Overview
A diffuse phase field model is a mathematical model for describing microstructural phenomena and for predicting morphological evolution on the mesoscale. It is applied to a wide variety of material processes such as solidification, coarsening in alloys, crack propagation and martensitic transformations.
The phase field models are usually based on a free energy functional depending on an order parameter (the phase field). The interfacial dynamics is modeled by a partial evolution equation for the order parameter. For a system of two components, the values of the solution are close to two different values, that represent the two phases, and varies smoothly between these values in the zone around the interface. The evolution equation for the order parameter is typically coupled with an additional evolution equation, which comprises the balance of momentum or energy. This often leads to highly nonlinear PDE-systems of elliptic-parabolic type with constraints. Such PDE-systems are investigated at WIAS concerning their analytically properties such as existence, uniqueness and regularity of solutions. In a further step, numerical simulations of the PDE-systems are carried out at WIAS.
Since the interfaces in a diffuse phase field model have a small transition area no boundary conditions are needed. In particular, no assumptions on the shape of the interfaces or mutual distributions are required. For this reason phase field models have also become a useful tool for numerical simulations, predicting complex morphological evolutions.
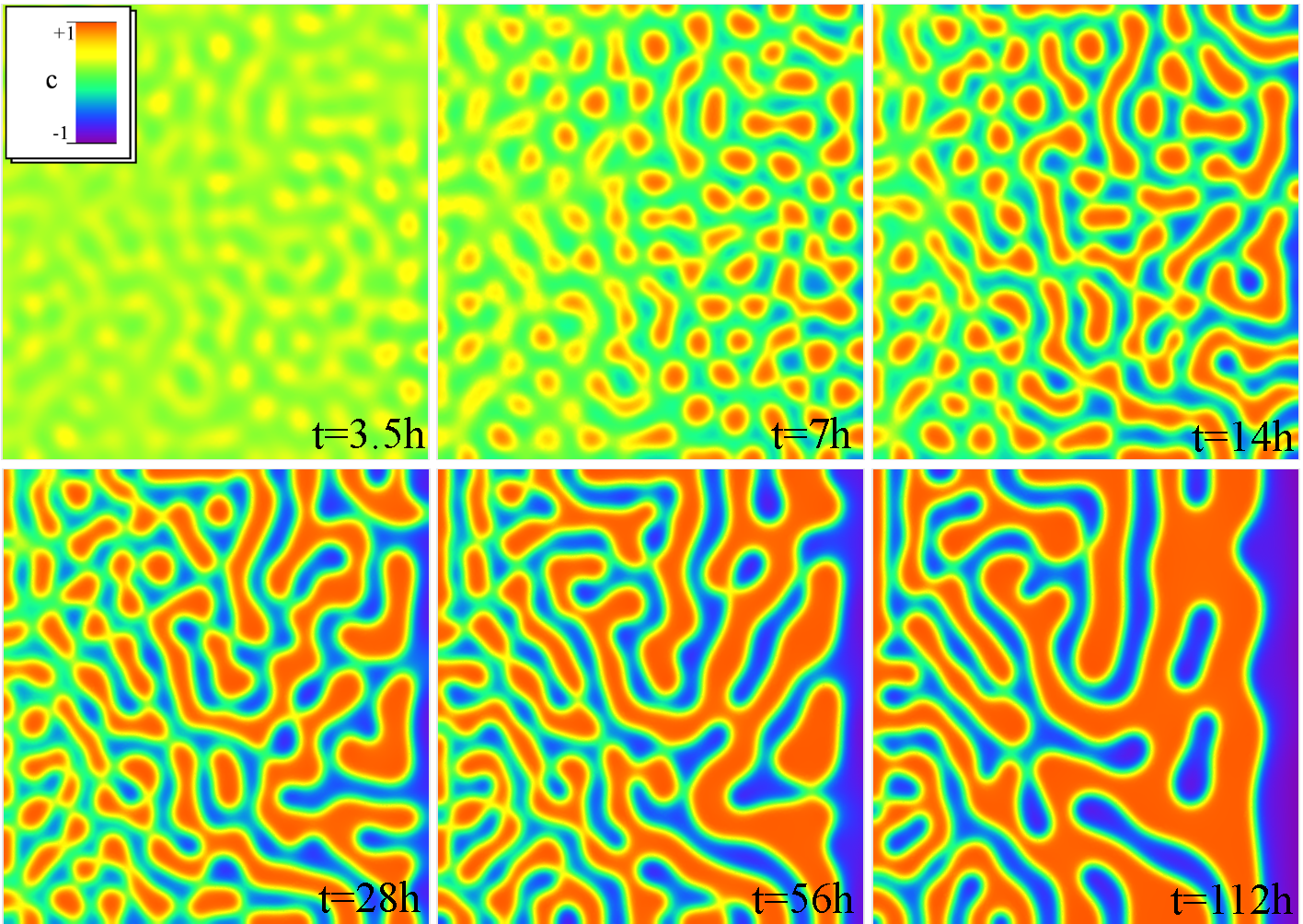
(Markus Radszuweit)
Typical applications where phase field models are utilized are for instance for phase separation, coarsening and damage processes. The picture displays coarsening processes and crack propagtion in binary alloys.
These processes can be described by Cahn-Hilliard equations where the order parameter models the chemical concentration in the binary alloy coupled with elasticity and a variational inequality for the inner damage variable.
Publications
 Monographs
Monographs
-
M. Hintermüller, D. Wegner, Distributed and Boundary Control Problems for the Semidiscrete Cahn--Hilliard/Navier--Stokes System with Nonsmooth Ginzburg--Landau Energies, in: Topological Optimization and Optimal Transport in the Applied Sciences, M. Bergounioux, E. Oudet, M. Rumpf, G. Carlier, Th. Champion, F. Santambrogio, eds., 17 of Radon Series on Computational and Applied Mathematics, De Gruyter, Berlin, 2017, pp. 40--63, (Chapter Published).
-
H.-Chr. Kaiser, D. Knees, A. Mielke, J. Rehberg, E. Rocca, M. Thomas, E. Valdinoci, eds., PDE 2015: Theory and Applications of Partial Differential Equations, 10 of Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, American Institute of Mathematical Science, Springfield, 2017, iv+933 pages, (Collection Published).
-
P. Colli, A. Favini, E. Rocca, G. Schimperna, J. Sprekels, eds., Solvability, Regularity, and Optimal Control of Boundary Value Problems for PDEs: In Honour of Prof. Gianni Gilardi, 22 of Springer INdAM Series, Springer International Publishing AG, Cham, 2017, xii+571 pages, (Collection Published).
Abstract
This volume gathers contributions in the field of partial differential equations, with a focus on mathematical models in phase transitions, complex fluids and thermomechanics. These contributions are dedicated to Professor Gianni Gilardi on the occasion of his 70th birthday. It particularly develops the following thematic areas: nonlinear dynamic and stationary equations; well-posedness of initial and boundary value problems for systems of PDEs; regularity properties for the solutions; optimal control problems and optimality conditions; feedback stabilization and stability results. Most of the articles are presented in a self-contained manner, and describe new achievements and/or the state of the art in their line of research, providing interested readers with an overview of recent advances and future research directions in PDEs. -
P. Colli, A. Damlamian, N. Kenmochi, M. Mimura, J. Sprekels, eds., Proceedings of International Conference on: Nonlinear Phenomena with Energy Dissipation: Mathematical Analysis, Modeling and Simulation, 29 of Gakuto International Series Mathematical Sciences and Applications, Gakkōtosho, Tokyo, 2008, 475 pages, (Collection Published).
-
P. Colli, N. Kenmochi, J. Sprekels, eds., Dissipative Phase Transitions, 71 of Series on Advances in Mathematics for Applied Sciences, World Scientific, Singapore, 2006, xii+300 pages, (Collection Published).
 Articles in Refereed Journals
Articles in Refereed Journals
-
TH. Eiter, L. Schmeller, Weak solutions to a model for phase separation coupled with finite-strain viscoelasticity subject to external distortion, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 35 (2025), pp. 2425--2463, DOI 10.1142/S0218202525500435 .
Abstract
We study the coupling of a viscoelastic deformation governed by a Kelvin--Voigt model at equilibrium, based on the concept of second-grade nonsimple materials, with a plastic deformation due to volumetric swelling, described via a phase-field variable subject to a Cahn--Hilliard model expressed in a Lagrangian frame. Such models can be used to describe the time evolution of hydrogels in terms of phase separation within a deformable substrate. The equations are mainly coupled via a multiplicative decomposition of the deformation gradient into both contributions and via a Korteweg term in the Eulerian frame. To treat time-dependent Dirichlet conditions for the deformation, an auxiliary variable with fixed boundary values is introduced, which results in another multiplicative structure. Imposing suitable growth conditions on the elastic and viscous potentials, we construct weak solutions to this quasistatic model as the limit of time-discrete solutions to incremental minimization problems. The limit passage is possible due to additional regularity induced by the hyperelastic and viscous stresses. -
R. Lasarzik, E. Rocca, R. Rossi, Existence and weak-strong uniqueness for damage systems in viscoelasticity, Nonlinearity, 38 (2025), pp. 125016/1--125016/59, DOI 10.1088/1361-6544/ae1433 .
Abstract
In this paper we investigate the existence of solutions and their weak-strong uniqueness property for a PDE system modelling damage in viscoelastic materials. In fact, we address two solution concepts, emphweak and emphstrong solutions. For the former, we obtain a global-in-time existence result, but the highly nonlinear character of the system prevents us from proving their uniqueness. For the latter, we prove local-in-time existence. Then, we show that the strong solution, as long as it exists, is unique in the class of weak solutions. This emphweak-strong uniqueness statement is proved by means of a suitable relative energy inequality. -
M. Heida, M. Landstorfer, M. Liero, Homogenization of a porous intercalation electrode with phase separation, Multiscale Modeling & Simulation. A SIAM Interdisciplinary Journal, 22 (2024), pp. 1068--1096, DOI 10.1137/21M1466189 .
Abstract
In this work, we derive a new model framework for a porous intercalation electrode with a phase separating active material upon lithium intercalation. We start from a microscopic model consisting of transport equations for lithium ions in an electrolyte phase and intercalated lithium in a solid active phase. Both are coupled through a Neumann--boundary condition modeling the lithium intercalation reaction. The active material phase is considered to be phase separating upon lithium intercalation. We assume that the porous material is a given periodic microstructure and perform analytical homogenization. Effectively, the microscopic model consists of a diffusion and a Cahn--Hilliard equation, whereas the limit model consists of a diffusion and an Allen--Cahn equation. Thus we observe a Cahn--Hilliard to Allen--Cahn transition during the upscaling process. In the sense of gradient flows, the transition goes in hand with a change in the underlying metric structure of the PDE system. -
A. Mielke, T. Roubíček, Qualitative study of a geodynamical rate-and-state model for elastoplastic shear flows in crustal faults, Interfaces and Free Boundaries. Mathematical Analysis, Computation and Applications, 26 (2024), pp. 245--282, DOI 10.4171/IFB/506 .
Abstract
The Dieterich--Ruina rate-and-state friction model is transferred to a bulk variant and the state variable (aging) influencing the dissipation mechanism is here combined also with a damage influencing standardly the elastic response. As the aging has a separate dynamics, the overall model does not have a standard variational structure. A one-dimensional model is investigated as far as the steady-state existence, localization of the cataclastic core, and its time response, too. Computational experiments with a damage-free variant show stick-slip behavior (i.e. seismic cycles of tectonic faults) as well as stable slip under very large velocities. -
A.K. Barua, R. Chew, L. Shuwang, J. Lowengrub, A. Münch, B. Wagner, Sharp-interface problem of the Ohta--Kawasaki model for symmetric diblock copolymers, Journal of Computational Physics, 481 (2023), pp. 112032/1--112032/23, DOI 10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112032 .
Abstract
The Ohta-Kawasaki model for diblock-copolymers is well known to the scientific community of diffuse-interface methods. To accurately capture the long-time evolution of the moving interfaces, we present a derivation of the corresponding sharp-interface limit using matched asymptotic expansions, and show that the limiting process leads to a Hele-Shaw type moving interface problem. The numerical treatment of the sharp-interface limit is more complicated due to the stiffness of the equations. To address this problem, we present a boundary integral formulation corresponding to a sharp interface limit of the Ohta-Kawasaki model. Starting with the governing equations defined on separate phase domains, we develop boundary integral equations valid for multi-connected domains in a 2D plane. For numerical simplicity we assume our problem is driven by a uniform Dirichlet condition on a circular far-field boundary. The integral formulation of the problem involves both double- and single-layer potentials due to the modified boundary condition. In particular, our formulation allows one to compute the nonlinear dynamics of a non-equilibrium system and pattern formation of an equilibrating system. Numerical tests on an evolving slightly perturbed circular interface (separating the two phases) are in excellent agreement with the linear analysis, demonstrating that the method is stable, efficient and spectrally accurate in space. -
G.L. Celora, R. Blossey, A. Münch, B. Wagner, Counterion-controlled phase equilibria in a charge-regulated polymer solution, Journal of Chemical Physics, 159 (2023), pp. 184902/1--184902/17, DOI 10.1063/5.0169610 .
Abstract
We study phase equilibria in a minimal model of charge-regulated polymer solutions. Our model consists of a single polymer species whose charge state arises from protonation-deproto- nation processes in the presence of a dissolved acid, whose anions serve as screening counteri- ons. We explicitly account for variability in the polymers' charge states. Homogeneous equilibria in this model system are characterised by the total concentration of polymers, the concentration of counter-ions and the charge distributions of polymers which can be computed with the help of analytical approximations. We use these analytical results to characterise how parameter values and solution acidity influence equilibrium charge distributions and identify for which regimes uni- modal and multi-modal charge distributions arise. We then study the interplay between charge regulation, solution acidity and phase separation. We find that charge regulation has a significant impact on polymer solubility and allows for non-linear responses to the solution acidity: re-entrant phase behaviour is possible in response to increasing solution acidity. Moreover, we show that phase separation can yield to the coexistence of local environments characterised by different charge distributions and mixture com -
G.L. Celora, M.G. Hennessy, A. Münch, B. Wagner, S.L. Waters, The dynamics of a collapsing polyelectrolyte gel, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 83 (2023), pp. 1146--1171, DOI 10.1137/21M1419726 .
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, Cahn--Hilliard--Brinkman model for tumor growth with possibly singular potentials, Nonlinearity, 36 (2023), pp. 4470--4500, DOI https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6544/ace2a7 .
Abstract
We analyze a phase field model for tumor growth consisting of a Cahn--Hilliard--Brinkman system, ruling the evolution of the tumor mass, coupled with an advection-reaction-diffusion equation for a chemical species acting as a nutrient. The main novelty of the paper concerns the discussion of the existence of weak solutions to the system covering all the meaningful cases for the nonlinear potentials; in particular, the typical choices given by the regular, the logarithmic, and the double obstacle potentials are admitted in our treatise. Compared to previous results related to similar models, we suggest, instead of the classical no-flux condition, a Dirichlet boundary condition for the chemical potential appearing in the Cahn--Hilliard-type equation. Besides, abstract growth conditions for the source terms that may depend on the solution variables are postulated. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, Optimal control of a nonconserved phase field model of Caginalp type with thermal memory and double obstacle potential, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 16 (2023), pp. 2305--2325, DOI 10.3934/dcdss.2022210 .
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate optimal control problems for a nonlinear state system which constitutes a version of the Caginalp phase field system modeling nonisothermal phase transitions with a nonconserved order parameter that takes thermal memory into account. The state system, which is a first-order approximation of a thermodynamically consistent system, is inspired by the theories developed by Green and Naghdi. It consists of two nonlinearly coupled partial differential equations that govern the phase dynamics and the universal balance law for internal energy, written in terms of the phase variable and the so-called thermal displacement, i.e., a primitive with respect to time of temperature. We extend recent results obtained for optimal control problems in which the free energy governing the phase transition was differentiable (i.e., of regular or logarithmic type) to the nonsmooth case of a double obstacle potential. As is well known, in this nondifferentiable case standard methods to establish the existence of appropriate Lagrange multipliers fail. This difficulty is overcome utilizing of the so-called deep quench approach. Namely, the double obstacle potential is approximated by a family of (differentiable) logarithmic ones for which the existence of optimal controls and first-order necessary conditions of optimality in terms of the adjoint state variables and a variational inequality are known. By proving appropriate bounds for the adjoint states of the approximating systems, we can pass to the limit in the corresponding first-order necessary conditions, thereby establishing meaningful first-order necessary optimality conditions also for the case of the double obstacle potential. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, On a Cahn--Hilliard system with source term and thermal memory, Nonlinear Analysis. An International Mathematical Journal, 240 (2024), pp. 113461/1--113461/16 (published online on 14.12.2023), DOI 10.1016/j.na.2023.113461 .
Abstract
A nonisothermal phase field system of Cahn--Hilliard type is introduced and analyzed mathematically. The system constitutes an extension of the classical Caginalp model for nonisothermal phase transitions with a conserved order parameter. It couples a Cahn--Hilliard type equation with source term for the order parameter with the universal balance law of internal energy. In place of the standard Fourier form, the constitutive law of the heat flux is assumed in the form given by the theory developed by Green and Naghdi, which accounts for a possible thermal memory of the evolution. This has the consequence that the balance law of internal energy becomes a second-order in time equation for the thermal displacement or freezing index, that is, a primitive with respect to time of the temperature. Another particular feature of our system is the presence of the source term in the equation for the order parameter, which entails additional mathematical difficulties because the mass conservation of the order parameter is lost. We provide several mathematical results under general assumptions on the source term and the double-well nonlinearity governing the evolution: existence and continuous dependence results are shown for weak and strong solutions to the corresponding initial-boundary value problem. -
M. Ebeling-Rump, D. Hömberg, R. Lasarzik, On a two-scale phasefield model for topology optimization, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 17 (2024), pp. 326--361 (published online on 26.11.2023), DOI 10.3934/dcdss.2023206 .
