: Modern view, Rencontres de Statistiques Mathématiques 10, December 13 - 17, 2010, Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (CIRM), Luminy, France, December 15, 2010.
-
V. Panov, Pricing Bermudan options via dimension reduction, Klausurtagung des SFB 649, June 4 - 6, 2009, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Motzen, June 5, 2009.
-
V. Panov, Solving classification task using detection of non-Gaussian components, Haindorf Seminar 2009, February 12 - 15, 2009, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, CASE --- Center for Applied Statistics and Economics, Hejnice, Czech Republic, February 14, 2009.
-
D. Peschka, Dewetting of thin liquid films on viscoelastic substrates, European Coating Symposium, September 7 - 9, 2009, Karlsruhe, September 7, 2009.
-
D. Belomestny, Estimation of the jump activity of a Lévy process from low frequency data, Haindorf Seminar 2009, February 12 - 15, 2009, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, CASE -- Center for Applied Statistics and Economics, Hejnice, Czech Republic, February 12, 2009.
-
D. Belomestny, Regression methods for stochastic control problems and their convergence analysis, Fourth General Conference on Advanced Mathematical Methods in Finance, May 4 - 10, 2009, University of Oslo, Norway, May 9, 2009.
-
D. Belomestny, Spectral estimation of the fractional order of a Lévy process, Workshop ``Statistical Inference for Lévy Processes with Applications to Finance'', July 15 - 17, 2009, EURANDOM, Eindhoven, Netherlands, July 16, 2009.
-
G. Blanchard, Convergence du gradient conjugué fonctionnel pour l'apprentissage statistique, École Normale Supérieure, Paris, France, March 16, 2009.
-
G. Blanchard, Non-asymptotic adaptive control of the family-wise error rate in multiple testing, Journées Statistiques du Sud 2009, June 17 - 19, 2009, Université de Provence Aix-Marseille I, Porquerolles, France, June 17, 2009.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Clustering accompanied by visualization and validation, 11th Conference of the International Federation of Classification Societies (IFCS 2009), March 13 - 18, 2009, Technische Universität Dresden, March 13, 2009.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Explorative statistische Methoden in der Archäometrie: von Daten zu Distanzen und weiter zu Gruppierungen, Curt-Engelhorn-Zentrum Archäometrie Mannheim, July 9, 2009.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Geochemical and statistical investigation of Roman stamped tiles of the Legio XXI Rapax, 11th Conference of the International Federation of Classification Societies (IFCS 2009), March 13 - 18, 2009, Technische Universität Dresden, March 14, 2009.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Remarks on Validation of Hierarchical Clustering, First Bilateral German-Polish Symposium on Data Analysis and its Applications, October 8 - 10, 2009, RWTH Aachen, October 10, 2009.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Zur Klassifikation römischer Ziegel von Fundorten im südlichen Obergermanien, Tagung ``Archäometrie und Denkmalpflege 2009'', March 25 - 28, 2009, Pinakothek der Moderne, München, March 26, 2009.
-
N. Serdyukova, Local parametric estimation under noise misspecification in regression problem, Workshop on structure adapting methods, November 6 - 8, 2009, WIAS, November 7, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Adaptive local parametric estimation, Université Joseph Fourier Grenoble I, Équipe de Statistique et Modélisation Stochastique, Laboratoire Jean Kuntzmann, France, February 26, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Adaptive local parametric methods in imaging, Technische Universität Kaiserslautern, Fachbereich Mathematik, January 23, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Cross concentration in semiparametric estimation, Rencontres de Statistiques Mathématiques 9, December 14 - 18, 2009, International Center for Mathematical Meetings (CIRM), Marseille, France, December 15, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Modern nonparametric statistics (block lecture), October 2 - 13, 2009, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Analyse de l'Information (ENSAI), Rennes, France.
-
V. Spokoiny, Modern nonparametric statistics (block lecture), October 18 - 29, 2009, Yale University, New Haven, USA.
-
V. Spokoiny, Modern nonparametric statistics (block lecture), January 13 - 16, 2009, École Nationale de la Statistique et de l'Analyse de l'Information (ENSAI), Rennes, France.