Abstract
In this article, we consider a gradient flow stemming from a problem in two-scale topology optimization. We use the phase-field method, where a Ginzburg--Landau term with obstacle potential is added to the cost functional, which contains the usual compliance but also an additional contribution including a local volume constraint in a penalty term. The minimization of such an energy by its gradient-flow is analyzed in this paper. We use an regularization and discretization of the associated state-variable to show the existence of weak solutions to the considered system. -
E. Meca, A.W. Fritsch, J. Iglesias--Artola, S. Reber, B. Wagner, Predicting disordered regions driving phase separation of proteins under variable salt concentration, Frontiers in Physics, section Biophysics, 11 (2023), pp. 1213304/1--1213304/13, DOI 10.3389/fphy.2023.1213304 .
Abstract
We determine the intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) of phase separating proteins and investigate their impact on liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) with a random-phase approx- imation (RPA) that accounts for variable salt concentration. We focus on two proteins, PGL-3 and FUS, known to undergo LLPS. For PGL-3 we predict that an IDR near the C-terminus pro- motes LLPS, which we validate through direct comparison with in vitro experimental results. For the structurally more complex protein FUS the role of the low complexity (LC) domain in LLPS is not as well understood. Apart from the LC domain we here identify two IDRs, one near the N-terminus and another near the C-terminus. Our RPA analysis of these domains predict that, surprisingly, the IDR at the N-terminus (aa 1-285) and not the LC domain promotes LLPS of FUS by comparison to in vitro experiments under physiological temperature and salt conditions. -
D. Peschka, L. Heltai, Model hierarchies and higher-order discretisation of time-dependent thin-film free boundary problems with dynamic contact angle, Journal of Computational Physics, 464 (2022), pp. 111325/1--111325/22, DOI 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111325 .
Abstract
We present a mathematical and numerical framework for the physical problem of thin-film fluid flows over planar surfaces including dynamic contact angles. In particular, we provide algorithmic details and an implementation of higher-order spatial and temporal discretisation of the underlying free boundary problem using the finite element method. The corresponding partial differential equation is based on a thermodynamic consistent energetic variational formulation of the problem using the free energy and viscous dissipation in the bulk, on the surface, and at the moving contact line. Model hierarchies for limits of strong and weak contact line dissipation are established, implemented and studied. We analyze the performance of the numerical algorithm and investigate the impact of the dynamic contact angle on the evolution of two benchmark problems: gravity-driven sliding droplets and the instability of a ridge. -
G.L. Celora, M.G. Hennessy, A. Münch, B. Wagner, S.L. Waters, A kinetic model of a polyelectrolyte gel undergoing phase separation, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 160 (2022), pp. 104771/1--104771/27, DOI 10.1016/j.jmps.2021.104771 .
Abstract
In this study we use non-equilibrium thermodynamics to systematically derive a phase-field model of a polyelectrolyte gel coupled to a thermodynamically consistent model for the salt solution surrounding the gel. The governing equations for the gel account for the free energy of the internal interfaces which form upon phase separation, as well as finite elasticity and multi-component transport. The fully time-dependent model describes the evolution of small changes in the mobile ion concentrations and follows their impact on the large-scale solvent flux and the emergence of long-time pattern formation in the gel. We observe a strong acceleration of the evolution of the free surface when the volume phase transition sets in, as well as the triggering of spinodal decomposition that leads to strong inhomogeneities in the lateral stresses, potentially leading to experimentally visible patterns. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Well-posedness and optimal control for a Cahn--Hilliard--Oono system with control in the mass term, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 15 (2022), pp. 2135--2172, DOI 10.3934/dcdss.2022001 .
Abstract
The paper treats the problem of optimal distributed control of a Cahn--Hilliard--Oono system in Rd, 1 ≤ d ≤ 3 with the control located in the mass term and admitting general potentials that include both the case of a regular potential and the case of some singular potential. The first part of the paper is concerned with the dependence of the phase variable on the control variable. For this purpose, suitable regularity and continuous dependence results are shown. In particular, in the case of a logarithmic potential, we need to prove an ad hoc strict separation property, and for this reason we have to restrict ourselves to the case d = 2. In the rest of the work, we study the necessary first-order optimality conditions, which are proved under suitable compatibility conditions on the initial datum of the phase variable and the time derivative of the control, at least in case of potentials having unbounded domain -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Optimal control of a phase field system of Caginalp type with fractional operators, Pure and Applied Functional Analysis, 7 (2022), pp. 1597--1635.
Abstract
In their recent work “Well-posedness, regularity and asymptotic analyses for a fractional phase field system” (Asymptot. Anal. 114 (2019), 93--128), two of the present authors have studied phase field systems of Caginalp type, which model nonconserved, nonisothermal phase transitions and in which the occurring diffusional operators are given by fractional versions in the spectral sense of unbounded, monotone, selfadjoint, linear operators having compact resolvents. In this paper, we complement this analysis by investigating distributed optimal control problems for such systems. It is shown that the associated control-to-state operator is Fréchet differentiable between suitable Banach spaces, and meaningful first-order necessary optimality conditions are derived in terms of a variational inequality and the associated adjoint state variables. -
P. Colli, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, Analysis and optimal control theory for a phase field model of Caginalp type with thermal memory, Communications in Optimization Theory, 2022 (2022), pp. 4/1--4/31, DOI 10.23952/cot.2022.4 .
Abstract
A nonlinear extension of the Caginalp phase field system is considered that takes thermal memory into account. The resulting model, which is a first-order approximation of a thermodynamically consistent system, is inspired by the theories developed by Green and Naghdi. Two equations, resulting from phase dynamics and the universal balance law for internal energy, are written in terms of the phase variable (representing a non-conserved order parameter) and the so-called thermal displacement, i.e., a primitive with respect to time of temperature. Existence and continuous dependence results are shown for weak and strong solutions to the corresponding initial-boundary value problem. Then, an optimal control problem is investigated for a suitable cost functional, in which two data act as controls, namely, the distributed heat source and the initial temperature. Fréchet differentiability between suitable Banach spaces is shown for the control-to-state operator, and meaningful first-order necessary optimality conditions are derived in terms of variational inequalities involving the adjoint variables. Eventually, characterizations of the optimal controls are given. -
P. Colli, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, Optimal control problems with sparsity for tumor growth models involving variational inequalities, Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 194 (2022), pp. 25--58, DOI 10.1007/s10957-022-02000-7 .
Abstract
This paper treats a distributed optimal control problem for a tumor growth model of Cahn--Hilliard type including chemotaxis. The evolution of the tumor fraction is governed by a variational inequality corresponding to a double obstacle nonlinearity occurring in the associated potential. In addition, the control and state variables are nonlinearly coupled and, furthermore, the cost functional contains a nondifferentiable term like the $L^1$--norm in order to include sparsity effects which is of utmost relevance, especially time sparsity, in the context of cancer therapies as applying a control to the system reflects in exposing the patient to an intensive medical treatment. To cope with the difficulties originating from the variational inequality in the state system, we employ the so-called “deep quench approximation” in which the convex part of the double obstacle potential is approximated by logarithmic functions. For such functions, first-order necessary conditions of optimality can be established by invoking recent results. We use these results to derive corresponding optimality conditions also for the double obstacle case, by deducing a variational inequality in terms of the associated adjoint state variables. The resulting variational inequality can be exploited to also obtain sparsity results for the optimal controls. -
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Analysis of a tumor model as a multicomponent deformable porous medium, Interfaces and Free Boundaries. Mathematical Analysis, Computation and Applications, 24 (2022), pp. 235--262, DOI 10.4171/IFB/472 .
Abstract
We propose a diffuse interface model to describe tumor as a multicomponent deformable porous medium. We include mechanical effects in the model by coupling the mass balance equations for the tumor species and the nutrient dynamics to a mechanical equilibrium equation with phase-dependent elasticity coefficients. The resulting PDE system couples two Cahn--Hilliard type equations for the tumor phase and the healthy phase with a PDE linking the evolution of the interstitial fluid to the pressure of the system, a reaction-diffusion type equation for the nutrient proportion, and a quasistatic momentum balance. We prove here that the corresponding initial-boundary value problem has a solution in appropriate function spaces. -
A.F.M. TER Elst, A. Linke, J. Rehberg, On the numerical range of sectorial forms, Pure and Applied Functional Analysis, 7 (2022), pp. 1931--1940.
Abstract
We provide a sharp and optimal generic bound for the angle of the sectorial form associated to a non-symmetric second-order elliptic differential operator with various boundary conditions. Consequently this gives an, in general, sharper H∞-angle for the H∞-calculus on Lp for all p ∈ (1, ∞) if the coefficients are real valued. -
A. Mielke, S. Reichelt, Traveling fronts in a reaction-diffusion equation with a memory term, Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations, 36 (2024), pp. S487--S513 (published online on 23.02.2022), DOI 10.1007/s10884-022-10133-6 .
Abstract
Based on a recent work on traveling waves in spatially nonlocal reaction-diffusion equations, we investigate the existence of traveling fronts in reaction-diffusion equations with a memory term. We will explain how such memory terms can arise from reduction of reaction-diffusion systems if the diffusion constants of the other species can be neglected. In particular, we show that two-scale homogenization of spatially periodic systems can induce spatially homogeneous systems with temporal memory.The existence of fronts is proved using comparison principles as well as a reformulation trick involving an auxiliary speed that allows us to transform memory terms into spatially nonlocal terms. Deriving explicit bounds and monotonicity properties of the wave speed of the arising traveling front, we are able to establish the existence of true traveling fronts for the original problem with memory. Our results are supplemented by numerical simulations.
-
C. Giardinà, C. Giberti, E. Magnanini, Approximating the cumulant generating function of triangles in the Erdös-Rényi random graph, Journal of Statistical Physics, 182 (2021), pp. 23/1--23/22, DOI 10.1007/s10955-021-02707-3 .
Abstract
We study the pressure of the “edge-triangle model”, which is equivalent to the cumulant generating function of triangles in the Erdös--Rényi random graph. The investigation involves a population dynamics method on finite graphs of increasing volume, as well as a discretization of the graphon variational problem arising in the infinite volume limit. As a result, we locate a curve in the parameter space where a one-step replica symmetry breaking transition occurs. Sampling a large graph in the broken symmetry phase is well described by a graphon with a structure very close to t he one of an equi-bipartite graph. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, An asymptotic analysis for a generalized Cahn--Hilliard system with fractional operators, Journal of Evolution Equations, 21 (2021), pp. 2749--2778, DOI 10.1007/s00028-021-00706-1 .
Abstract
In a recent paper the same authors have proved existence, uniqueness and regularity results for a class of viscous and nonviscous Cahn--Hilliard systems of two operator equations in which nonlinearities of double-well type, like regular or logarithmic potentials, as well as nonsmooth potentials with indicator functions, were admitted. The operators appearing in the system equations are fractional powers in the spectral sense of general linear operators, which are densely defined, unbounded, selfadjoint, and monotone in the Hilbert space of square-integrable functions on a bounded and smooth three-dimensional domain, and have compact resolvents. Here, for the case of the viscous system, we analyze the asymptotic behavior of the solution as the fractional power coefficient of the second operator tends to zero. We prove convergence to a phase relaxation problem at the limit, and we also investigate this limiting problem, in which an additional term containing the projection of the phase variable on the kernel of the second operator appears. -
P. Colli, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, Second-order analysis of an optimal control problem in a phase field tumor growth model with singular potentials and chemotaxis, ESAIM. Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations, 27 (2021), pp. 73/1--73/46, DOI 10.1051/cocv/2021072 .
Abstract
This paper concerns a distributed optimal control problem for a tumor growth model of Cahn--Hilliard type including chemotaxis with possibly singular anpotentials, where the control and state variables are nonlinearly coupled. First, we discuss the weak well-posedness of the system under very general assumptions for the potentials, which may be singular and nonsmooth. Then, we establish the strong well-posedness of the system in a reduced setting, which however admits the logarithmic potential: this analysis will lay the foundation for the study of the corresponding optimal control problem. Concerning the optimization problem, we address the existence of minimizers and establish both first-order necessary and second-order sufficient conditions for optimality. The mathematically challenging second-order analysis is completely performed here, after showing that the solution mapping is twice continuously differentiable between suitable Banach spaces via the implicit function theorem. Then, we completely identify the second-order Fréchet derivative of the control-to-state operator and carry out a thorough and detailed investigation about the related properties. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Deep quench approximation and optimal control of general Cahn--Hilliard systems with fractional operators and double obstacle potentials, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 14 (2021), pp. 243--271, DOI 10.3934/dcdss.2020213 .
Abstract
Recently, the authors derived well-posedness and regularity results for general evolutionary operator equations having the structure of a Cahn--Hilliard system. The involved operators were fractional versions in the spectral sense of general linear operators that have compact resolvents and are densely defined, unbounded, selfadjoint, and monotone in a Hilbert space of functions. The class of admissible double-well potentials driving the phase separation process modeled by the Cahn--Hilliard system included polynomial, logarithmic, and double obstacle nonlinearities. In a subsequent paper, distributed optimal control problems for such systems were investigated, where only differentiable polynomial and logarithmic potentials were admitted. Existence of optimizers and first-order optimality conditions were derived. In this paper, these results are complemented for nondifferentiable double obstacle nonlinearities. It is well known that for such nonlinearities standard constraint qualifications to construct Lagrange multipliers cannot be applied. To overcome this difficulty, we follow the so-called “deep quench” method, which has proved to be a powerful tool in optimal control problems with double obstacle potentials. We give a general convergence analysis of the deep quench approximation, including an error estimate, and demonstrate that its use leads to meaningful first-order necessary optimality conditions. -
J. Sprekels, F. Tröltzsch, Sparse optimal control of a phase field system with singular potentials arising in the modeling of tumor growth, ESAIM. Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations, 27 (2021), pp. S26/1--S26/27, DOI 10.1051/cocv/2020088 .
Abstract
In this paper, we study an optimal control problem for a nonlinear system of reaction-diffusion equations that constitutes a simplified and relaxed version of a thermodynamically consistent phase field model for tumor growth originally introduced in [13]. The model takes the effect of chemotaxis into account but neglects velocity contributions. The unknown quantities of the governing state equations are the chemical potential, the (normalized) tumor fraction, and the nutrient extra-cellular water concentration. The equation governing the evolution of the tumor fraction is dominated by the variational derivative of a double-well potential which may be of singular (e.g., logarithmic) type. In contrast to the recent paper [10] on the same system, we consider in this paper sparsity effects, which means that the cost functional contains a nondifferentiable (but convex) contribution like the L1-norm. For such problems, we derive first-order necessary optimality conditions and conditions for directional sparsity, both with respect to space and time, where the latter case is of particular interest for practical medical applications in which the control variables are given by the administration of cytotoxic drugs or by the supply of nutrients. In addition to these results, we prove that the corresponding control-to-state operator is twice continuously differentiable between suitable Banach spaces, using the implicit function theorem. This result, which complements and sharpens a differentiability result derived in [10], constitutes a prerequisite for a future derivation of second-order sufficient optimality conditions. -
R. Lasarzik, Analysis of a thermodynamically consistent Navier--Stokes--Cahn--Hilliard model, Nonlinear Analysis. An International Mathematical Journal, 213 (2021), pp. 112526/1--112526/33, DOI 10.1016/j.na.2021.112526 .
Abstract
In this paper, existence of generalized solutions to a thermodynamically consistent Navier--Stokes--Cahn--Hilliard model introduced in [19] is proven in any space dimension. The generalized solvability concepts are measure-valued and dissipative solutions. The measure-valued formulation incorporates an entropy inequality and an energy inequality instead of an energy balance in a nowadays standard way, the Gradient flow of the internal variable is fulfilled in a weak and the momentum balance in a measure-valued sense. In the dissipative formulation, the distributional relations of the momentum balance and the energy as well as entropy inequality are replaced by a relative energy inequality. Additionally, we prove the weak-strong uniqueness of the proposed solution concepts and that all generalized solutions with additional regularity are indeed strong solutions. -
M. Landstorfer, B. Prifling, V. Schmidt, Mesh generation for periodic 3D microstructure models and computation of effective properties, Journal of Computational Physics, 431 (2021), pp. 110071/1--110071/20 (published online on 23.12.2020), DOI https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.110071 .
Abstract
Understanding and optimizing effective properties of porous functional materials, such as permeability or conductivity, is one of the main goals of materials science research with numerous applications. For this purpose, understanding the underlying 3D microstructure is crucial since it is well known that the materials? morphology has an significant impact on their effective properties. Because tomographic imaging is expensive in time and costs, stochastic microstructure modeling is a valuable tool for virtual materials testing, where a large number of realistic 3D microstructures can be generated and used as geometry input for spatially-resolved numerical simulations. Since the vast majority of numerical simulations is based on solving differential equations, it is essential to have fast and robust methods for generating high-quality volume meshes for the geometrically complex microstructure domains. The present paper introduces a novel method for generating volume-meshes with periodic boundary conditions based on an analytical representation of the 3D microstructure using spherical harmonics. Due to its generality, the present method is applicable to many scientific areas. In particular, we present some numerical examples with applications to battery research by making use of an already existing stochastic 3D microstructure model that has been calibrated to eight differently compacted cathodes. -
R. Chill, H. Meinlschmidt, J. Rehberg, On the numerical range of second order elliptic operators with mixed boundary conditions in L$^p$, Journal of Evolution Equations, 21 (2021), pp. 3267--3288 (published online on 20.10.2020), DOI 10.1007/s00028-020-00642-6 .
Abstract
We consider second order elliptic operators with real, nonsymmetric coefficient functions which are subject to mixed boundary conditions. The aim of this paper is to provide uniform resolvent estimates for the realizations of these operators on Lp in a most direct way and under minimal regularity assumptions on the domain. This is analogous to the main result in [7]. Ultracontractivity of the associated semigroups is also considered. All results are for two different form domains realizing mixed boundary conditions. We further consider the case of Robin- instead of classical Neumann boundary conditions and also allow for operators inducing dynamic boundary conditions. The results are complemented by an intrinsic characterization of elements of the form domains inducing mixed boundary conditions. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Asymptotic analysis of a tumor growth model with fractional operators, Asymptotic Analysis, 120 (2020), pp. 41--72, DOI 10.3233/ASY-191578 .
Abstract
In this paper, we study a system of three evolutionary operator equations involving fractional powers of selfadjoint, monotone, unbounded, linear operators having compact resolvents. This system constitutes a generalized and relaxed version of a phase field system of Cahn--Hilliard type modelling tumor growth that has originally been proposed in Hawkins-Daarud et al. (Int. J. Numer. Math. Biomed. Eng. 28 (2012), 3--24). The original phase field system and certain relaxed versions thereof have been studied in recent papers co-authored by the present authors and E. Rocca. The model consists of a Cahn--Hilliard equation for the tumor cell fraction φ, coupled to a reaction-diffusion equation for a function S representing the nutrient-rich extracellular water volume fraction. Effects due to fluid motion are neglected. Motivated by the possibility that the diffusional regimes governing the evolution of the different constituents of the model may be of different (e.g., fractional) type, the present authors studied in a recent note a generalization of the systems investigated in the abovementioned works. Under rather general assumptions, well-posedness and regularity results have been shown. In particular, by writing the equation governing the evolution of the chemical potential in the form of a general variational inequality, also singular or nonsmooth contributions of logarithmic or of double obstacle type to the energy density could be admitted. In this note, we perform an asymptotic analysis of the governing system as two (small) relaxation parameters approach zero separately and simultaneously. Corresponding well-posedness and regularity results are established for the respective cases; in particular, we give a detailed discussion which assumptions on the admissible nonlinearities have to be postulated in each of the occurring cases. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Longtime behavior for a generalized Cahn--Hilliard system with fractional operators, Atti della Accademia Peloritana dei Pericolanti. Classe di Scienze, Fisiche, Matematiche e Naturali. AAPP. Physical, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences, 98 (2020), pp. A4/1--A4/18, DOI 10.1478/AAPP.98S2A4 .
Abstract
In this contribution, we deal with the longtime behavior of the solutions to the fractional variant of the Cahn--Hilliard system, with possibly singular potentials, which we recently investigated in the paper "Well-posedness and regularity for a generalized fractional CahnHilliard system". More precisely, we give a complete characterization of the Omega-limit of the phase parameter. The characterization depends on the first eigenvalue of one of the involved operators: if this eigenvalue is positive, then the chemical potential vanishes at infinity, and every element of the Omega-limit is a stationary solution to the phase equation; if it is zero instead, then every element of the Omega-limit solves a problem containing a real function which is related to the chemical potential. Such a function is nonunique and time dependent, in general, as we show by means of an example; however, we give sufficient conditions for it to be uniquely determined and constant. -
M.G. Hennessy, A. Münch, B. Wagner, Phase separation in swelling and deswelling hydrogels with a free boundary, Physical Review E. Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 101 (2020), pp. 032501/1--032501/14, DOI 10.1103/PhysRevE.101.032501 .
Abstract
We present a full kinetic model of a hydrogel that undergoes phase separation during swelling and deswelling. The model accounts for the interfacial energy of coexisting phases, finite strain of the polymer network, andsolvent transport across free boundaries. For the geometry of an initially dry layer bonded to a rigid substrate,the model predicts that forcing solvent into the gel at a fixed rate can induce a volume phase transition, whichgives rise to coexisting phases with different degrees of swelling, in systems where this cannot occur in the free-swelling case. While a nonzero shear modulus assists in the propagation of the transition front separating thesephases in the driven-swelling case, increasing it beyond a critical threshold suppresses its formation. Quenchinga swollen hydrogel induces spinodal decomposition, which produces several highly localized, highly swollenphases which coarsen and are then ejected from free boundary. The wealth of dynamic scenarios of this systemis discussed using phase-plane analysis and numerical solutions in a one-dimensional setting. -
O. Souček, M. Heida, J. Málek, On a thermodynamic framework for developing boundary conditions for Korteweg-type fluids, International Journal of Engineering Science, 154 (2020), pp. 103316/1--103316/28, DOI 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2020.103316 .
Abstract
We provide a derivation of several classes of boundary conditions for fluids of Korteweg-type using a simple and transparent thermodynamic approach that automatically guarentees that the derived boundary conditions are compatible with the second law of thermodynamics. The starting assumption of our approach is to describe the boundary of the domain as the membrane separating two different continua, one inside the domain, and the other outside the domain. With this viewpoint one may employ the framework of continuum thermodynamics involving singular surfaces. This approach allows us to identify, for various classes of surface Helmholtz free energies, the corresponding surface entropy production mechanisms. By establishing the constitutive relations that guarantee that the surface entropy production is non-negative, we identify a new class of boundary conditions, which on one hand generalizes in a nontrivial manner the Navier's slip boundary conditions, and on the other hand describes dynamic and static contact angle conditions. We explore the general model in detail for a particular case of Korteweg fluid where the Helmholtz free energy in the bulk is that of a van der Waals fluid. We perform a series of numerical experiments to document the basic qualitative features of the novel boundary conditions and their practical applicability to model phenomena such as the contact angle hysteresis. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Deep quench approximation and optimal control of general Cahn--Hilliard systems with fractional operators and double obstacle potentials, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 14 (2021), pp. 243--271 (published online on 21.12.2019), DOI 10.3934/dcdss.2020213 .
Abstract
In the recent paper ”Well-posedness and regularity for a generalized fractional Cahn--Hilliard system”, the same authors derived general well-posedness and regularity results for a rather general system of evolutionary operator equations having the structure of a Cahn--Hilliard system. The operators appearing in the system equations were fractional versions in the spectral sense of general linear operators A and B having compact resolvents and are densely defined, unbounded, selfadjoint, and monotone in a Hilbert space of functions defined in a smooth domain. The associated double-well potentials driving the phase separation process modeled by the Cahn--Hilliard system could be of a very general type that includes standard physically meaningful cases such as polynomial, logarithmic, and double obstacle nonlinearities. In the subsequent paper ”Optimal distributed control of a generalized fractional Cahn--Hilliard system” (Appl. Math. Optim. (2018), https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-018-9540-7) by the same authors, an analysis of distributed optimal control problems was performed for such evolutionary systems, where only the differentiable case of certain polynomial and logarithmic double-well potentials could be admitted. Results concerning existence of optimizers and first-order necessary optimality conditions were derived, where more restrictive conditions on the operators A and B had to be assumed in order to be able to show differentiability properties for the associated control-to-state operator. In the present paper, we complement these results by studying a distributed control problem for such evolutionary systems in the case of nondifferentiable nonlinearities of double obstacle type. For such nonlinearities, it is well known that the standard constraint qualifications cannot be applied to construct appropriate Lagrange multipliers. To overcome this difficulty, we follow here the so-called ”deep quench” method. This technique, in which the nondifferentiable double obstacle nonlinearity is approximated by differentiable logarithmic nonlinearities, was first developed by P. Colli, M.H. Farshbaf-Shaker and J. Sprekels in the paper ”A deep quench approach to the optimal control of an Allen--Cahn equation with dynamic boundary conditions and double obstacles” (Appl. Math. Optim. 71 (2015), pp. 1-24) and has proved to be a powerful tool in a number of optimal control problems with double obstacle potentials in the framework of systems of Cahn--Hilliard type. We first give a general convergence analysis of the deep quench approximation that includes an error estimate and then demonstrate that its use leads in the double obstacle case to appropriate first-order necessary optimality conditions in terms of a variational inequality and the associated adjoint state system. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Optimal velocity control of a convective Cahn--Hilliard system with double obstacles and dynamic boundary conditions: A `deep quench' approach, Journal of Convex Analysis, 26 (2019), pp. 485--514.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate a distributed optimal control problem for a convective viscous Cahn-Hilliard system with dynamic boundary conditions. Such systems govern phase separation processes between two phases taking place in an incompressible fluid in a container and, at the same time, on the container boundary. The cost functional is of standard tracking type, while the control is exerted by the velocity of the fluid in the bulk. In this way, the coupling between the state (given by the associated order parameter and chemical potential) and control variables in the governing system of nonlinear partial differential equations is bilinear, which presents a difficulty for the analysis. In contrast to the previous paper Optimal velocity control of a viscous Cahn-Hilliard system with convection and dynamic boundary conditions by the same authors, the bulk and surface free energies are of double obstacle type, which renders the state constraint nondifferentiable. It is well known that for such cases standard constraint qualifications are not satisfied so that standard methods do not apply to yield the existence of Lagrange multipliers. In this paper, we overcome this difficulty by taking advantage of results established in the quoted paper for logarithmic nonlinearities, using a so-called `deep quench approximation'. We derive results concerning the existence of optimal controls and the first-order necessary optimality conditions in terms of a variational inequality and the associated adjoint system. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Recent results on well-posedness and optimal control for a class of generalized fractional Cahn--Hilliard systems, Control and Cybernetics, 48 (2019), pp. 153--197.
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Well-posedness and regularity for a fractional tumor growth model, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 28 (2019), pp. 343--375.
Abstract
2613 -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Well-posedness and regularity for a generalized fractional Cahn--Hilliard system, Rendiconti Lincei -- Matematica e Applicazioni, 30 (2019), pp. 437--478.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate a rather general system of two operator equations that has the structure of a viscous or nonviscous Cahn--Hilliard system in which nonlinearities of double-well type occur. Standard cases like regular or logarithmic potentials, as well as non-differentiable potentials involving indicator functions, are admitted. The operators appearing in the system equations are fractional versions of general linear operators A and B, where the latter are densely defined, unbounded, self-adjoint and monotone in a Hilbert space of functions defined in a smooth domain and have compact resolvents. In this connection, we remark the fact that our definition of the fractional power of operators uses the approach via spectral theory. Typical cases are given by standard second-order elliptic differential operators (e.g., the Laplacian) with zero Dirichlet or Neumann boundary conditions, but also other cases like fourth-order systems or systems involving the Stokes operator are covered by the theory. We derive in this paper general well-posedness and regularity results that extend corresponding results which are known for either the non-fractional Laplacian with zero Neumann boundary condition or the fractional Laplacian with zero Dirichlet condition. These results are entirely new if at least one of the operators A and B differs from the Laplacian. It turns out that the first eigenvalue λ1 of A plays an important und not entirely obvious role: if λ1 is positive, then the operators A and B may be completely unrelated; if, however, λ1 equals zero, then it must be simple and the corresponding one-dimensional eigenspace has to consist of the constant functions and to be a subset of the domain of definition of a certain fractional power of B. We are able to show general existence, uniqueness, and regularity results for both these cases, as well as for both the viscous and the nonviscous system. -
P. Colli, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, Optimal control of a phase field system modelling tumor growth with chemotaxis and singular potentials, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 83 (2021), pp. 2017--2049 (published online on 21.10.2019), and 2021 Correction to: Optimal control of a phase field system modelling tumor growth with chemotaxis and singular potentials (https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-021-09771-x), DOI 10.1007/s00245-019-09618-6 .
Abstract
A distributed optimal control problem for an extended model of phase field type for tumor growth is addressed. In this model, the chemotaxis effects are also taken into account. The control is realized by two control variables that design the dispensation of some drugs to the patient. The cost functional is of tracking type, whereas the potential setting has been kept quite general in order to allow regular and singular potentials to be considered. In this direction, some relaxation terms have been introduced in the system. We show the well-posedness of the state system, the Fréchet differentiability of the control-to-state operator in a suitable functional analytic framework, and, lastly, we characterize the first-order necessary conditions of optimality in terms of a variational inequality involving the adjoint variables. -
S.P. Frigeri, C.G. Gal, M. Grasselli, J. Sprekels, Strong solutions to nonlocal 2D Cahn--Hilliard--Navier--Stokes systems with nonconstant viscosity, degenerate mobility and singular potential, Nonlinearity, 32 (2019), pp. 678--727, DOI 10.1088/1361-6544/aaedd0 .
Abstract
We consider a nonlinear system which consists of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations coupled with a convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation. This is a diffuse interface model which describes the motion of an incompressible isothermal mixture of two (partially) immiscible fluids having the same density. We suppose that the viscosity depends smoothly on the order parameter as well as the mobility. Moreover, we assume that the mobility is degenerate at the pure phases and that the potential is singular (e.g. of logarithmic type). This system is endowed with no-slip boundary condition for the (average) velocity and homogeneous Neumann boundary condition for the chemical potential. Thus the total mass is conserved. In the two-dimensional case, this problem was already analyzed in some joint papers of the first three authors. However, in the present general case, only the existence of a global weak solution, the (conditional) weak-strong uniqueness and the existence of the global attractor were proven. Here we are able to establish the existence of a (unique) strong solution through an approximation procedure based on time discretization. As a consequence, we can prove suitable uniform estimates which allow us to show some smoothness of the global attractor. Finally, we discuss the existence of strong solutions for the convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation, with a given velocity field, in the three dimensional case as well. -
G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Asymptotic limits and optimal control for the Cahn--Hilliard system with convection and dynamic boundary conditions, Nonlinear Analysis. An International Mathematical Journal, 178 (2019), pp. 1--31, DOI 10.1016/j.na.2018.07.007 .
Abstract
In this paper, we study initial-boundary value problems for the Cahn--Hilliard system with convection and nonconvex potential, where dynamic boundary conditions are assumed for both the associated order parameter and the corresponding chemical potential. While recent works addressed the case of viscous Cahn--Hilliard systems, the `pure' nonviscous case is investigated here. In its first part, the paper deals with the asymptotic behavior of the solutions as time approaches infinity. It is shown that the $omega$-limit of any trajectory can be characterized in terms of stationary solutions, provided the initial data are sufficiently smooth. The second part of the paper deals with the optimal control of the system by the fluid velocity. Results concerning existence and first-order necessary optimality conditions are proved. Here, we have to restrict ourselves to the case of everywhere defined smooth potentials. In both parts of the paper, we start from corresponding known results for the viscous case, derive sufficiently strong estimates that are uniform with respect to the (positive) viscosity parameter, and then let the viscosity tend to zero to establish the sought results for the nonviscous case. -
J. Sprekels, H. Wu, Optimal distributed control of a Cahn--Hilliard--Darcy system with mass sources, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 83 (2021), pp. 489--530 (published online on 24.01.2019), DOI 10.1007/s00245-019-09555-4 .
Abstract
In this paper, we study an optimal control problem for a two-dimensional Cahn--Hilliard--Darcy system with mass sources that arises in the modeling of tumor growth. The aim is to monitor the tumor fraction in a finite time interval in such a way that both the tumor fraction, measured in terms of a tracking type cost functional, is kept under control and minimal harm is inflicted to the patient by administering the control, which could either be a drug or nutrition. We first prove that the optimal control problem admits a solution. Then we show that the control-to-state operator is Fréchet differentiable between suitable Banach spaces and derive the first-order necessary optimality conditions in terms of the adjoint variables and the usual variational inequality. -
E. Meca Álvarez, A. Münch, B. Wagner, Localized instabilities and spinodal decomposition in driven systems in the presence of elasticity, Physical Review E. Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 97 (2018), pp. 012801/1--012801/12, DOI 10.1103/PhysRevE.97.012801 .
Abstract
We study numerically and analytically the instabilities associated with phase separation in a solid layer on which an external material flux is imposed. The first instability is localized within a boundary layer at the exposed free surface by a process akin to spinodal decomposition. In the limiting static case, when there is no material flux, the coherent spinodal decomposition is recovered. In the present problem stability analysis of the time-dependent and non-uniform base states as well as numerical simulations of the full governing equations are used to establish the dependence of the wavelength and onset of the instability on parameter settings and its transient nature as the patterns eventually coarsen into a flat moving front. The second instability is related to the Mullins-Sekerka instability in the presence of elasticity and arises at the moving front between the two phases when the flux is reversed. Stability analyses of the full model and the corresponding sharp-interface model are carried out and compared. Our results demonstrate how interface and bulk instabilities can be analysed within the same framework which allows to identify and distinguish each of them clearly. The relevance for a detailed understanding of both instabilities and their interconnections in a realistic setting are demonstrated for a system of equations modelling the lithiation/delithiation processes within the context of Lithium ion batteries. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, On a Cahn--Hilliard system with convection and dynamic boundary conditions, Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata. Serie Quarta. Fondazione Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata, c/o Dipartimento di Matematica ``U. Dini'', Firenze; Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg. English, French, German, Italian, English abstracts., 197 (2018), pp. 1445--1475, DOI 10.1007/s10231-018-0732-1 .
Abstract
This paper deals with an initial and boundary value problem for a system coupling equation and boundary condition both of Cahn--Hilliard type; an additional convective term with a forced velocity field, which could act as a control on the system, is also present in the equation. Either regular or singular potentials are admitted in the bulk and on the boundary. Both the viscous and pure Cahn--Hilliard cases are investigated, and a number of results is proven about existence of solutions, uniqueness, regularity, continuous dependence, uniform boundedness of solutions, strict separation property. A complete approximation of the problem, based on the regularization of maximal monotone graphs and the use of a Faedo--Galerkin scheme, is introduced and rigorously discussed. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, On the longtime behavior of a viscous Cahn--Hilliard system with convection and dynamic boundary conditions, Journal of Elliptic and Parabolic Equations, 4 (2018), pp. 327--347, DOI 10.1007/s41808-018-0021-6 .
Abstract
In this paper, we study the longtime asymptotic behavior of a phase separation process occurring in a three-dimensional domain containing a fluid flow of given velocity. This process is modeled by a viscous convective Cahn--Hilliard system, which consists of two nonlinearly coupled second-order partial differential equations for the unknown quantities, the chemical potential and an order parameter representing the scaled density of one of the phases. In contrast to other contributions, in which zero Neumann boundary conditions were are assumed for both the chemical potential and the order parameter, we consider the case of dynamic boundary conditions, which model the situation when another phase transition takes place on the boundary. The phase transition processes in the bulk and on the boundary are driven by free energies functionals that may be nondifferentiable and have derivatives only in the sense of (possibly set-valued) subdifferentials. For the resulting initial-boundary value system of Cahn--Hilliard type, general well-posedness results have been established in piera recent contribution by the same authors. In the present paper, we investigate the asymptotic behavior of the solutions as times approaches infinity. More precisely, we study the ω-limit (in a suitable topology) of every solution trajectory. Under the assumptions that the viscosity coefficients are strictly positive and that at least one of the underlying free energies is differentiable, we prove that the omegalimit is meaningful and that all of its elements are solutions to the corresponding stationary system, where the component representing the chemical potential is a constant. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Optimal distributed control of a generalized fractional Cahn--Hilliard system, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 82 (2020), pp. 551--589 (published online on 15.11.2018), DOI 10.1007/s00245-018-9540-7 .