-
V. Spokoiny, Non-Gaussian component analysis, Workshop ``Semiparametric and Nonparametric Methods in Econometrics'', April 4 - 11, 2009, Banff International Research Station for Mathematical Innovation and Discovery, Canada, April 6, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Parameter tuning in statistical inverse problem, European Meeting of Statisticians (EMS2009), July 20 - 22, 2009, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, July 21, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Saddle point model selection, 2nd Humboldt-Princeton Conference: Perceiving and Measuring Financial Risk: Credit, Energy and Illiquidity, October 30 - 31, 2009, Princeton University, USA, October 30, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Saddle point model selection, Université Toulouse 1 Capitole, Toulouse School of Economics, France, November 24, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Saddle point model selection, Workshop on structure adapting methods, November 6 - 8, 2009, WIAS, November 7, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Saddle point model selection for inverse problems, Workshop ``Challenges in Statistical Theory: Complex Data Structures and Algorithmic Optimization'', August 23 - 29, 2009, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, August 26, 2009.
-
V. Spokoiny, Sparse non-Gaussian component analysis, Workshop ``Sparse Recovery Problems in High Dimensions: Statistical Inference and Learning Theory'', March 15 - 21, 2009, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, March 16, 2009.
-
M. Elagin, Comparison of some methods for the adaptive volatility estimation, Haindorf Seminar 2008 (Klausurtagung des SFB 649), February 7 - 10, 2008, Hejnice, Czech Republic, February 9, 2008.
-
K. Tabelow, Structure adaptive smoothing medical images, 22. Treffpunkt Medizintechnik: Fortschritte in der medizinischen Bildgebung, Charité, Campus Virchow Klinikum Berlin, May 22, 2008.
-
K. Tabelow, Strukturadaptive Bild- und Signalverarbeitung, Workshop of scshape Matheon with Siemens AG (Health Care Sector) in cooperation with Center of Knowledge Interchange (CKI) of Technische Universität (TU) Berlin and Siemens AG, TU Berlin, July 8, 2008.
-
E. Giacomini, Dynamic semiparametric factor modus in risk preferences estimation, 2008 North American Winter Meetings of the Econometric Society, January 4 - 6, 2008, North American Econometric Society, New Orleans, USA, January 6, 2008.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Clustering, multivariate visualization and validation, 30th Fall Meeting of the German Classification Society, Berlin, Gesellschaft für Klassifikation e.V., Berlin, November 14, 2008.
-
H.-J. Mucha, Mapping find spots of Roman military brickstamps in Mogontiacum (Mainz) and archeometrical analysis, Annual Meeting of Gesellschaft für Klassifikation, July 16 - 18, 2008, Helmut-Schmidt-Universität, Hamburg, August 17, 2008.
-
J. Polzehl, New developments in structural adaptive smoothing: Images, fMRI and DWI, University of Tromsoe, Norway, May 27, 2008.
-
J. Polzehl, Smoothing fMRI and DWI data using the propagation-separation approach, University of Utah, Computing and Scientific Imaging Institute, Salt Lake City, USA, September 11, 2008.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing using the propagation-separation approach, University of Chicago, Department of Statistics, USA, September 3, 2008.
-
A. Rohde, Spatially adaptive comparison of multivariate samples via randomization, Université Paris VI ``Pierre et Marie Curie'', France, March 10, 2008.
-
A. Rohde, Spatially adaptive comparison of multivariate samples via randomization, Universität Bern, Switzerland, February 20, 2008.
-
N. Serdyukova, Dependence on the dimension for complexity of approximation of random fields, 4. Doktorandenkonferenz Stochastik, September 4 - 6, 2008, Technische Universität Berlin, September 6, 2008.
-
V. Spokoiny, Foundations and applications of modern nonparametric statistics (block lecture), May 15 - 16, 2008, Graduate School ``Mathematics and Practice'', Technische Universität Kaiserslautern/Fraunhofer Institut für Techno- und Wirtschaftsmathematik.
-
V. Spokoiny, Local parametric modeling of nonstationary time series, International Workshop on Recent Advances in Time Series Analysis, June 8 - 11, 2008, University of Cyprus, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Protaras, June 11, 2008.
-
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, H.U. Voss, Increasing SNR in high resolution fMRI by spatially adaptive smoothing, Human Brain Mapping Conference 2007, Chicago, USA, June 10 - 14, 2007.
-
K. Tabelow, A3: Image and signal processing in medicine and biosciences, A-Day des sc Matheon, Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin (ZIB), December 5, 2007.
-
K. Tabelow, Improving data quality in fMRI and DTI by structural adaptive smoothing, Cornell University, Weill Medical College, New York, USA, June 18, 2007.
-
K. Tabelow, Structural adaptive signal detection in fMRI and structure enhancement in DTI, International Workshop on Image Analysis in the Life Sciences, Theory and Applications, February 28 - March 2, 2007, Johannes Kepler Universität Linz, Austria, March 2, 2007.
-
K. Tabelow, Structural adaptive smoothing in medical imagine, WIAS Day, WIAS Berlin, February 22, 2007.
-
K. Tabelow, Structural adaptive smoothing in medical imaging, Seminar ``Visualisierung und Datenanalyse'', Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin (ZIB), January 30, 2007.
-
J. Polzehl, Propagation-separation procedures for image processing, International Workshop on Image Analysis in the Life Sciences, Theory and Applications, February 28 - March 2, 2007, Johannes Kepler Universität Linz, Austria, March 2, 2007.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing in imaging problems, Spring Seminar Series, University of Minnesota, School of Statistics, College of Liberal Arts, USA, May 24, 2007.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing procedures by propagation-separation methods, Final meeting of the DFG Priority Program 1114, November 7 - 9, 2007, Freiburg, November 7, 2007.
-
K. Tabelow, J. Polzehl, H.U. Voss, V. Spokoiny, Analyzing fMRI experiments with structural adaptive smoothing methods, Human Brain Mapping Conference, Florence, Italy, June 12 - 15, 2006.
-
K. Tabelow, Analyzing fMRI experiments with structural adaptive smoothing methods, BCCN PhD Symposium 2006, June 7 - 8, 2006, Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Berlin, Bad Liebenwalde, June 8, 2006.
-
K. Tabelow, Image and signal processing in medicine and biosciences, Evaluation Colloquium of the DFG Research Center sc Matheon, Berlin, January 24 - 25, 2006.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing by propagation-separation, 69th Annual Meeting of the IMS and 5th International Symposium on Probability and its Applications, July 30 - August 4, 2006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, July 30, 2006.
-
K. Tabelow, Adaptive weights smoothing in the analysis of fMRI data, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, SFB 386, December 8, 2005.
-
K. Tabelow, Detecting shape and borders of activation areas infMRI data, Forschungsseminar ''Mathematische Statistik'', WIAS, Berlin, November 23, 2005.
-
K. Tabelow, Spatially adaptive smoothing infMRI analysis, Neuroimaging Center, Cahrité, Berlin, November 10, 2005.
-
J. Polzehl, Adaptive smoothing by propagation-separation, Australian National University, Center of Mathematics and its Applications, Canberra, March 31, 2005.
-
J. Polzehl, Image reconstruction and edge enhancement by structural adaptive smoothing, 55th Session of the International Statistical Institute (ISI), April 5 - 12, 2005, Sydney, Australia, April 8, 2005.
-
J. Polzehl, Propagation-separation at work: Main ideas and applications, National University of Singapore, Department of Probability Theory and Statistics, March 24, 2005.
-
J. Polzehl, Spatially adaptive smoothing: A propagation-separation approach for imaging problems, Joint Statistical Meetings, August 7 - 11, 2005, Minneapolis, USA, August 11, 2005.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing by propagation-separation methods, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, SFB 386, December 7, 2005.
-
J.G.M. Schoenmakers, Robust Libor modelling and pricing of derivative products, Delft University of Technology, Netherlands, June 9, 2005.