Abstract
In the recent paper “Well-posedness and regularity for a generalized fractional Cahn--Hilliard system” by the same authors, general well-posedness results have been established for a class of evolutionary systems of two equations having the structure of a viscous Cahn--Hilliard system, in which nonlinearities of double-well type occur. The operators appearing in the system equations are fractional versions in the spectral sense of general linear operators A,B, having compact resolvents, which are densely defined, unbounded, selfadjoint, and monotone in a Hilbert space of functions defined in a smooth domain. In this work we complement the results given in quoted paper by studying a distributed control problem for this evolutionary system. The main difficulty in the analysis is to establish a rigorous Fréchet differentiability result for the associated control-to-state mapping. This seems only to be possible if the state stays bounded, which, in turn, makes it necessary to postulate an additional global boundedness assumption. One typical situation, in which this assumption is satisfied, arises when B is the negative Laplacian with zero Dirichlet boundary conditions and the nonlinearity is smooth with polynomial growth of at most order four. Also a case with logarithmic nonlinearity can be handled. Under the global boundedness assumption, we establish existence and first-order necessary optimality conditions for the optimal control problem in terms of a variational inequality and the associated adjoint state system. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Optimal velocity control of a viscous Cahn--Hilliard system with convection and dynamic boundary conditions, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 56 (2018), pp. 1665--1691, DOI 10.1137/17M1146786 .
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate a distributed optimal control problem for a convective viscous Cahn--Hilliard system with dynamic boundary conditions. Such systems govern phase separation processes between two phases taking place in an incompressible fluid in a container and, at the same time, on the container boundary. The cost functional is of standard tracking type, while the control is exerted by the velocity of the fluid in the bulk. In this way, the coupling between the state (given by the associated order parameter and chemical potential) and control variables in the governing system of nonlinear partial differential equations is bilinear, which presents an additional difficulty for the analysis. The nonlinearities in the bulk and surface free energies are of logarithmic type, which entails that the thermodynamic forces driving the phase separation process may become singular. We show existence for the optimal control problem under investigation, prove the Fréchet differentiability of the associated control-to-state mapping in suitable Banach spaces, and derive the first-order necessary optimality conditions in terms of a variational inequality and the associated adjoint system. Due to the strong nonlinear couplings between state variables and control, the corresponding proofs require a considerable analytical effort. -
S. Frigeri, M. Grasselli, J. Sprekels, Optimal distributed control of two-dimensional nonlocal Cahn--Hilliard--Navier--Stokes systems with degenerate mobility and singular potential, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 81 (2020), pp. 889--931 (published online on 24.09.2018), DOI 10.1007/s00245-018-9524-7 .
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a two-dimensional diffuse interface model for the phase separation of an incompressible and isothermal binary fluid mixture with matched densities. This model consists of the Navier-Stokes equations, nonlinearly coupled with a convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation. The system rules the evolution of the volume-averaged velocity of the mixture and the (relative) concentration difference of the two phases. The aim of this work is to study an optimal control problem for such a system, the control being a time-dependent external force acting on the fluid. We first prove the existence of an optimal control for a given tracking type cost functional. Then we study the differentiability properties of the control-to-state map, and we establish first-order necessary optimality conditions. These results generalize the ones obtained by the first and the third authors jointly with E. Rocca in [19]. There the authors assumed a constant mobility and a regular potential with polynomially controlled growth. Here, we analyze the physically more relevant case of a degenerate mobility and a singular (e.g., logarithmic) potential. This is made possible by the existence of a unique strong solution which was recently proved by the authors and C. G. Gal in [14]. -
M. Hintermüller, M. Hinze, Ch. Kahle, T. Keil, A goal-oriented dual-weighted adaptive finite element approach for the optimal control of a nonsmooth Cahn--Hilliard--Navier--Stokes system, Optimization and Engineering. International Multidisciplinary Journal to Promote Optimization Theory & Applications in Engineering Sciences, 19 (2018), pp. 629--662, DOI 10.1007/s11081-018-9393-6 .
Abstract
This paper is concerned with the development and implementation of an adaptive solution algorithm for the optimal control of a time-discrete Cahn--Hilliard--Navier--Stokes system with variable densities. The free energy density associated to the Cahn--Hilliard system incorporates the double-obstacle potential which yields an optimal control problem for a family of coupled systems in each time instant of a variational inequality of fourth order and the Navier--Stokes equation. A dual-weighed residual approach for goal-oriented adaptive finite elements is presented which is based on the concept of C-stationarity. The overall error representation depends on primal residual weighted by approximate dual quantities and vice versa as well as various complementary mismatch errors. Details on the numerical realization of the adaptive concept and a report on numerical tests are given. -
S. Bergmann, D.A. Barragan-Yani, E. Flegel, K. Albe, B. Wagner, Anisotropic solid-liquid interface kinetics in silicon: An atomistically informed phase-field model, Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 25 (2017), pp. 065015/1--065015/20, DOI 10.1088/1361-651X/aa7862 .
Abstract
We present an atomistically informed parametrization of a phase-field model for describing the anisotropic mobility of liquid-solid interfaces in silicon. The model is derived from a consistent set of atomistic data and thus allows to directly link molecular dynamics and phase field simulations. Expressions for the free energy density, the interfacial energy and the temperature and orientation dependent interface mobility are systematically fitted to data from molecular dynamics simulations based on the Stillinger-Weber interatomic potential. The temperature-dependent interface velocity follows a Vogel-Fulcher type behavior and allows to properly account for the dynamics in the undercooled melt. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Optimal distributed control of a diffuse interface model of tumor growth, Nonlinearity, 30 (2017), pp. 2518--2546.
Abstract
In this paper, a distributed optimal control problem is studied for a diffuse interface model of tumor growth which was proposed by Hawkins--Daruud et al. in citeHZO. The model consists of a Cahn-Hilliard equation for the tumor cell fraction $vp$ coupled to a reaction-diffusion equation for a function $s$ representing the nutrient-rich extracellular water volume fraction. The distributed control $u$ monitors as a right-hand side the equation for $s$ and can be interpreted as a nutrient supply or a medication, while the cost function, which is of standard tracking type, is meant to keep the tumor cell fraction under control during the evolution. We show that the control-to-state operator is Fréchet differentiable between appropriate Banach spaces and derive the first-order necessary optimality conditions in terms of a variational inequality involving the adjoint state variables. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Asymptotic analyses and error estimates for a Cahn--Hilliard type phase field system modelling tumor growth, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 10 (2017), pp. 37--54.
Abstract
This paper is concerned with a phase field system of Cahn--Hilliard type that is related to a tumor growth model and consists of three equations in gianni terms of the variables order parameter, chemical potential and nutrient concentration. This system has been investigated in the recent papers citeCGH and citeCGRS gianni from the viewpoint of well-posedness, long time bhv and asymptotic convergence as two positive viscosity coefficients tend to zero at the same time. Here, we continue the analysis performed in citeCGRS by showing two independent sets of results as just one of the coefficents tends to zero, the other remaining fixed. We prove convergence results, uniqueness of solutions to the two resulting limit problems, and suitable error estimates -
CH. Heinemann, Ch. Kraus, E. Rocca, R. Rossi, A temperature-dependent phase-field model for phase separation and damage, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 225 (2017), pp. 177--247.
Abstract
In this paper we study a model for phase separation and damage in thermoviscoelastic materials. The main novelty of the paper consists in the fact that, in contrast with previous works in the literature (cf., e.g., [C. Heinemann, C. Kraus: Existence results of weak solutions for Cahn-Hilliard systems coupled with elasticity and damage. Adv. Math. Sci. Appl. 21 (2011), 321--359] and [C. Heinemann, C. Kraus: Existence results for diffuse interface models describing phase separation and damage. European J. Appl. Math. 24 (2013), 179--211]), we encompass in the model thermal processes, nonlinearly coupled with the damage, concentration and displacement evolutions. More in particular, we prove the existence of "entropic weak solutions", resorting to a solvability concept first introduced in [E. Feireisl: Mathematical theory of compressible, viscous, and heat conducting fluids. Comput. Math. Appl. 53 (2007), 461--490] in the framework of Fourier-Navier-Stokes systems and then recently employed in [E. Feireisl, H. Petzeltová, E. Rocca: Existence of solutions to a phase transition model with microscopic movements. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 32 (2009), 1345--1369], [E. Rocca, R. Rossi: "Entropic" solutions to a thermodynamically consistent PDE system for phase transitions and damage. SIAM J. Math. Anal., 47 (2015), 2519--2586] for the study of PDE systems for phase transition and damage. Our global-in-time existence result is obtained by passing to the limit in a carefully devised time-discretization scheme. -
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Unsaturated deformable porous media flow with thermal phase transition, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 27 (2017), pp. 2675--2710, DOI 10.1142/S0218202517500555 .
Abstract
In the present paper, a continuum model is introduced for fluid flow in a deformable porous medium, where the fluid may undergo phase transitions. Typically, such problems arise in modeling liquid-solid phase transformations in groundwater flows. The system of equations is derived here from the conservation principles for mass, momentum, and energy and from the Clausius-Duhem inequality for entropy. It couples the evolution of the displacement in the matrix material, of the capillary pressure, of the absolute temperature, and of the phase fraction. Mathematical results are proved under the additional hypothesis that inertia effects and shear stresses can be neglected. For the resulting highly nonlinear system of two PDEs, one ODE and one ordinary differential inclusion with natural initial and boundary conditions, existence of global in time solutions is proved by means of cut-off techniques and suitable Moser-type estimates. -
M. Hintermüller, T. Keil, D. Wegner, Optimal control of a semidiscrete Cahn--Hilliard--Navier--Stokes system with non-matched fluid densities, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 55 (2017), pp. 1954--1989.
-
S.P. Frigeri, Global existence of weak solutions for a nonlocal model for two-phase flows of incompressible fluids with unmatched densities, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 26 (2016), pp. 1957--1993.
Abstract
We consider a diffuse interface model for an incompressible isothermal mixture of two viscous Newtonian fluids with different densities in a bounded domain in two or three space dimensions. The model is the nonlocal version of the one recently derived by Abels, Garcke and Grün and consists of a Navier-Stokes type system coupled with a convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation. The density of the mixture depends on an order parameter. For this nonlocal system we prove existence of global dissipative weak solutions for the case of singular double-well potentials and non degenerate mobilities. To this goal we devise an approach which is completely independent of the one employed by Abels, Depner and Garcke to establish existence of weak solutions for the local Abels et al. model. -
M. Dai, E. Feireisl, E. Rocca, G. Schimperna, M.E. Schonbek, On asymptotic isotropy for a hydrodynamic model of liquid crystals, Asymptotic Analysis, 97 (2016), pp. 189--210.
Abstract
We study a PDE system describing the motion of liquid crystals by means of the Q?tensor description for the crystals coupled with the incompressible Navier-Stokes system. Using the method of Fourier splitting, we show that solutions of the system tend to the isotropic state at the rate (1 + t)?? as t ? ? 1 for a certain ? > 2 . -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, A boundary control problem for the viscous Cahn--Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 73 (2016), pp. 195--225, DOI 10.1007/s00245-015-9299-z .
Abstract
A boundary control problem for the viscous Cahn-Hilliard equations with possibly singular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions is studied and first order necessary conditions for optimality are proved. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, On an application of Tikhonov's fixed point theorem to a nonlocal Cahn--Hilliard type system modeling phase separation, Journal of Differential Equations, 260 (2016), pp. 7940--7964.
Abstract
This paper investigates a nonlocal version of a model for phase separation on an atomic lattice that was introduced by P. Podio-Guidugli in Ric. Mat. 55 (2006) 105-118. The model consists of an initial-boundary value problem for a nonlinearly coupled system of two partial differential equations governing the evolution of an order parameter ρ and the chemical potential μ. Singular contributions to the local free energy in the form of logarithmic or double-obstacle potentials are admitted. In contrast to the local model, which was studied by P. Podio-Guidugli and the present authors in a series of recent publications, in the nonlocal case the equation governing the evolution of the order parameter contains in place of the Laplacian a nonlocal expression that originates from nonlocal contributions to the free energy and accounts for possible long-range interactions between the atoms. It is shown that just as in the local case the model equations are well posed, where the technique of proving existence is entirely different: it is based on an application of Tikhonov's fixed point theorem in a rather unusual separable and reflexive Banach space. -
M. Korzec, A. Münch, E. Süli, B. Wagner, Anisotropy in wavelet based phase field models, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems. Series B. A Journal Bridging Mathematics and Sciences, 21 (2016), pp. 1167--1187.
Abstract
Anisotropy is an essential feature of phase-field models, in particular when describing the evolution of microstructures in solids. The symmetries of the crystalline phases are reflected in the interfacial energy by introducing corresponding directional dependencies in the gradient energy coefficients, which multiply the highest order derivative in the phase-field model. This paper instead considers an alternative approach, where the anisotropic gradient energy terms are replaced by a wavelet analogue that is intrinsically anisotropic and linear. In our studies we focus on the classical coupled temperature - Ginzburg-Landau type phase-field model for dendritic growth. For the resulting derivative-free wavelet analogue existence, uniqueness and continuous dependence on initial data for weak solutions is proved. The ability to capture dendritic growth similar to the results obtained from classical models is investigated numerically. -
M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, C. Hecht, Optimal control of elastic vector-valued Allen--Cahn variational inequalities, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 54 (2016), pp. 129--152.
Abstract
In this paper we consider a elastic vector-valued Allen--Cahn MPCC (Mathematical Programs with Complementarity Constraints) problem. We use a regularization approach to get the optimality system for the subproblems. By passing to the limit in the optimality conditions for the regularized subproblems, we derive certain generalized first-order necessary optimality conditions for the original problem. -
S.P. Frigeri, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Optimal distributed control of a nonlocal Cahn--Hilliard/Navier--Stokes system in two dimensions, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 54 (2016), pp. 221 -- 250.
Abstract
We study a diffuse interface model for incompressible isothermal mixtures of two immiscible fluids coupling the Navier-Stokes system with a convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation in two dimensions of space. We apply recently proved well-posedness and regularity results in order to establish existence of optimal controls as well as first-order necessary optimality conditions for an associated optimal control problem in which a distributed control is applied to the fluid flow. -
CH. Heinemann, K. Sturm, Shape optimisation for a class of semilinear variational inequalities with applications to damage models, SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 48 (2016), pp. 3579--3617, DOI 10.1137/16M1057759 .
Abstract
The present contribution investigates shape optimisation problems for a class of semilinear elliptic variational inequalities with Neumann boundary conditions. Sensitivity estimates and material derivatives are firstly derived in an abstract operator setting where the operators are defined on polyhedral subsets of reflexive Banach spaces. The results are then refined for variational inequalities arising from minimisation problems for certain convex energy functionals considered over upper obstacle sets in $H^1$. One particularity is that we allow for dynamic obstacle functions which may arise from another optimisation problems. We prove a strong convergence property for the material derivative and establish state-shape derivatives under regularity assumptions. Finally, as a concrete application from continuum mechanics, we show how the dynamic obstacle case can be used to treat shape optimisation problems for time-discretised brittle damage models for elastic solids. We derive a necessary optimality system for optimal shapes whose state variables approximate desired damage patterns and/or displacement fields. -
E. Rocca, R. Rossi, ``Entropic'' solutions to a thermodynamically consistent PDE system for phase transitions and damage, SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 74 (2015), pp. 2519--2586.
Abstract
In this paper we analyze a PDE system modelling (non-isothermal) phase transitions and dam- age phenomena in thermoviscoelastic materials. The model is thermodynamically consistent: in particular, no small perturbation assumption is adopted, which results in the presence of quadratic terms on the right-hand side of the temperature equation, only estimated in L^1. The whole system has a highly nonlinear character. We address the existence of a weak notion of solution, referred to as “entropic”, where the temperature equation is formulated with the aid of an entropy inequality, and of a total energy inequality. This solvability concept reflects the basic principles of thermomechanics as well as the thermodynamical consistency of the model. It allows us to obtain global-in-time existence theorems without imposing any restriction on the size of the initial data. We prove our results by passing to the limit in a time discretization scheme, carefully tailored to the nonlinear features of the PDE system (with its “entropic” formulation), and of the a priori estimates performed on it. Our time-discrete analysis could be useful towards the numerical study of this model. -
E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Optimal distributed control of a nonlocal convective Cahn--Hilliard equation by the velocity in three dimensions, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 53 (2015), pp. 1654--1680.
Abstract
In this paper we study a distributed optimal control problem for a nonlocal convective Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility and singular potential in three dimensions of space. While the cost functional is of standard tracking type, the control problem under investigation cannot easily be treated via standard techniques for two reasons: the state system is a highly nonlinear system of PDEs containing singular and degenerating terms, and the control variable, which is given by the velocity of the motion occurring in the convective term, is nonlinearly coupled to the state variable. The latter fact makes it necessary to state rather special regularity assumptions for the admissible controls, which, while looking a bit nonstandard, are however quite natural in the corresponding analytical framework. In fact, they are indispensable prerequisites to guarantee the well-posedness of the associated state system. In this contribution, we employ recently proved existence, uniqueness and regularity results for the solution to the associated state system in order to establish the existence of optimal controls and appropriate first-order necessary optimality conditions for the optimal control problem. -
S.P. Frigeri, M. Grasselli, E. Rocca, A diffuse interface model for two-phase incompressible flows with nonlocal interactions and nonconstant mobility, Nonlinearity, 28 (2015), pp. 1257--1293.
Abstract
We consider a diffuse interface model for incompressible isothermal mixtures of two immiscible fluids with matched constant densities. This model consists of the Navier-Stokes system coupled with a convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation with non-constant mobility. We first prove the existence of a global weak solution in the case of non-degenerate mobilities and regular potentials of polynomial growth. Then we extend the result to degenerate mobilities and singular (e.g. logarithmic) potentials. In the latter case we also establish the existence of the global attractor in dimension two. Using a similar technique, we show that there is a global attractor for the convective nonlocal Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility and singular potential in dimension three. -
M. Heida, Existence of solutions for two types of generalized versions of the Cahn--Hilliard equation, Applications of Mathematics, 60 (2015), pp. 51--90.