-
J. Polzehl, Local likelihood modeling by structural adaptive smoothing, University of Minnesota, School of Statistics, Minneapolis, USA, September 9, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, On a nonstationary structural adaptive approach to volatility estimation, University of Gothenburg, Centre for Finance, Sweden, May 5, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Smoothing by adaptive weights: An overview, Chalmers University of Technology, Department of Mathematical Statistics, Gothenburg, Sweden, May 11, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing methods, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Institut für Mathematische Stochastik, January 14, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing methods, Tandem-Workshop on Non-linear Optimization at the Crossover of Discrete Geometry and Numerical Analysis, July 15 - 16, 2004, Technische Universität Berlin, Institut für Mathematik, July 15, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing methods and possible applications in imaging, Charité Berlin, NeuroImaging Center, Berlin, July 1, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing methods for imaging problems, Annual Conference of Deutsche Mathematiker-Vereinigung (DMV), September 13 - 17, 2004, Heidelberg, September 14, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing methods for imaging problems, German-Israeli Binational Workshop, October 20 - 22, 2004, Ollendorff Minerva Center for Vision and Image Sciences, Technion, Haifa, Israel, October 21, 2004.
-
J. Polzehl, Adaptive smoothing procedures for image processing, Workshop on Nonlinear Analysis of Multidimensional Signals, February 25 - 28, 2003, Teistungenburg, February 25, 2003.
-
J. Polzehl, Image processing using Adaptive Weights Smoothing, Uppsala University, Department of Mathematics, Sweden, May 7, 2003.
-
J. Polzehl, Local likelihood modeling by Adaptive Weights Smoothing, Joint Statistical Meetings, August 3 - 7, 2003, San Francisco, USA, August 6, 2003.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptation I: Pointwise adaptive smoothing and imaging, University of Tromso, Department of Mathematics, Norway, April 11, 2002.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptation I: Varying coefficient regression modeling by adaptive weights smoothing, Workshop on Nonparametric Smoothing in Complex Statistical Models, April 27 - May 4, 2002, Ascona, Switzerland, April 30, 2002.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptation II: Time series and estimation of dimension reduction spaces, University of Tromso, Department of Mathematics, Norway, April 17, 2002.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptation methods in imaging, Joint Statistical Meetings 2002, August 11 - 15, 2002, New York, USA, August 12, 2002.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive smoothing and its applications in imaging and time series, Uppsala University, Department of Mathematics, Sweden, May 2, 2002.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural-adaptive smoothing methods, French-German Seminar, Universität Potsdam, April 6, 2002.
-
J. Polzehl, Can structural assumptions be used to improve nonparametric estimates?, University of Minnesota, School of Statistics, Minneapolis, USA, May 31, 2001.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptation in nonparametric regression, Workshop on High-Dimensional Nonlinear Statistical Modelling, September 15 - 19, 2001, Wulkow, September 16, 2001.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaption --- A method to estimate the effective dimension reduction space, Closed Meeting of Sfb 373, May 17 - 19, 2001, Wulkow, May 18, 2001.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaption in non-parametric smoothing, Departamento de Estadistica y Econometria, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain, March 2, 2001.
-
J. Polzehl, Structural adaptive estimation, Bayer AG, Leverkusen, November 29, 2001.
-
J. Polzehl, Adaptive weights smoothing with applications in imaging, Universität Essen, Fachbereich Mathematik, Sfb 475, November 6, 2000.
-
J. Polzehl, Adaptive weights smoothing with applications to image denoising and signal detection, Université Catholique de Louvain-la-Neuve, Institut de Statistique, Belgium, September 29, 2000.
-
J. Polzehl, Functional and dynamic Magnet Resonance Imaging using adaptive weights smoothing, Workshop "`Mathematical Methods in Brain Mapping"', Université de Montréal, Centre de Recherches Mathématiques, Canada, December 11, 2000.
-
J. Polzehl, Spatially adaptive procedures for signal detection in fMRI, Tagung "`Controlling Complexity for Strong Stochastic Dependencies"', September 10 - 16, 2000, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, September 11, 2000.
-
J. Polzehl, Spatially adaptive smoothing techniques for signal detection in functional and dynamic Magnet Resonance Imaging, Human Brain Mapping 2000, San Antonio, Texas, USA, June 12 - 16, 2000.
 External Preprints
External Preprints
-
M. Kantner, L. Mertenskötter, Accurate evaluation of self-heterodyne laser linewidth measurements using Wiener filters, Preprint no. arXiv:2301.10645, Cornell University, 2023, DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2301.10645 .