Abstract
We show existence of solutions to two types of generalized anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard problems: In the first case, we assume the mobility to be dependent on the concentration and its gradient, where the system is supplied with dynamic boundary conditions. In the second case, we deal with classical no-flux boundary conditions where the mobility depends on concentration u, gradient of concentration ?u and the chemical potential ?u?s?(u). The existence is shown using a newly developed generalization of gradient flows by the author and the theory of Young measures. -
M. Heida, On systems of Cahn--Hilliard and Allen--Cahn equations considered as gradient flows in Hilbert spaces, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 423 (2015), pp. 410--455.
-
E. Bonetti, Ch. Heinemann, Ch. Kraus, A. Segatti, Modeling and analysis of a phase field system for damage and phase separation processes in solids, Journal of Partial Differential Equations, 258 (2015), pp. 3928--3959.
Abstract
In this work, we analytically investigate a multi-component system for describing phase separation and damage processes in solids. The model consists of a parabolic diffusion equation of fourth order for the concentration coupled with an elliptic system with material dependent coefficients for the strain tensor and a doubly nonlinear differential inclusion for the damage function. The main aim of this paper is to show existence of weak solutions for the introduced model, where, in contrast to existing damage models in the literature, different elastic properties of damaged and undamaged material are regarded. To prove existence of weak solutions for the introduced system, we start with a regularized version. Then, by passing to the limit, existence results of weak solutions for the proposed model are obtained via suitable variational techniques. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Vanishing viscosities and error estimate for a Cahn--Hilliard type phase field system related to tumor growth, Nonlinear Analysis. Real World Applications. An International Multidisciplinary Journal, 26 (2015), pp. 93--108.
Abstract
In this paper we perform an asymptotic analysis for two different vanishing viscosity coefficients occurring in a phase field system of Cahn--Hilliard type that was recently introduced in order to approximate a tumor growth model. In particular, we extend some recent results obtained in [Colli-Gilardi-Hilhorst 2015], letting the two positive viscosity parameters tend to zero independently from each other and weakening the conditions on the initial data in such a way as to maintain the nonlinearities of the PDE system as general as possible. Finally, under proper growth conditions on the interaction potential, we prove an error estimate leading also to the uniqueness result for the limit system. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, A boundary control problem for the pure Cahn--Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions, Advances in Nonlinear Analysis, 4 (2015), pp. 311--325.
Abstract
A boundary control problem for the pure Cahn--Hilliard equations with possibly singular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions is studied and first-order necessary conditions for optimality are proved. -
P. Colli, M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Optimal boundary control of a viscous Cahn--Hilliard system with dynamic boundary condition and double obstacle potentials, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 53 (2015), pp. 2696--2721.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate optimal boundary control problems for Cahn--Hilliard variational inequalities with a dynamic boundary condition involving double obstacle potentials and the Laplace--Beltrami operator. The cost functional is of standard tracking type, and box constraints for the controls are prescribed. We prove existence of optimal controls and derive first-order necessary conditions of optimality. The general strategy, which follows the lines of the recent approach by Colli, Farshbaf-Shaker, Sprekels (see Appl. Math. Optim., 2014) to the (simpler) Allen--Cahn case, is the following: we use the results that were recently established by Colli, Gilardi, Sprekels in the preprint arXiv:1407.3916 [math.AP] for the case of (differentiable) logarithmic potentials and perform a so-called “deep quench limit”. Using compactness and monotonicity arguments, it is shown that this strategy leads to the desired first-order necessary optimality conditions for the case of (non-differentiable) double obstacle potentials. -
P. Colli, M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Second-order analysis of a boundary control problem for the viscous Cahn--Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions, Annals of the Academy of Romanian Scientists. Mathematics and its Applications., 7 (2015), pp. 41--66.
Abstract
In this paper we establish second-order sufficient optimality conditions for a boundary control problem that has been introduced and studied by three of the authors in the preprint arXiv:1407.3916. This control problem regards the viscous Cahn--Hilliard equation with possibly singular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions. -
P. Colli, M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, J. Sprekels, A deep quench approach to the optimal control of an Allen--Cahn equation with dynamic boundary conditions and double obstacles, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 71 (2015), pp. 1--24.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate optimal control problems for Allen-Cahn variational inequalities with a dynamic boundary condition involving double obstacle potentials and the Laplace-Beltrami operator. The approach covers both the cases of distributed controls and of boundary controls. The cost functional is of standard tracking type, and box constraints for the controls are prescribed. We prove existence of optimal controls and derive first-order necessary conditions of optimality. The general strategy is the following: we use the results that were recently established by two of the authors for the case of (differentiable) logarithmic potentials and perform a so-called “deep quench limit”. Using compactness and monotonicity arguments, it is shown that this strategy leads to the desired first-order necessary optimality conditions for the case of (non-differentiable) double obstacle potentials. -
P. Colli, J. Sprekels, Optimal control of an Allen--Cahn equation with singular potentials and dynamic boundary condition, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 53 (2015), pp. 213--234.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate optimal control problems for Allen--Cahn equations with singular nonlinearities and a dynamic boundary condition involving singular nonlinearities and the Laplace--Beltrami operator. The approach covers both the cases of distributed controls and of boundary controls. The cost functional is of standard tracking type, and box constraints for the controls are prescribed. Parabolic problems with nonlinear dynamic boundary conditions involving the Laplace--Beltrami operation have recently drawn increasing attention due to their importance in applications, while their optimal control was apparently never studied before. In this paper, we first extend known well-posedness and regularity results for the state equation and then show the existence of optimal controls and that the control-to-state mapping is twice continuously Fréchet differentiable between appropriate function spaces. Based on these results, we establish the first-order necessary optimality conditions in terms of a variational inequality and the adjoint state equation, and we prove second-order sufficient optimality conditions. -
E. Feireisl, E. Rocca, G. Schimperna, A. Zarnescu, Nonisothermal nematic liquid crystal flows with the Ball--Majumdar free energy, Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata. Serie Quarta. Fondazione Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata, c/o Dipartimento di Matematica ``U. Dini'', Firenze; Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg. English, French, German, Italian, English abstracts., 194 (2015), pp. 1269--1299.
Abstract
In this paper we prove the existence of global in time weak solutions for an evolutionary PDE system modelling nonisothermal Landau-de Gennes nematic liquid crystal (LC) flows in three dimensions of space. In our model, the incompressible Navier-Stokes system for the macroscopic velocity $vu$ is coupled to a nonlinear convective parabolic equation describing the evolution of the Q-tensor $QQ$, namely a tensor-valued variable representing the normalized second order moments of the probability distribution function of the LC molecules. The effects of the (absolute) temperature $vt$ are prescribed in the form of an energy balance identity complemented with a global entropy production inequality. Compared to previous contributions, we can consider here the physically realistic singular configuration potential $f$ introduced by Ball and Majumdar. This potential gives rise to severe mathematical difficulties since it introduces, in the Q-tensor equation, a term which is at the same time singular in $QQ$ and degenerate in $vt$. To treat it a careful analysis of the properties of $f$, particularly of its blow-up rate, is carried out. -
M.G. Hennessy, V.M. Burlakov, A. Münch, B. Wagner, A. Goriely, Controlled topological transitions in thin-film phase separation, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 75 (2015), pp. 38--60.
Abstract
In this paper the evolution of a binary mixture in a thin-film geometry with a wall at the top and bottom is considered. Bringing the mixture into its miscibility gap so that no spinodal decomposition occurs in the bulk, a slight energetic bias of the walls towards each one of the constituents ensures the nucleation of thin boundary layers that grow until the constituents have moved into one of the two layers. These layers are separated by an interfacial region, where the composition changes rapidly. Conditions that ensure the separation into two layers with a thin interfacial region are investigated based on a phase-field model and using matched asymptotic expansions a corresponding sharp-interface problem for the location of the interface is established. It is then argued that a thus created two-layer system is not at its energetic minimum but destabilizes into a controlled self-replicating pattern of trapezoidal vertical stripes by minimizing the interfacial energy between the phases while conserving their area. A quantitative analysis of this mechanism is carried out via a new thin-film model for the free interfaces, which is derived asymptotically from the sharp-interface model. -
M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, A relaxation approach to vector-valued Allen--Cahn MPEC problems, Applied Mathematics and Optimization. An International Journal with Applications to Stochastics, 72 (2015), pp. 325--351.
-
CH. Heinemann, Ch. Kraus, Complete damage in linear elastic materials -- Modeling, weak formulation and existence results, Calculus of Variations and Partial Differential Equations, 54 (2015), pp. 217--250.
Abstract
We introduce a complete damage model with a time-depending domain for linear-elastically stressed solids under time-varying Dirichlet boundary conditions. The evolution of the system is described by a doubly nonlinear differential inclusion for the damage process and a quasi-static balance equation for the displacement field. For the introduced complete damage model, we propose a classical formulation and a corresponding suitable weak formulation in an $SBV$-framework. We show that the classical differential inclusion can be regained from the notion of weak solutions under certain regularity assumptions. The main aim of this work is to prove local-in-time existence and global-in-time existence in some weaker sense for the introduced model. In contrast to incomplete damage theories, the material can be exposed to damage in the proposed model in such a way that the elastic behavior may break down on the damaged parts of the material, i.e. we loose coercivity properties of the free energy. This leads to several mathematical difficulties. For instance, it might occur that not completely damaged material regions are isolated from the Dirichlet boundary. In this case, the deformation field cannot be controlled in the transition from incomplete to complete damage. To tackle this problem, we consider the evolution process on a time-depending domain. In this context, two major challenges arise: Firstly, the time-dependent domain approach leads to jumps in the energy which have to be accounted for in the energy inequality of the notion of weak solutions. To handle this problem, several energy estimates are established by $Gamma$-convergence techniques. Secondly, the time-depending domain might have bad smoothness properties such that Korn's inequality cannot be applied. To this end, a covering result for such sets with smooth compactly embedded domains has been shown. -
CH. Heinemann, Ch. Kraus, Existence of weak solutions for a PDE system describing phase separation and damage processes including inertial effects, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 35 (2015), pp. 2565--2590.
Abstract
In this paper, we consider a coupled PDE system describing phase separation and damage phenomena in elastically stressed alloys in the presence of inertial effects. The material is considered on a bounded Lipschitz domain with mixed boundary conditions for the displacement variable. The main aim of this work is to establish existence of weak solutions for the introduced hyperbolic-parabolic system. To this end, we first generalize the notion of weak solution introduced in WIAS 1520. Then we prove existence of weak solutions by means of regularization, time-discretization and different variational techniques. -
CH. Heinemann, Ch. Kraus, Existence of weak solutions for a hyperbolic-parabolic phase field system with mixed boundary conditions on non-smooth domains, SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 47 (2015), pp. 2044--2073.
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to prove existence of weak solutions of hyperbolic-parabolic evolution inclusions defined on Lipschitz domains with mixed boundary conditions describing, for instance, damage processes and elasticity with inertial effects. To this end, we first present a suitable weak formulation in order to deal with such evolution inclusions. Then, existence of weak solutions is proven by utilizing time-discretization, $H^2$--regularization and variational techniques. -
CH. Heinemann, E. Rocca, Damage processes in thermoviscoelastic materials with damage-dependent thermal expansion coefficients, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 38 (2015), pp. 4587--4612.
Abstract
In this paper we prove existence of global in time weak solutions for a highly nonlinear PDE system arising in the context of damage phenomena in thermoviscoelastic materials. The main novelty of the present contribution with respect to the ones already present in the literature consists in the possibility of taking into account a damage-dependent thermal expansion coefficient. This term implies the presence of nonlinear couplings in the PDE system, which make the analysis more challenging. -
E. Rocca, R. Rossi, A degenerating PDE system for phase transitions and damage, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 24 (2014), pp. 1265--1341.
-
G. Aki, W. Dreyer, J. Giesselmann, Ch. Kraus, A quasi-incompressible diffuse interface model with phase transition, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 24 (2014), pp. 827--861.
Abstract
This work introduces a new thermodynamically consistent diffuse model for two-component flows of incompressible fluids. For the introduced diffuse interface model, we investigate physically admissible sharp interface limits by matched asymptotic techniques. To this end, we consider two scaling regimes where in one case we recover the Euler equations and in the other case the Navier-Stokes equations in the bulk phases equipped with admissible interfacial conditions. For the Navier-Stokes regime, we further assume the densities of the fluids are close to each other in the sense of a small parameter which is related to the interfacial thickness of the diffuse model. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Krejčí, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Analysis of a time discretization scheme for a nonstandard viscous Cahn--Hilliard system, ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis, 48 (2014), pp. 1061--1087.
Abstract
In this paper we propose a time discretization of a system of two parabolic equations describing diffusion-driven atom rearrangement in crystalline matter. The equations express the balances of microforces and microenergy; the two phase fields are the order parameter and the chemical potential. The initial and boundary-value problem for the evolutionary system is known to be well posed. Convergence of the discrete scheme to the solution of the continuous problem is proved by a careful development of uniform estimates, by weak compactness and a suitable treatment of nonlinearities. Moreover, for the difference of discrete and continuous solutions we prove an error estimate of order one with respect to the time step. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, A continuous dependence result for a nonstandard system of phase field equations, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 37 (2014), pp. 1318--1324.
Abstract
The present note deals with a nonstandard systems of differential equations describing a two-species phase segregation. This system naturally arises in the asymptotic analysis carried out recently by the same authors, as the diffusion coefficient in the equation governing the evolution of the order parameter tends to zero. In particular, an existence result has been proved for the limit system in a very general framework. On the contrary, uniqueness was shown by assuming a constant mobility coefficient. Here, we generalize this result and prove a continuous dependence property in the case that the mobility coefficient suitably depends on the chemical potential. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, A vanishing diffusion limit in a nonstandard system of phase field equations, Evolution Equations and Control Theory, 3 (2014), pp. 257--275.
Abstract
We are concerned with a nonstandard phase field model of Cahn--Hilliard type. The model, which was introduced by Podio-Guidugli (Ric. Mat. 2006), describes two-species phase segregation and consists of a system of two highly nonlinearly coupled PDEs. It has been recently investigated by Colli, Gilardi, Podio-Guidugli, and Sprekels in a series of papers: see, in particular, SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2011, and Boll. Unione Mat. Ital. 2012. In the latter contribution, the authors can treat the very general case in which the diffusivity coefficient of the parabolic PDE is allowed to depend nonlinearly on both variables. In the same framework, this paper investigates the asymptotic limit of the solutions to the initial-boundary value problems as the diffusion coefficient $sigma$ in the equation governing the evolution of the order parameter tends to zero. We prove that such a limit actually exists and solves the limit problem, which couples a nonlinear PDE of parabolic type with an ODE accounting for the phase dynamics. In the case of a constant diffusivity, we are able to show uniqueness and to improve the regularity of the solution. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, On the Cahn--Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions and a dominating boundary potential, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 419 (2014), pp. 972--994.
Abstract
The Cahn--Hilliard and viscous Cahn--Hilliard equations with singular and possibly nonsmooth potentials and dynamic boundary condition are considered and some well-posedness and regularity results are proved. -
S. Melchionna, E. Rocca, On a nonlocal Cahn--Hilliard equation with a reaction term, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 24 (2014), pp. 461--497.
Abstract
We prove existence, uniqueness, regularity and separation properties for a nonlocal Cahn- Hilliard equation with a reaction term. We deal here with the case of logarithmic potential and degenerate mobility as well an uniformly lipschitz in u reaction term g(x, t, u). -
A. Miranville, E. Rocca, G. Schimperna, A. Segatti, The Penrose--Fife phase-field model with coupled dynamic boundary conditions, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 34 (2014), pp. 4259--4290.
-
W. Dreyer, J. Giesselmann, Ch. Kraus, A compressible mixture model with phase transition, Physica D. Nonlinear Phenomena, 273--274 (2014), pp. 1--13.
Abstract
We introduce a new thermodynamically consistent diffuse interface model of Allen-Cahn/Navier-Stokes type for multi-component flows with phase transitions and chemical reactions. For the introduced diffuse interface model, we investigate physically admissible sharp interface limits by matched asymptotic techniques. We consider two scaling regimes, i.e. a non-dissipative and a dissipative regime, where we recover in the sharp interface limit a generalized Allen-Cahn/Euler system for mixtures with chemical reactions in the bulk phases equipped with admissible interfacial conditions. The interfacial conditions satify, for instance, a Young-Laplace and a Stefan type law. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, An asymptotic analysis for a nonstandard Cahn--Hilliard system with viscosity, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 6 (2013), pp. 353--368.
Abstract
This paper is concerned with a diffusion model of phase-field type, consisting of a parabolic system of two partial differential equations, interpreted as balances of microforces and microenergy, for two unknowns: the problem's order parameter $rho$ and the chemical potential $mu$; each equation includes a viscosity term -- respectively, $varepsilon,partial_tmu$ and $delta,partial_trho$ -- with $varepsilon$ and $delta$ two positive parameters; the field equations are complemented by Neumann homogeneous boundary conditions and suitable initial conditions. In a recent paper [5], we proved that this problem is well-posed and investigated the long-time behavior of its $(varepsilon,delta)-$solutions. Here we discuss the asymptotic limit of the system as $eps$ tends to 0. We prove convergence of $(varepsilon,delta)-$solutions to the corresponding solutions for the case $eps$ =0, whose long-time behavior we characterize; in the proofs, we employ compactness and monotonicity arguments. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Global existence and uniqueness for a singular/degenerate Cahn--Hilliard system with viscosity, Journal of Differential Equations, 254 (2013), pp. 4217--4244.
Abstract
Existence and uniqueness are investigated for a nonlinear diffusion problem of phase-field type, consisting of a parabolic system of two partial differential equations, complemented by Neumann homogeneous boundary conditions and initial conditions. This system aims to model two-species phase segregation on an atomic [19]; in the balance equations of microforces and microenergy, the two unknowns are the order parameter $rho$ and the chemical potential $mu$. A simpler version of the same system has recently been discussed in [8]. In this paper, a fairly more general phase-field equation for $rho$ is coupled with a genuinely nonlinear diffusion equation for $mu$. The existence of a global-in-time solution is proved with the help of suitable a priori estimates. In the case of costant atom mobility, a new and rather unusual uniqueness proof is given, based on a suitable combination of variables. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Continuous dependence for a nonstandard Cahn--Hilliard system with nonlinear atom mobility, Rendiconti del Seminario Matematico. Universita e Politecnico Torino, 70 (2012), pp. 27--52.
Abstract
This note is concerned with a nonlinear diffusion problem of phase-field type, consisting of a parabolic system of two partial differential equations, complemented by Neumann homogeneous boundary conditions and initial conditions. The system arises from a model of two-species phase segregation on an atomic lattice [Podio-Guidugli 2006]; it consists of the balance equations of microforces and microenergy; the two unknowns are the order parameter $rho$ and the chemical potential $mu$. Some recent results obtained for this class of problems is reviewed and, in the case of a nonconstant and nonlinear atom mobility, uniqueness and continuous dependence on the initial data are shown with the help of a new line of argumentation developed in Colli/Gilardi/Podio-Guidugli/Sprekels 2012. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Distributed optimal control of a nonstandard system of phase field equations, Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics, 24 (2012), pp. 437--459.
Abstract
We investigate a distributed optimal control problem for a phase field model of Cahn-Hilliard type. The model describes two-species phase segregation on an atomic lattice under the presence of diffusion; it has been introduced recently in [4], on the basis of the theory developed in [15], and consists of a system of two highly nonlinearly coupled PDEs. For this reason, standard arguments of optimal control theory do not apply directly, although the control constraints and the cost functional are of standard type. We show that the problem admits a solution, and we derive the first-order necessary conditions of optimality. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Global existence for a strongly coupled Cahn--Hilliard system with viscosity, Bollettino della Unione Matematica Italiana. Serie 9, 5 (2012), pp. 495--513.
Abstract
An existence result is proved for a nonlinear diffusion problem of phase-field type, consisting of a parabolic system of two partial differential equations, complemented by Neumann homogeneous boundary conditions and initial conditions. This system is meant to model two-species phase segregation on an atomic lattice under the presence of diffusion. A similar system has been recently introduced and analyzed in [CGPS11]. Both systems conform to the general theory developed in [Pod06]: two parabolic PDEs, interpreted as balances of microforces and microenergy, are to be solved for the order parameter $rho$ and the chemical potential $mu$. In the system studied in this note, a phase-field equation in $rho$ fairly more general than in [CGPS11] is coupled with a highly nonlinear diffusion equation for $mu$, in which the conductivity coefficient is allowed to depend nonlinearly on both variables. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Analysis and optimal boundary control of a nonstandard system of phase field equations, Milan Journal of Mathematics, 80 (2012), pp. 119--149.
Abstract
We investigate a nonstandard phase field model of Cahn-Hilliard type. The model, which was introduced in Podio-Guidugli (2006), describes two-species phase segregation and consists of a system of two highly nonlinearly coupled PDEs. It has been studied recently in Colli, Gilardi, Podio-Guidugli, and Sprekels (2011a and b) for the case of homogeneous Neumann boundary conditions. In this paper, we investigate the case that the boundary condition for one of the unknowns of the system is of third kind and nonhomogeneous. For the resulting system, we show well-posedness, and we study optimal boundary control problems. Existence of optimal controls is shown, and the first-order necessary optimality conditions are derived. Owing to the strong nonlinear couplings in the PDE system, standard arguments of optimal control theory do not apply directly, although the control constraints and the cost functional will be of standard type. -
W. Dreyer, F. Duderstadt, M. Hantke, G. Warnecke, Bubbles in liquids with phase transition, Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics, 24 (2012), pp. 461--483.
Abstract
We consider a bubble of vapor and inert gas surrounded by the corresponding liquid phase. We study the behavior of the bubble due to phase change, i.e. condensation and evaporation, at the interface. Special attention is given to the effects of surface tension and heat production on the bubble dynamics as well as the propagation of acoustic elastic waves by including slight compressibility of the liquid phase. Separately we study the influence of the three phenomena heat conduction, elastic waves, and phase transition on the evolution of the bubble. The objective is to derive relations including the mass, momentum, and energy transfer between the phases. We find ordinary differential equations, in the cases of heat transfer and the emission of acoustic waves partial differential equations, that describe the bubble dynamics. From numerical evidence we deduce that the effect of phase transition and heat transfer on the behavior of the radius of the bubble is negligible. It turns out that the elastic waves in the liquid are of greatest importance to the dynamics of the bubble radius. The phase transition has a strong influence on the evolution of the temperature, in particular at the interface. Furthermore the phase transition leads to a drastic change of the water content in the bubble, so that a rebounding bubble is only possible, if it contains in addition an inert gas. In a forthcoming paper the equations derived are sought in order to close equations for multi-phase mixture balance laws for dispersed bubbles in liquids involving phase change. Also the model is used to make comparisons with experimental data on the oscillation of a laser induced bubble. For this case it was necessary to include the effect of an inert gas in the thermodynamic modeling of the phase transition. -
G. Aki, J. Daube, W. Dreyer, J. Giesselmann, M. Kränkel, Ch. Kraus, A diffuse interface model for quasi-incompressible flows: Sharp interface limits and numerics, ESAIM Proceedings, 38 (2012), pp. 54--77.
Abstract
In this contribution, we investigate a diffuse interface model for quasi-incompressible flows. We determine corresponding sharp interface limits of two different scalings. The sharp interface limit is deduced by matched asymptotic expansions of the fields in powers of the interface. In particular, we study solutions of the derived system of inner equations and discuss the results within the general setting of jump conditions for sharp interface models. Furthermore, we treat, as a subproblem, the convective Cahn-Hilliard equation numerically by a Local Discontinuous Galerkin scheme. -
S. Bartels, R. Müller, Error control for the approximation of Allen--Cahn and Cahn--Hilliard equations with a logarithmic potential, Numerische Mathematik, 119 (2011), pp. 409--435.
Abstract
A fully computable upper bound for the finite element approximation error of Allen-Cahn and Cahn-Hilliard equations with logarithmic potentials is derived. Numerical experiments show that for the sharp interface limit this bound is robust past topological changes. Modifications of the abstract results to derive quasi-optimal error estimates in different norms for lowest order finite element methods are discussed and lead to weaker conditions on the residuals under which the conditional error estimates hold. -
S. Bartels, R. Müller, Quasi-optimal and robust a posteriori error estimates in $L^infty(L^2)$ for the approximation of Allen--Cahn equations past singularities, Mathematics of Computation, 80 (2011), pp. 761--780.
Abstract
Optimal a posteriori error estimates in $L^infty(0,T;L^2(O))$ are derived for the finite element approximation of Allen-Cahn equations. The estimates depend on the inverse of a small parameter only in a low order polynomial and are valid past topological changes of the evolving interface. The error analysis employs an elliptic reconstruction of the approximate solution and applies to a large class of conforming, nonconforming, mixed, and discontinuous Galerkin methods. Numerical experiments illustrate the theoretical results. -
P. Colli, P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, A nonlocal quasilinear multi-phase system with nonconstant specific heat and heat conductivity, Journal of Differential Equations, 251 (2011), pp. 1354--1387.
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Well-posedness and long-time behavior for a nonstandard viscous Cahn--Hilliard system, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 71 (2011), pp. 1849--1870.
Abstract
We study a diffusion model of phase field type, consisting of a system of two partial differential equations encoding the balances of microforces and microenergy; the two unknowns are the order parameter and the chemical potential. By a careful development of uniform estimates and the deduction of certain useful boundedness properties, we prove existence and uniqueness of a global-in-time smooth solution to the associated initial/boundary-value problem; moreover, we give a description of the relative $omega$-limit set. -
K. Hermsdörfer, Ch. Kraus, D. Kröner, Interface conditions for limits of the Navier--Stokes--Korteweg model, Interfaces and Free Boundaries. Mathematical Analysis, Computation and Applications, 13 (2011), pp. 239--254.
Abstract
In this contribution we will study the behaviour of the pressure across phase boundaries in liquid-vapour flows. As mathematical model we will consider the static version of the Navier-Stokes-Korteweg model which belongs to the class of diffuse interface models. From this static equation a formula for the pressure jump across the phase interface can be derived. If we perform then the sharp interface limit we see that the resulting interface condition for the pressure seems to be inconsistent with classical results of hydrodynamics. Therefore we will present two approaches to recover the results of hydrodynamics in the sharp interface limit at least for special situations. -
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Phase separation in a gravity field, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems -- Series S, 4 (2011), pp. 391-407.
-
S. Bartels, R. Müller, A posteriori error controlled local resolution of evolving interfaces for generalized Cahn--Hilliard equations, Interfaces and Free Boundaries. Mathematical Analysis, Computation and Applications, 12 (2010), pp. 45--73.
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, A temperature-dependent phase segregation problem of the Allen--Cahn type, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 20 (2010), pp. 219-234.
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Existence and uniqueness of a global-in-time solution to a phase segregation problem of the Allen--Cahn type, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 20 (2010), pp. 519-541.
-
H. Garcke, Ch. Kraus, An anisotropic, inhomogeneous, elastically modified Gibbs--Thomson law as singular limit of a diffuse interface model, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 20 (2010), pp. 511--545.
Abstract
We consider the sharp interface limit of a diffuse phase field model with prescribed total mass taking into account a spatially inhomogeneous anisotropic interfacial energy and an elastic energy. The main aim is the derivation of a weak formulation of an anisotropic, inhomogeneous, elastically modified Gibbs-Thomson law in the sharp interface limit. To this end we show that one can pass to the limit in the weak formulation of the Euler-Lagrange equation of the diffuse phase field energy. -
W. Dreyer, Ch. Kraus, On the van der Waals--Cahn--Hilliard phase-field model and its equilibria conditions in the sharp interface limit, Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A. Mathematics, 140 A (2010), pp. 1161--1186.
Abstract
We study the equilibria of liquid--vapor phase transitions of a single substance at constant temperature and relate the sharp interface model of classical thermodynamics to a phase field model that determines the equilibria by the stationary van der Waals--Cahn--Hilliard theory.
For two reasons we reconsider this old problem. 1. Equilibria in a two phase system can be established either under fixed total volume of the system or under fixed external pressure. The latter case implies that the domain of the two--phase system varies. However, in the mathematical literature rigorous sharp interface limits of phase transitions are usually considered under fixed volume. This brings the necessity to extend the existing tools for rigorous sharp interface limits to changing domains since in nature most processes involving phase transitions run at constant pressure. 2. Thermodynamics provides for a single substance two jump conditions at the sharp interface, viz. the continuity of the specific Gibbs free energies of the adjacent phases and the discontinuity of the corresponding pressures, which is balanced by the mean curvature. The existing estimates for rigorous sharp interface limits show only the first condition. We identify the cause of this phenomenon and develop a strategy that yields both conditions up to the first order.
The necessary information on the equilibrium conditions are achieved by an asymptotic expansion of the density which is valid for an arbitrary double well potential. We establish this expansion by means of local energy estimates, uniform convergence results of the density and estimates on the Laplacian of the density. -
J. Sprekels, H. Wu, A note on parabolic equation with nonlinear dynamical boundary condition, Nonlinear Analysis. Theory, Methods & Applications. An International Multidisciplinary Journal. Series A: Theory and Methods, 72 (2010), pp. 3028--3048.
-
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, A bottle in a freezer, SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 41 (2009), pp. 1851-1873.
-
TH. Böhme, W. Dreyer, W.H. Müller, Determination of stiffness and higher gradient coefficients by means of the embedded atom method: An approach for binary alloys, Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics, 18 (2007), pp. 411--441.
-
P. Colli, P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Nonlinear evolution inclusions arising from phase change models, Czechoslovak Mathematical Journal, 57 (2007), pp. 1067-1098.
-
C. Lefter, J. Sprekels, Optimal boundary control of a phase field system modeling nonisothermal phase transitions, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 17 (2007), pp. 181-194.
-
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, A nonlocal phase-field model with nonconstant specific heat, Interfaces and Free Boundaries. Mathematical Analysis, Computation and Applications, 9 (2007), pp. 285--306.
-
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Nonlocal temperature-dependent phase-field models for non-isothermal phase transitions, Journal of the London Mathematical Society. Second Series, 76 (2007), pp. 197-210.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, Long time behaviour of a singular phase transition model, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 15 (2006), pp. 1119-1135.
-
W. Dreyer, B. Wagner, Sharp-interface model for eutectic alloys. Part I: Concentration dependent surface tension, Interfaces and Free Boundaries. Mathematical Analysis, Computation and Applications, 7 (2005), pp. 199--227.
-
J. Griepentrog, On the unique solvability of a nonlocal phase separation problem for multicomponent systems, Banach Center Publications, 66 (2004), pp. 153-164.
-
O. Klein, Asymptotic behaviour for a phase-field model with hysteresis in one-dimensional thermo-visco-plasticity, Applications of Mathematics, 49 (2004), pp. 309--341.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, Nonlocal phase-field models for non-isothermal phase transitions and hysteresis, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 14 (2004), pp. 593--612.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, U. Stefanelli, One-dimensional thermo-visco-plastic processes with hysteresis and phase transitions, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications, 13 (2003), pp. 695-712.
-
O. Klein, P. Krejčí, Outwards pointing hysteresis operators and asymptotic behaviour of evolution equations, Nonlinear Analysis. Real World Applications. An International Multidisciplinary Journal, 4 (2003), pp. 755--785.
-
O. Klein, C. Verdi, A posteriori error estimates for a time discrete scheme for a phase-field system of Penrose-Fife type, IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 23 (2003), pp. 55--80.
-
J. Sprekels, S. Zheng, Global existence and asymptotic behaviour for a nonlocal phase-field model for non-isothermal phase transitions, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 279 (2003), pp. 97-110.
-
E. Bonetti, P. Colli, W. Dreyer, G. Gilardi, G. Schimperna, J. Sprekels, On a model for phase separation in binary alloys driven by mechanical effects, Physica D. Nonlinear Phenomena, 165 (2002), pp. 48--65.
-
N. Kenmochi, J. Sprekels, Phase-field systems with vectorial order parameters including diffusional hysteresis effects, Communications on Pure and Applied Analysis, 1 (2002), pp. 495-511.
-
J. Sprekels, P. Krejčí, Phase-field systems for multi-dimensional Prandtl-Ishlinskii operators with non-polyhedral characteristics, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 25 (2002), pp. 309-325.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, S. Zheng, Asymptotic behaviour for a phase-field system with hysteresis, Journal of Differential Equations, 175 (2001), pp. 88--107.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, A hysteresis approach to phase-field models, Nonlinear Analysis. Theory, Methods & Applications. An International Multidisciplinary Journal. Series A: Theory and Methods, 39 (2000), pp. 569--586.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, Phase-field models with hysteresis, Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 252 (2000), pp. 198--219.
-
G. Gilardi, P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, Hysteresis in phase-field models with thermal memory, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 23 (2000), pp. 909--922.
-
W. Dreyer, W.H. Müller, A study of the coarsening in tin/lead solders, International Journal of Solids and Structures, 37 (2000), pp. 3841--3871.
-
W. Dreyer, W.H. Müller, Computer modeling of micromorphological change by phase field models: Applications to metals and ceramics, Journal of the Australasian Ceramic Society, 36 (2000), pp. 83--94.
 Contributions to Collected Editions
Contributions to Collected Editions
-
K. Hopf, Global existence analysis of energy-reaction-diffusion systems, in: Report 29: Variational Methods for Evolution (hybrid meeting), A. Mielke, M. Peletier, D. Slepcev, eds., 17 of Oberwolfach Reports, European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Zurich, 2021, pp. 1418--1421, DOI 10.4171/OWR/2020/29 .
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Nonlocal phase field models of viscous Cahn--Hilliard type, in: Topics in Applied Analysis and Optimisation, M. Hintermüller, J.F. Rodrigues, eds., CIM Series in Mathematical Sciences, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham, 2019, pp. 71--100, DOI 10.1007/978-3-030-33116-0 .
Abstract
A nonlocal phase field model of viscous Cahn--Hilliard type is considered. This model constitutes a nonlocal version of a model for two-species phase segregation on an atomic lattice under the presence of diffusion that has been studied in a series of papers by P. Podio-Guidugli and the present authors. The resulting system of differential equations consists of a highly nonlinear parabolic equation coupled to a nonlocal ordinary differential equation, which has singular terms that render the analysis difficult. Some results are presented on the well-posedness and stability of the system as well as on the distributed optimal control problem. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, J. Sprekels, Limiting problems for a nonstandard viscous Cahn--Hilliard system with dynamic boundary conditions, in: Proceedings of the INdAM-ISIMM Workshop on Trends on Applications of Mathematics to Mechanics, Rome, Italy, September 2016, E. Rocca, U. Stefanelli, L. Truskinovsky, A. Visintin, eds., 27 of Springer INdAM Series, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2018, pp. 217--242, DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-75940-1_11 .
Abstract
This note is concerned with a nonlinear diffusion problem of phase-field type, consisting of a parabolic system of two partial differential equations, complemented by boundary and initial conditions. The system arises from a model of two-species phase segregation on an atomic lattice and was introduced by Podio-Guidugli in Ric. Mat. 55 (2006), pp.105--118. The two unknowns are the phase parameter and the chemical potential. In contrast to previous investigations about this PDE system, we consider here a dynamic boundary condition for the phase variable that involves the Laplace-Beltrami operator and models an additional nonconserving phase transition occurring on the surface of the domain. We are interested to some asymptotic analysis and first discuss the asymptotic limit of the system as the viscosity coefficient of the order parameter equation tends to 0: the convergence of solutions to the corresponding solutions for the limit problem is proven. Then, we study the long-time behavior of the system for both problems, with positive or zero viscosity coefficient, and characterize the omega-limit set in both cases. -
P. Colli, J. Sprekels, Optimal boundary control of a nonstandard Cahn--Hilliard system with dynamic boundary condition and double obstacle inclusions, in: Solvability, Regularity, and Optimal Control of Boundary Value Problems for PDEs: In Honour of Prof. Gianni Gilardi, P. Colli, A. Favini, E. Rocca, G. Schimperna, J. Sprekels, eds., 22 of Springer INdAM Series, Springer International Publishing AG, Cham, 2017, pp. 151--182, DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-64489-9 .