Abstract
Self-heterodyne beat note measurements are widely used for the experimental characterization of the frequency noise power spectral density (FN-PSD) and the spectral linewidth of lasers. The measured data, however, must be corrected for the transfer function of the experimental setup in a post-processing routine. The standard approach disregards the detector noise and thereby induces reconstruction artifacts, i.e., spurious spikes, in the reconstructed FN-PSD. We introduce an improved post-processing routine based on a parametric Wiener filter that is free from reconstruction artifacts, provided a good estimate of the signal-to-noise ratio is supplied. Building on this potentially exact reconstruction, we develop a new method for intrinsic laser linewidth estimation that is aimed at deliberate suppression of unphysical reconstruction artifacts. Our method yields excellent results even in the presence of strong detector noise, where the intrinsic linewidth plateau is not even visible using the standard method. The approach is demonstrated for simulated time series from a stochastic laser model including 1 / f-type noise. -
V. Spokoiny, Mixed Laplace approximation for marginal posterior and Bayesian inference in error-in-operator model, Preprint no. arXiv:2305.08193, Cornell University, 2023, DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2305.09336 .
-
Y.-W. Sun, K. Papagiannouli, V. Spokoiny, High dimensional change-point detection: A complete graph approach, Preprint no. arXiv:2203.08709, Cornell University, 2022, DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2203.08709 .
Abstract
The aim of online change-point detection is for a accurate, timely discovery of structural breaks. As data dimension outgrows the number of data in observation, online detection becomes challenging. Existing methods typically test only the change of mean, which omit the practical aspect of change of variance. We propose a complete graph-based, change-point detection algorithm to detect change of mean and variance from low to high-dimensional online data with a variable scanning window. Inspired by complete graph structure, we introduce graph-spanning ratios to map high-dimensional data into metrics, and then test statistically if a change of mean or change of variance occurs. Theoretical study shows that our approach has the desirable pivotal property and is powerful with prescribed error probabilities. We demonstrate that this framework outperforms other methods in terms of detection power. Our approach has high detection power with small and multiple scanning window, which allows timely detection of change-point in the online setting. Finally, we applied the method to financial data to detect change-points in S&P 500 stocks. -
V. Artem, A. Gasnikov, P. Dvurechensky, V. Spokoiny, Accelerated gradient methods with absolute and relative noise in the gradient, Preprint no. arXiv:2102.02921, Cornell University, 2022, DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2102.02921 .
-
V. Spokoiny, Dimension free non-asymptotic bounds on the accuracy of high dimensional Laplace approximation, Preprint no. arXiv:2204.11038, Cornell University, 2022, DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2204.11038 .
Abstract
This note attempts to revisit the classical results on Laplace approximation in a modern non-asymptotic and dimension free form. Such an extension is motivated by applications to high dimensional statistical and optimization problems. The established results provide explicit non-asymptotic bounds on the quality of a Gaussian approximation of the posterior distribution in total variation distance in terms of the so called empheffective dimension ( dimL ). This value is defined as interplay between information contained in the data and in the prior distribution. In the contrary to prominent Bernstein - von Mises results, the impact of the prior is not negligible and it allows to keep the effective dimension small or moderate even if the true parameter dimension is huge or infinite. We also address the issue of using a Gaussian approximation with inexact parameters with the focus on replacing the Maximum a Posteriori (MAP) value by the posterior mean and design the algorithm of Bayesian optimization based on Laplace iterations. The results are specified to the case of nonlinear regression. -
V. Spokoiny, Finite samples inference and critical dimension for stochastically linear models, Preprint no. arXiv:2201.06327, Cornell University, 2022, DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2201.06327 .
Abstract
The aim of this note is to state a couple of general results about the properties of the penalized maximum likelihood estimators (pMLE) and of the posterior distribution for parametric models in a non-asymptotic setup and for possibly large or even infinite parameter dimension. We consider a special class of stochastically linear smooth (SLS) models satisfying two major conditions: the stochastic component of the log-likelihood is linear in the model parameter, while the expected log-likelihood is a smooth function. The main results simplify a lot if the expected log-likelihood is concave. For the pMLE, we establish a number of finite sample bounds about its concentration and large deviations as well as the Fisher and Wilks expansion. The later results extend the classical asymptotic Fisher and Wilks Theorems about the MLE to the non-asymptotic setup with large parameter dimension which can depend on the sample size. For the posterior distribution, our main result states a Gaussian approximation of the posterior which can be viewed as a finite sample analog of the prominent Bernstein--von Mises Theorem. In all bounds, the remainder is given explicitly and can be evaluated in terms of the effective sample size and effective parameter dimension. The results are dimension and coordinate free. In spite of generality, all the presented bounds are nearly sharp and the classical asymptotic results can be obtained as simple corollaries. An interesting case of logit regression with smooth or truncation priors is used to specify the results and to explain the main notions. -
A. Daneshmand, G. Scutari, P. Dvurechensky, A. Gasnikov, Newton method over networks is fast up to the statistical precision, Preprint no. arXiv:2102.06780, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2021.