Abstract
In this paper, we study an optimal boundary control problem for a model for phase separation taking place in a spatial domain that was introduced by P.Podio-Guidugli in Ric. Mat. 55 (2006), pp.105-118. The model consists of a strongly coupled system of nonlinear parabolic differential inclusions, in which products between the unknown functions and their time derivatives occur that are difficult to handle analytically; the system is complemented by initial and boundary conditions. For the order parameter of the phase separation process, a dynamic boundary condition involving the Laplace-Beltrami operator is assumed, which models an additional nonconserving phase transition occurring on the surface of the domain. We complement in this paper results that were established in the recent contribution appeared in Evol. Equ. Control Theory 6 (2017), pp. 35-58, by the two authors and Gianni Gilardi. In contrast to that paper, in which differentiable potentials of logarithmic type were considered, we investigate here the (more difficult) case of nondifferentiable potentials of double obstacle type. For such nonlinearities, the standard techniques of optimal control theory to establish the existence of Lagrange multipliers for the state constraints are known to fail. To overcome these difficulties, we employ the following line of approach: we use the results contained in the preprint arXiv:1609.07046 [math.AP] (2016), pp. 1-30, for the case of (differentiable) logarithmic potentials and perform a so-called "deep quench limit". Using compactness and monotonicity arguments, it is shown that this strategy leads to the desired first-order necessary optimality conditions for the case of (nondifferentiable) double obstacle potentials. -
A. Mielke, Free energy, free entropy, and a gradient structure for thermoplasticity, in: Innovative Numerical Approaches for Multi-Field and Multi-Scale Problems. In Honor of Michael Ortiz's 60th Birthday, K. Weinberg, A. Pandolfi, eds., 81 of Lecture Notes in Applied and Computational Mechanics, Springer International Publishing Switzerland, Cham, 2016, pp. 135--160.
Abstract
In the modeling of solids the free energy, the energy, and the entropy play a central role. We show that the free entropy, which is defined as the negative of the free energy divided by the temperature, is similarly important. The derivatives of the free energy are suitable thermodynamical driving forces for reversible (i.e. Hamiltonian) parts of the dynamics, while for the dissipative parts the derivatives of the free entropy are the correct driving forces. This difference does not matter for isothermal cases nor for local materials, but it is relevant in the non-isothermal case if the densities also depend on gradients, as is the case in gradient thermoplasticity.
Using the total entropy as a driving functional, we develop gradient structures for quasistatic thermoplasticity, which again features the role of the free entropy. The big advantage of the gradient structure is the possibility of deriving time-incremental minimization procedures, where the entropy-production potential minus the total entropy is minimized with respect to the internal variables and the temperature.
We also highlight that the usage of an auxiliary temperature as an integrating factor in Yang/Stainier/Ortiz "A variational formulation of the coupled thermomechanical boundary-value problem for general dissipative solids" (J. Mech. Physics Solids, 54, 401-424, 2006) serves exactly the purpose to transform the reversible driving forces, obtained from the free energy, into the needed irreversible driving forces, which should have been derived from the free entropy. This reconfirms the fact that only the usage of the free entropy as driving functional for dissipative processes allows us to derive a proper variational formulation. -
A. Mielke, Evolutionary relaxation of a two-phase model, in: Scales in Plasticity, Mini-Workshop, November 8--14, 2015, G.A. Francfort, S. Luckhaus, eds., 12 of Oberwolfach Reports, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, 2015, pp. 3027--3030.
-
D. Knees, R. Kornhuber, Ch. Kraus, A. Mielke, J. Sprekels, C3 -- Phase transformation and separation in solids, in: MATHEON -- Mathematics for Key Technologies, M. Grötschel, D. Hömberg, J. Sprekels, V. Mehrmann ET AL., eds., 1 of EMS Series in Industrial and Applied Mathematics, European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Zurich, 2014, pp. 189--203.
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Global solution to a phase transition problem of the Allen--Cahn type, in: Nonlinear Evolution Equations and Mathematical Modeling, Proceedings of the RIMS Symposium held at the Research Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Kyoto University, October 20--23, 2009, T. Aiki, ed., 1693 of Sūrikaisekikenkyūsho Kōkyūroku, Kyoto, 2010, pp. 104-110.
-
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Liquid-solid phase transitions in a deformable container, in: Continuous Media with Microstructure, B. Albers, ed., Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 2010, pp. 285-300.
-
O. Klein, P. Krejčí, Asymptotic behaviour of evolution equations involving outwards pointing hysteresis operators, in: Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Hysteresis and Micromagnetic Modeling, Salamanca, Spain, 28--30 May 2003, L. Lopez-Dias, L. Torres, O. Alejos, eds., 343 of Physica B: Condensed Matter, Elsevier B.V., 2004, pp. 53-58.
-
P. Krejčí, J. Sprekels, Phase-field systems and vector hysteresis operators, in: Free Boundary Problems: Theory and Applications II, N. Kenmochi, ed., 14 of Gakuto Int. Series Math. Sci. & Appl., Gakkōtosho, Tokyo, 2000, pp. 295--310.
 Preprints, Reports, Technical Reports
Preprints, Reports, Technical Reports
-
S. Zendehroud, O. Kleinjung, P. Loche, L. Bocquet, R.R. Netz, E. Ipocoana, D. Peschka, M. Thomas, Combined effects of evaporation, sedimentation and solute crystallization on the dynamics of aerosol size distributions on multiple length and time scales, Preprint no. 3256, WIAS, Berlin, 2026, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3256 .
Abstract, PDF (1975 kByte)
We investigate three aspects of aerosol-mediated air-borne viral infection mechanisms on different length and time scales. First, we address the evolution of the size distribution of a non-interacting ensemble of droplets that are subject to evaporation and sedimentation using a sharp droplet-air interface model. From the exact solution of the evolution equation we derive the viral load in the air and show that it depends sensitively on the relative humidity. Secondly, from Molecular Dynamics simulations we extract the molecular reflection coefficient of single water molecules from the air-water interface. This parameter determines the water condensation and evaporation rate at a liquid droplet surface and therefore the evaporation rate of aqueous droplets. We find the reflection of water to be negligible at room temperature but to rise significantly at elevated temperatures and for grazing incidence angles. Thirdly, we derive a thermodynamically consistent three-dimensional diffuse-interface model for solute-containing droplets that is formulated as a three-phase Cahn--Hilliard/Allen--Cahn system. By numerically solving the coupled system of equations, we explore representative scenarios that show that this model reproduces and generalizes features of the sharp-interface model. These interconnected studies on the dynamics of aerosol droplet evaporation are relevant in order to quantitatively assess the airborne infection risk under varying environmental conditions. -
M. Heida, M. Landstorfer, Modeling of porous battery Electrodes with multiple phase transitions -- Part I: Modeling and homogenization, Preprint no. 3251, WIAS, Berlin, 2025, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3251 .
Abstract, PDF (1108 kByte)
We derive a thermodynamically consistent multiscale model for a porous intercalation battery in a half-cell configuration. Starting from microscopically resolved balance equations, the model rigorously couples cation and anion transport in the electrolyte with electron transport and solid- state diffusion in the active material through intercalation reactions. The derivation is based on non-equilibrium thermodynamics and periodic homogenization. The central novelty of this work lies in the systematic incorporation of multi-well free energy functions for intercalated cations into a homogenized DFN-type porous-electrode framework. This modeling choice leads to non-monotonic chemical potentials and enables a macroscopic descrip- tion of phase separation and multiple phase transitions within the electrode. While multi-well free energies are well established at the particle scale, their integration into homogenized porous- electrode models has so far been lacking. By extending the homogenization framework to include Cahn--Hilliard-type regularizations, phase-transition effects are retained at the electrode level. The resulting model exhibits an intrinsically coupled 3D+3D structure, in which macroscopic transport in the electrolyte is coupled to fully resolved microscopic diffusion within active parti- cles. This coupling naturally induces memory effects and time lags in the macroscopic voltage response, which cannot be captured by reduced single-scale models. Although the microscopic dynamics possess an underlying gradient-flow structure, we adopt a formal asymptotic approach to obtain a tractable DFN-type model suitable for practical simulations. This paper constitutes Part I of a three-part series and is devoted to the systematic derivation and mathematical formulation of the model. Numerical analysis, discretization strategies, simula- tion studies of transient cycling behavior, and experimental validation are deferred to Parts II and III. Part II focuses on finite C-rates, while Part III addresses open-circuit voltage conditions, where the predictive capabilities of the framework are investigated in detail. -
P. Colli, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, On the hyperbolic relaxation of the chemical potential in a phase field tumor growth model, Preprint no. 3234, WIAS, Berlin, 2025, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3234 .
Abstract, PDF (307 kByte)
In this paper, we study a phase field model for a tumor growth model of Cahn--Hilliard type in which the often assumed parabolic relaxation of the chemical potential is replaced by a hyperbolic one. We show that the resulting initial-boundary value problem is well posed and that its solutions depend continuously on two given functions: one appearing in the mass balance equation and one in the nutrient equation, representing, respectively, sources of drugs (e.g. chemotherapy) and antiangiogenic therapy. We also discuss regularity properties of the solutions. Moreover, in the case of a constant proliferation function, we rigorously analyze the asymptotic behavior as the coefficient of the inertial term tends to zero, establishing convergence to the corresponding viscous Cahn--Hilliard tumor growth model. Our results apply to a broad class of double-well potentials, including nonsmooth ones. -
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, A. Signori, J. Sprekels, On Brinkman flows with curvature-induced phase separation in binary mixtures, Preprint no. 3218, WIAS, Berlin, 2025, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3218 .
Abstract, PDF (333 kByte)
The mathematical analysis of diffuse-interface models for multiphase flows has attracted significant attention due to their ability to capture complex interfacial dynamics, including curvature effects, within a unified, energetically consistent framework. In this work, we study a novel Brinkman--Cahn--Hilliard system, coupling a sixth-order phase-field evolution with a Brinkman-type momentum equation featuring variable shear viscosity. The Cahn--Hilliard equation includes a nonconservative source term accounting for mass exchange, and the velocity equation contains a non divergence-free forcing term. We establish the existence of weak solutions in a divergence-free variational framework, and, in the case of constant mobility and shear viscosity, prove uniqueness and continuous dependence on the forcing. Additionally, we analyze the Darcy limit, providing existence results for the corresponding reduced system. -
M.I. Gau, K. Hopf, Well-posedness and relaxation in a simplified model for viscoelastic phase separation via Hilbertian gradient flows, Preprint no. 3212, WIAS, Berlin, 2025, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3212 .
Abstract, PDF (481 kByte)
This article is concerned with a gradient-flow approach to a Cahn--Hilliard model for viscoelastic phase separation introduced by Zhou et al. (Phys. Rev. E, 2006) in its variant with constant mobility. By means of time-incremental minimisation and generalised contractivity estimates, we establish the global well-posedness of the Cauchy problem for moderately regular initial data. For general finite-energy data we obtain the existence of gradient-flow solutions and a stability estimate of weak--strong type. We further study the asymptotic behaviour for relaxation time and bulk modulus depending on a small parameter. Depending on the scaling, we recover the Cahn--Hilliard, the mass-conserving Allen--Cahn or the viscous Cahn--Hilliard equation. A challenge in the well-posedness analysis is the failure of semiconvexity of the appropriate driving functional, which is caused by a phase-dependence of the bulk modulus. -
K. Hopf, J. King, A. Münch, B. Wagner, Interface dynamics in a degenerate Cahn--Hilliard model for viscoelastic phase separation, Preprint no. 3149, WIAS, Berlin, 2024, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3149 .
Abstract, PDF (474 kByte)
The formal sharp-interface asymptotics in a degenerate Cahn--Hilliard model for viscoelastic phase separation with cross-diffusive coupling to a bulk stress variable are shown to lead to non-local lower-order counterparts of the classical surface diffusion flow. The diffuse-interface model is a variant of the Zhou--Zhang--E model and has an Onsager gradient-flow structure with a rank-deficient mobility matrix reflecting the ODE character of stress relaxation. In the case of constant coupling, we find that the evolution of the zero level set of the order parameter approximates the so-called intermediate surface diffusion flow. For non-constant coupling functions monotonically connecting the two phases, our asymptotic analysis leads to a family of third order whose propagation operator behaves like the square root of the minus Laplace--Beltrami operator at leading order. In this case, the normal velocity of the moving sharp interface arises as the Lagrange multiplier in a constrained elliptic equation, which is at the core of our derivation. The constrained elliptic problem can be solved rigorously by a variational argument, and is shown to encode the gradient structure of the effective geometric evolution law. The asymptotics are presented for deep quench, an intermediate free boundary problem based on the double-obstacle potential. -
M. Heida, A. Sikorski, M. Weber, Consistency and order 1 convergence of cell-centered finite volume discretizations of degenerate elliptic problems in any space dimension, Preprint no. 2913, WIAS, Berlin, 2022, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2913 .
Abstract, PDF (601 kByte)
We study consistency of cell-centered finite difference methods for elliptic equations with degenerate coefficients in any space dimension $dgeq2$. This results in order of convergence estimates in the natural weighted energy norm and in the weighted discrete $L^2$-norm on admissible meshes. The cells of meshes under consideration may be very irregular in size. We particularly allow the size of certain cells to remain bounded from below even in the asymptotic limit. For uniform meshes we show that the order of convergence is at least 1 in the energy semi-norm, provided the discrete and continuous solutions exist and the continuous solution has $H^2$ regularity. -
M.G. Hennessy, G.L. Celora, A. Münch, S.L. Waters, B. Wagner, Asymptotic study of the electric double layer at the interface of a polyelectrolyte gel and solvent bath, Preprint no. 2751, WIAS, Berlin, 2020, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2751 .
Abstract, PDF (2265 kByte)
An asymptotic framework is developed to study electric double layers that form at the inter-face between a solvent bath and a polyelectrolyte gel that can undergo phase separation. The kinetic model for the gel accounts for the finite strain of polyelectrolyte chains, free energy ofinternal interfaces, and Stefan?Maxwell diffusion. By assuming that the thickness of the doublelayer is small compared to the typical size of the gel, matched asymptotic expansions are used toderive electroneutral models with consistent jump conditions across the gel-bath interface in two-dimensional plane-strain as well as fully three-dimensional settings. The asymptotic frameworkis then applied to cylindrical gels that undergo volume phase transitions. The analysis indicatesthat Maxwell stresses are responsible for generating large compressive hoop stresses in the double layer of the gel when it is in the collapsed state, potentially leading to localised mechanicalinstabilities that cannot occur when the gel is in the swollen state. When the energy cost of in-ternal interfaces is sufficiently weak, a sharp transition between electrically neutral and chargedregions of the gel can occur. This transition truncates the double layer and causes it to have finitethickness. Moreover, phase separation within the double layer can occur. Both of these featuresare suppressed if the energy cost of internal interfaces is sufficiently high. Thus, interfacial freeenergy plays a critical role in controlling the structure of the double layer in the gel. -
G.L. Celora, M.G. Hennessy, A. Münch, S.L. Waters, B. Wagner, Spinodal decomposition and collapse of a polyelectrolyte gel, Preprint no. 2731, WIAS, Berlin, 2020, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2731 .
Abstract, PDF (2259 kByte)
The collapse of a polyelectrolyte gel in a (monovalent) salt solution is analysed using a new model that includes interfacial gradient energy to account for phase separation in the gel, finite elasticity and multicomponent transport. We carry out a linear stability analysis to determine the stable and unstable spatially homogeneous equilibrium states and how they phase separate into localized regions that eventually coarsen to a new stable state. We then investigate the problem of a collapsing gel as a response to increasing the salt concentration in the bath. A phase space analysis reveals that the collapse is obtained by a front moving through the gel that eventually ends in a new stable equilibrium. For some parameter ranges, these two routes to gel shrinking occur together. -
V. Barbu, P. Colli, G. Gilardi, G. Marinoschi, E. Rocca, Sliding modes for a phase-field system, Preprint no. 2133, WIAS, Berlin, 2015, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.2133 .
Abstract, PDF (295 kByte)
In the present contribution the sliding mode control (SMC) problem for a phase-field model of Caginalp type is considered. First we prove the well-posedness and some regularity results for the phase-field type state systems modified by the state- feedback control laws. Then, we show that the chosen SMC laws force the system to reach within finite time the sliding manifold (that we chose in order that one of the physical variables or a combination of them remains constant in time). We study three different types of feedback control laws: the first one appears in the internal energy balance and forces a linear combination of the temperature and the phase to reach a given (space dependent) value, while the second and third ones are added in the phase relation and lead the phase onto a prescribed target $phi^*$. While the control law is non-local in space for the first two problems, it is local in the third one, i.e., its value at any point and any time just depends on the value of the state. -
W. Dreyer, J. Giesselmann, Ch. Kraus, Modeling of compressible electrolytes with phase transition, Preprint no. 1955, WIAS, Berlin, 2014, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1955 .
Abstract, PDF (457 kByte)
A novel thermodynamically consistent diffuse interface model is derived for compressible electrolytes with phase transitions. The fluid mixtures may consist of N constituents with the phases liquid and vapor, where both phases may coexist. In addition, all constituents may consist of polarizable and magnetizable matter. Our introduced thermodynamically consistent diffuse interface model may be regarded as a generalized model of Allen-Cahn/Navier-Stokes/Poisson type for multi-component flows with phase transitions and electrochemical reactions. For the introduced diffuse interface model, we investigate physically admissible sharp interface limits by matched asymptotic techniques. We consider two scaling regimes, i.e. a non-coupled and a coupled regime, where the coupling takes place between the smallness parameter in the Poisson equation and the width of the interface. We recover in the sharp interface limit a generalized Allen-Cahn/Euler/Poisson system for mixtures with electrochemical reactions in the bulk phases equipped with admissible interfacial conditions. The interfacial conditions satisfy, for instance, a generalized Gibbs-Thomson law and a dynamic Young-Laplace law. -
J.A. Griepentrog, On regularity, positivity and long-time behavior of solutions to an evolution system of nonlocally interacting particles, Preprint no. 1932, WIAS, Berlin, 2014, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1932 .