-
A. Kroshnin, V. Spokoiny, A. Suvorikova, Multiplier bootstrap for Bures--Wasserstein barycenters, Preprint no. arXiv:2111.12612, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2021.
Abstract
Bures-Wasserstein barycenter is a popular and promising tool in analysis of complex data like graphs, images etc. In many applications the input data are random with an unknown distribution, and uncertainty quantification becomes a crucial issue. This paper offers an approach based on multiplier bootstrap to quantify the error of approximating the true Bures--Wasserstein barycenter Q? by its empirical counterpart Qn. The main results state the bootstrap validity under general assumptions on the data generating distribution P and specifies the approximation rates for the case of sub-exponential P. The performance of the method is illustrated on synthetic data generated from the weighted stochastic block model. -
A. Rogozin, A. Beznosikov, D. Dvinskikh, D. Kovalev, P. Dvurechensky, A. Gasnikov, Decentralized distributed optimization for saddle point problems, Preprint no. arXiv:2102.07758, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2021.
-
P. Dvurechensky, D. Kamzolov, A. Lukashevich, S. Lee, E. Ordentlich, C.A. Uribe, A. Gasnikov, Hyperfast second-order local solvers for efficient statistically preconditioned distributed optimization, Preprint no. arXiv:2102.08246, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2021.
-
Y.-W. Sun, K. Papagiannouli, V. Spokoiny, Online graph-based change-point detection for high dimensional data, Preprint no. arXiv:1906.03001, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2019.
Abstract
Online change-point detection (OCPD) is important for application in various areas such as finance, biology, and the Internet of Things (IoT). However, OCPD faces major challenges due to high-dimensionality, and it is still rarely studied in literature. In this paper, we propose a novel, online, graph-based, change-point detection algorithm to detect change of distribution in low- to high-dimensional data. We introduce a similarity measure, which is derived from the graph-spanning ratio, to test statistically if a change occurs. Through numerical study using artificial online datasets, our data-driven approach demonstrates high detection power for high-dimensional data, while the false alarm rate (type I error) is controlled at a nominal significant level. In particular, our graph-spanning approach has desirable power with small and multiple scanning window, which allows timely detection of change-point in the online setting. -
A. Kroshnin, V. Spokoiny, A. Suvorikova, Statistical inference for Bures--Wasserstein barycenters, Preprint no. arXiv:1901.00226, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2019.
-
N. Puchkin, V. Spokoiny, Structure-adaptive manifold estimation, Preprint no. arXiv:1906.05014, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2019.
Abstract
We consider a problem of manifold estimation from noisy observations. Many manifold learning procedures locally approximate a manifold by a weighted average over a small neighborhood. However, in the presence of large noise, the assigned weights become so corrupted that the averaged estimate shows very poor performance. We suggest a novel computationally efficient structure-adaptive procedure, which simultaneously reconstructs a smooth manifold and estimates projections of the point cloud onto this manifold. The proposed approach iteratively refines the weights on each step, using the structural information obtained at previous steps. After several iterations, we obtain nearly öracle" weights, so that the final estimates are nearly efficient even in the presence of relatively large noise. In our theoretical study we establish tight lower and upper bounds proving asymptotic optimality of the method for manifold estimation under the Hausdorff loss. Our finite sample study confirms a very reasonable performance of the procedure in comparison with the other methods of manifold estimation. -
N. Alia, V. John, S. Ollila, Re-visiting the single-phase flow model for liquid steel ladle stirred by gas, Preprint no. arXiv.1811.11535, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2018, DOI 10.1016/j.apm.2018.11.005 .
Abstract
Ladle stirring is an important step of the steelmaking process to homogenize the temperature and the chemical composition of the liquid steel and to remove inclusions before casting. Gas is injected from the bottom of the bath to induce a turbulent flow of the liquid steel. Multiphase modeling of ladle stirring can become computationally expensive, especially when used within optimal flow control problems. This paper focuses therefore on single-phase flow models. It aims at improving the existing models from the literature. Simulations in a 2d axial-symmetrical configuration, as well as, in a real 3d laboratory-scale ladle, are performed. The results obtained with the present model are in a relative good agreement with experimental data and suggest that it can be used as an efficient model in optimal flow control problems. -
A. Koziuk, V. Spokoiny, Instrumental variables regression, Preprint no. arXiv:1806.06111v1, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2018.
-
N. Buzun, V. Avanesov, Bootstrap for change point detection, Preprint no. arXiv:1710.07285, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2017.
-
V. Avanesov, N. Buzun , Change-point detection in high-dimensional covariance structure, Preprint no. arXiv:1610.03783, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2016.
Abstract
In this paper we introduce a novel approach for an important problem of change point detection. Specifically, we are interested in detection of an abrupt change in the covariance structure of a high-dimensional random process -- a problem, which has applications many areas e.g., neuroimaging and finance. The developed approach is essentially a testing procedure requiring a proper choice of a critical level. To that end a non-standard bootstrap scheme is proposed and theoretically justified under mild assumptions. Multiscale nature of the approach allows for a trade-off between sensitivity of change-point detection and localization of it. The approach can be naturally used in an on-line setting. A simulation study demonstrates that the approach matches the nominal level of false alarm probability and exhibits high power, outperforming competing approaches. -
A. Andresen, V. Spokoiny, Critical dimension in profile semiparametric estimation, Preprint no. arXiv:1303.4640, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2014.
-
A. Andresen, A note on critical dimensions in profile semiparametric estimation, Preprint no. arXiv:1410.4709, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2014.
-
A. Andresen, A result on the bias of sieve profile estimators, Preprint no. arXiv:1406.4045, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2014.
-
A. Andresen, Finite sample analysis of profile M-estimation in the single index model, Preprint no. arXiv:1406.4052, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2014.
-
T. Bodnar, Th. Dickhaus, False discovery rate control under Archimedean copula, Preprint no. arXiv:1305.3897, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2013.
-
V. Spokoiny, W. Wang, W.K. Härdle, Local quantile regression, Preprint no. arXiv:1208.5384, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Parametric estimation. Finite sample theory, Preprint no. arXiv:1111.3029, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2012.
-
V. Spokoiny, Roughness penalty, Wilks phenomenon, and Bernstein--von Mises theorem, Preprint no. arXiv:1205.0498, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2012.
-
W. Härdle, V. Spokoiny, Local quantile regression, Discussion paper no. 2011-005, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, SFB 649, 2011.
-
J. Kampen, On the multivariate Burgers equation and the incompressible Navier--Stokes equation (electronic only), Preprint no. arXiv:0910.5672, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2009.
-
S. Arlot, G. Blanchard, E. Roquain, Some non-asymptotic results on resampling in high dimension, I: Confidence regions, II: Multiple tests (electronic only), Preprint no. arXiv:0712.0775, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2009.
Abstract
We study generalized bootstrap confidence regions for the mean of a random vector whose coordinates have an unknown dependency structure. The random vector is supposed to be either Gaussian or to have a symmetric and bounded distribution. The dimensionality of the vector can possibly be much larger than the number of observations and we focus on a non-asymptotic control of the confidence level, following ideas inspired by recent results in learning theory. We consider two approaches, the first based on a concentration principle (valid for a large class of resampling weights) and the second on a direct resampled quantile, specifically using Rademacher weights. Several intermediate results established in the approach based on concentration principles are of self-interest. We also discuss the question of accuracy when using Monte-Carlo approximations of the resampled quantities. We present an application of these results to the one-sided and two-sided multiple testing problem, in which we derive several resampling-based step-down procedures providing a non-asymptotic FWER control. We compare our different procedures in a simulation study, and we show that they can outperform Bonferroni's or Holm's procedures as soon as the observed vector has sufficiently correlated coordinates.