Abstract, PDF (1279 kByte)
An analytical model for multicomponent systems of nonlocally interacting particles is presented. Its derivation is based on the principle of minimization of free energy under the constraint of conservation of particle number and justified by methods established in statistical mechanics. In contrast to the classical Cahn-Hilliard theory with higher order terms, the nonlocal theory leads to an evolution system of second order parabolic equations for the particle densities, weakly coupled by nonlinear and nonlocal drift terms, and state equations which involve both chemical and interaction potential differences. Applying fixed-point arguments and comparison principles we prove the existence of variational solutions in suitable Hilbert spaces for evolution systems. Moreover, using maximal regularity for nonsmooth parabolic boundary value problems in Sobolev-Morrey spaces and comparison principles, we show uniqueness, global regularity and uniform positivity of solutions under minimal assumptions on the regularity of interaction. Applying a refined version of the Łojasiewicz-Simon gradient inequality, this paves the way to the convergence of solutions to equilibrium states. We conclude our considerations with the presentation of simulation results for a phase separation process in ternary systems. -
W. Dreyer, F. Duderstadt, S.-J. Kimmerle, A study on the eigenstrain problem in solid mixtures, Preprint no. 1311, WIAS, Berlin, 2008, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1311 .
Abstract
We introduce a framework that is capable to model the appearance of mechanical stresses due to inelastic deformations. Among these we consider in particular thermal expansions, diffusion and phase transitions. Among the quantities of central importance are the eigenstrain and the misfit strain. They describe the phenomenon that different material volumes of a compact body may not be compatible to each other in a stress-free reference configuration, so that here a compact body may not exist. We shall show that it is possible to find a further reference configuration, where the body is compact but not free of stress. A typical example where misfit appears concerns a body whose local parts differently transform their phase. This might be a change of the crystal lattice from the ferrite to the austenite symmetry in steel, or the formation of liquid droplets in crystalline gallium arsenide. In both cases the new interior phase has with respect to the parent phase different volume or shape in its state that is free of stress. In this study we consider the eigenstrain problem for pure substances as well as for mixtures. In the latter case subtle arguments are needed for an appropriate description. Special focus is given to the equivalence of interface boundaries with discontinues and continues displacement vectors. -
W. Dreyer, D. Hömberg, Th. Petzold, A model for the austenite-ferrite phase transition in steel including misfit stress, Preprint no. 1310, WIAS, Berlin, 2008, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1310 .
Abstract, Postscript (730 kByte), PDF (445 kByte)
We present a thermodynamically consistent model to describe the austenite-ferrite phase transition in steel. We consider the influence of the mechanical displacement field due to eigenstrains caused by volumetric expansion. The model equations are derived in a systematical framework. They are based on the conservation laws for mass and momentum and the second law of thermodynamics. By means of numerical computations for a simplified interface controlled model, we examine the influence of the mechanical contributions to the transformation kinetics and the equilibrium states. -
TH. Böhme, W. Dreyer, F. Duderstadt, W.H. Müller, A higher gradient theory of mixtures for multi-component materials with numerical examples for binary alloys, Preprint no. 1286, WIAS, Berlin, 2007, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1286 .
Abstract, Postscript (15 MByte), PDF (2182 kByte)
A theory of mixture for multi-component materials is presented based on a novel, straightforward method for the exploitation of the Second Law of thermodynamics. In particular the constitutive equations for entropy, heat and diffusion flux as well as the stress tensor are formulated as a consequence of the non-negative entropy production. Furthermore we derive the established Gibbs equation as well as the Gibbs Duhem relation which also follow from the formalism. Moreover, it is illustrated, how local mechanical strains due to eigenstrains or external loadings, modify the free energy and, consequently, change the chemical potentials of the components. All consecutive steps are illustrated, first, for simple mixtures and, second, for a system containing two different phases. So-called higher gradients of the concentrations are considered, which take the nonuniform composition into account. It will also become apparent that more/other variables of modified/different physical pr oblems beyond the illustrated ones can be easily treated within the presented framework. This work ends with the specification to binary alloys and with the presentation of various numerical simulations. -
W. Dreyer, M. Gaberšček, J. Jamnik, Phase transition and hysteresis in a rechargeable lithium battery, Preprint no. 1284, WIAS, Berlin, 2007, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1284 .
Abstract, Postscript (3236 kByte), PDF (740 kByte)
We represent a model which describes the evolution of a phase transition that occurs in some part of a rechargeable lithium battery during the process of charging/discharging. The model is capable to simulate the hysteretic behavior of the voltage - charge characteristics. During discharging of the battery, the interstitial lattice sites of a small crystalline host system are filled up with lithium atoms and these are released again during charging. We show within the context of a sharp interface model that two mechanical phenomena go along with a phase transition that appears in the host system during supply and removal of lithium. At first the lithium atoms need more space than it is available by the interstitial lattice sites, which leads to a maximal relative change of the crystal volume of about $6%$. Furthermore there is an interface between two adjacent phases that has very large curvature of the order of magnitude 100 m, which evoke here a discontinuity of the normal component of the stress. In order to simulate the dynamics of the phase transitions and in particular the observed hysteresis we establish a new initial and boundary value problem for a nonlinear PDE system that can be reduced in some limiting case to an ODE system. -
W. Dreyer, Ch. Kraus, The equilibria of vapour-liquid systems revisited, Preprint no. 1238, WIAS, Berlin, 2007, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.1238 .
Abstract, Postscript (3894 kByte), PDF (624 kByte)
We study equilibrium conditions of liquid-vapour phase transitions for a single substance at constant temperature. The phase transitions are modelled by a classical sharp interface model with boundary contact energy. We revisit this old problem mainly for the following reasons. Equilibria in a two-phase system can be established either under fixed external pressure or under fixed total volume. These two different settings lead to distinct equilibria, a fact that is usually ignored in the literature. In nature and in most technical processes, the approach of a two-phase system to equilibrium runs at constant pressure, whereas mathematicians prefer to study processes in constant domains, i.e. at constant volume. Furthermore, in the literature the sharp interface of the liquid and the vapour phase is usually described by a surface with high symmetry like a plane interface or a radially symmetric interface which has the shape of the boundary of a ball. In this paper we establish equilibrium conditions for pressure control as well as for volume control with arbitrary shapes of the interface. The results are derived by methods of differential geometry. Further, the common features and differences of pressure and volume control are worked out for some simple cases.
 Talks, Poster
Talks, Poster
-
A. Erhardt, Nonlinear dynamics of complex biophysical processes, Berliner Oberseminar 'Nichtlineare partielle Differentialgleichungen' (Langenbach-Seminar), WIAS, January 7, 2026.
-
CH. Pohl, Modeling of solid-electrolyte interphase growth with non-equilibrium thermodynamics, 248th ECS Meeting, Session 'Electrolytes & Interfaces in Li-ion Batteries and Beyond', Chicago, USA, October 12 - 16, 2025.
-
A. Maltsi, Modeling thermoporoelasticity in photoacoustics, 19th Panhellenic Conference in Mathematical Analysis, December 18 - 20, 2025, National Technical University of Athens, Greece, December 19, 2025.
-
M.I. Gau, Gradient structures of viscoelastic phase separation, Gradient Flows Face-to-Face 5, September 16 - 19, 2025, Universidad de Granada, Spain, September 18, 2025.
-
M.I. Gau, Viscoelastic phase separation: Well-posedness and singular limit to viscous Cahn--Hilliard equation, 24th GAMM Seminar on Microstructures, January 30 - 31, 2025, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, January 30, 2025.
-
M.I. Gau, Viscoelastic phase separation: Well-posedness and singular limit to viscous Cahn--Hilliard equation, 95th Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM 2025), Section 14.05 ``Applied Analysis'', April 7 - 11, 2025, Poznan University of Technology, Poland, April 10, 2025.
-
R. Lasarzik, Weak solutions and weak-strong uniqueness for a Cahn--Hilliard--type model with chemotaxis, Workshop ``Free Boundaries and Growth'', December 9 - 12, 2025, Erwin Schrödinger International Institute for Mathematics and Physics, Wien, Austria, December 11, 2025.
-
B. Wagner, Dynamics of cellular patterns on hydrogel sheets, University of Oxford, Mathematical Institute, UK, November 22, 2024.
-
L. Schmeller, Gradient flows and moving contact lines, Seminar Prof. Sebastian Aland, Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg, Institut für Numerische Mathematik und Optimierung, February 8, 2023.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of multiphase fluids and droplets (online talk), Workshop ``Control Methods in Hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations'' (Hybrid Event), November 5 - 10, 2023, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, November 7, 2023.
-
L. Schmeller, K. Remini, Equilibrium droplets between experiment and theoretical predictions, SPP 2171 Workshop ``Wetting of Flexible, Adaptive, and Switchable Substrates'', December 5 - 8, 2022, Tagungszentrum an der Sternwarte, Göttingen, December 7, 2022.
-
L. Schmeller, Multi-phase dynamic systems at finite strain elasticity, Summer School: Mathematical Models for Bio-Medical Sciences, Lake Como, Italy, June 20 - 24, 2022.
-
L. Schmeller, Multiphase systems coupled with large deformations, MathBio22 -- Mathematical Models for Biological Multiscale Systems, September 12 - 14, 2022, WIAS Berlin, September 14, 2022.
-
L. Schmeller, Multiphase systems coupled with large deformations, Seminar ``Interfaces: Modeling, Analysis, Numerics'', November 21 - 25, 2022, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, November 21, 2022.
-
P. Pelech, Penrose--Fife model with activated phase transformation - existence and effective model for slowloading regimes, 92th Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM 2022), Session 08 ``Multiscales and Homogenization'', August 15 - 19, 2022, Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, August 18, 2022.
-
P. Vágner, Capacitance of the blocking YSZ I Au electrode, 18th Symposium on Modeling and Experimental Validation of Electrochemical Energy Technologies, March 14 - 16, 2022, DLR Institut für Technische Thermodynamik, Hohenkammer, March 16, 2022.
-
TH. Eiter, On the resolvent problems associated with rotating viscous flow, DMV Annual Meeting 2022, Section 09 ``Applied Analysis and Partial Differential Equations", September 12 - 16, 2022, Freie Universität Berlin, September 14, 2022.
-
TH. Eiter, On uniform resolvent estimates associated with time-periodic rotating viscous flow, Mathematical Fluid Mechanics in 2022 (Hybrid Event), August 22 - 26, 2022, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czech Republic, August 24, 2022.
-
A. Mielke, Existence and longtime behavior of solutions to a degenerate parabolic system, Journées Équations aux Dérivées Partielles 2022, May 30 - June 3, 2022, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Obernai, France, May 31, 2022.
-
K. Hopf, Global existence analysis of energy-reaction-diffusion systems, Workshop ``Variational Methods for Evolution'', September 13 - 19, 2020, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, September 15, 2020.
-
A. Mielke, On finite-strain thermo-viscoelasticity, Mechanics of Materials: Towards Predictive Methods for Kinetics in Plasticity, Fracture, and Damage, March 8 - 14, 2020, Mathematisches Forschungszentrum Oberwolfach, March 12, 2020.
-
D. Peschka, Gradient structures for flows of concentrated suspensions - jamming and free boundaries, 90th Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM 2019), Section S11 ``Interfacial Flows", February 18 - 22, 2019, Technische Universität Wien, Austria, February 20, 2019.
-
B. Wagner, S. Reber, J. Iglesias, A. Fritsch, E. Meca, Hierarchical spindle assembly: Sequence-dependent energy landscapes for a cytoplasmic condensate, Kick-Off Meeting DFG SPP 2191 ``Molecular Mechanisms of Functional Phase Separation'', Heidelberg, June 6 - 7, 2019.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of multiphase fluids and droplets, Colloquium of the Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, UK, June 7, 2019.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of multiphase fluids and droplets, Polish Academy of Sciences, Systems Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland, December 3, 2019.
-
J. Sprekels, Cahn--Hilliard systems with general fractional-order operators, Workshop ``Special Materials and Complex Systems'' (SMACS 2018), June 18 - 22, 2018, University of Milan/University of Pavia, Gargnano, Italy, June 22, 2018.
-
M. Thomas, Analysis and simulation for a phase-field fracture model at finite strains based on modified invariants, Workshop ``Special Materials and Complex Systems'' (SMACS 2018), June 18 - 22, 2018, University of Milan/University of Pavia, Gargnano, Italy, June 18, 2018.
-
M. Thomas, Reliable error estimates for phase-field models of brittle fracture, MATH+ Center Days 2018, October 31 - November 2, 2018, Zuse-Institut Berlin (ZIB), Berlin, October 31, 2018.
-
M. Hintermüller, Nonsmooth structures in PDE constrained optimization, Mathematisches Kolloquium, Universität Bielefeld, Fakultät für Mathematik, June 7, 2018.
-
T. Keil, Simulation and control of a nonsmooth Cahn--Hilliard Navier--Stokes system with variable fluid densities (with Carmen Graessle), Annual Meeting of the DFG Priority Programme 1962, October 9 - 11, 2017, Kremmen (Sommerfeld), October 11, 2017.
-
T. Keil, Strong stationarity conditions for the optimal control of a Cahn--Hilliard--Navier--Stokes system, 14th International Conference on Free Boundary Problems: Theory and Applications, Theme Session 8 ``Optimization and Control of Interfaces'', July 9 - 14, 2017, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, July 10, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Adaptive finite element solvers for MPECs in function space, SIAM Conference on Optimization, Minisymposium MS122 ``Recent Trends in PDE-Constrained Optimization'', May 22 - 25, 2017, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, May 25, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Non-smooth structures in PDE-constrained optimization, Mathematisches Kolloquium, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Fakultät für Mathematik, Essen, January 11, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of multiphase fluids and droplets, Kolloquium, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Department Mathematik, Erlangen, May 2, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of nonsmooth phase-field models, DFG-AIMS Workshop on ``Shape Optimization, Homogenization and Control'', March 13 - 16, 2017, Mbour, Senegal, March 14, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Recent trends in PDE-constrained optimization with non-smooth structures, Fourth Conference on Numerical Analysis and Optimization (NAOIV-2017), January 2 - 5, 2017, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman, January 4, 2017.
-
M. Thomas, From adhesive contact to brittle delamination in visco-elastodynamics, ERC Workshop on Modeling Materials and Fluids using Variational Methods, February 22 - 26, 2016, WIAS Berlin, Berlin, February 26, 2016.
-
M. Thomas, Rate-independent evolution of sets, INdAM-ISIMM Workshop on Trends on Applications of Mathematics to Mechanics, September 5 - 8, 2016, The International Society for the Interaction of Mechanics and Mathematics (ISIMM), Rome, Italy, September 6, 2016.
-
S.P. Frigeri, On a diffuse interface model of tumor growth, 9th European Conference on Elliptic and Parabolic Problems, May 23 - 27, 2016, University of Zurich, Institute of Mathematics, Gaeta, Italy, May 23, 2016.
-
E. Rocca, Optimal control of a nonlocal convective Cahn--Hilliard equation by the velocity, Numerical Analysis Seminars, Durham University, UK, March 13, 2015.
-
S.P. Frigeri, On a diffuse interface model of tumor growth, INdAM Workshop ``Special Materials in Complex Systems -- SMaCS 2015'', May 18 - 22, 2015, Rome, Italy, May 22, 2015.
-
S.P. Frigeri, On a nonlocal diffuse interface model for binary incompressible fluids with different densities, Mathematical Thermodynamics of Complex Fluids, June 28 - July 3, 2015, Fondazione CIME ``Roberto Conti'' (International Mathematical Summer Center), Cetraro, Italy, July 2, 2015.
-
S.P. Frigeri, Recent results on optimal control for Cahn--Hilliard/Navier--Stokes systems with nonlocal interactions, Control Theory and Related Topics, April 13 - 14, 2015, Politecnico di Milano, Italy, April 13, 2015.
-
CH. Heinemann, Damage processes in thermoviscoelastic materials with damage-dependent thermal expansion coefficients, 3rd Workshop of the GAMM Activity Group Analysis of Partial differential Equations, September 30 - October 2, 2015, Universität Kassel, Institut für Mathematik, October 1, 2015.
-
CH. Heinemann, On elastic Cahn--Hilliard systems coupled with evolution inclusions for damage processes, 86th Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM 2015), Young Researchers' Minisymposium 2, March 23 - 27, 2015, Lecce, Italy, March 23, 2015.
-
CH. Heinemann, Solvability of differential inclusions describing damage processes and applications to optimal control problems, Universität Essen-Duisburg, Fakultät für Mathematik, Essen, December 3, 2015.
-
J. Sprekels, Optimal boundary control problems for Cahn--Hilliard systems with dynamic boundary conditions, INdAM Workshop ``Special Materials in Complex Systems -- SMaCS 2015'', May 18 - 22, 2015, Rome, Italy, May 21, 2015.
-
M. Thomas, Rate-independent damage models with spatial BV-regularization --- Existence & fine properties of solutions, Oberseminar ``Angewandte Analysis'', Universität Freiburg, Abteilung für Angewandte Mathematik, Freiburg, February 10, 2015.
-
M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, A deep quench approach to the optimal control of an Allen--Cahn equation with dynamic boundary conditions, National Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Division of Computational Mathematics, Daejeon, Korea (Republic of), May 20, 2015.
-
M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, Multi-material phase field approach to structural topology optimization and its relation to sharp interface approach, University of Tokyo, Graduate School of Mathematical Sciences, Japan, October 6, 2015.
-
M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, Relating phase field and sharp interface approaches to structural topology optimization, National Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Division of Computational Mathematics, Daejeon, Korea (Republic of), May 13, 2015.
-
M.H. Farshbaf Shaker, Relating phase field and sharp interface approaches to structural topology optimization, Technische Universität Berlin, Institut für Mathematik, February 5, 2015.
-
CH. Heinemann, Well-posedness of strong solutions for a damage model in 2D, Universitá di Brescia, Department DICATAM -- Section of Mathematics, Italy, March 13, 2015.
-
A. Mielke, Evolutionary relaxation of a two-phase model, Mini-Workshop ``Scales in Plasticity'', November 8 - 14, 2015, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, November 11, 2015.
-
J. Sprekels, Optimal boundary control problems for Cahn--Hilliard systems with singular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions, Romanian Academy, Simeon Stoilow Institute of Mathematics, Bucharest, March 18, 2015.
-
E. Rocca, ``Entropic'' solutions to a thermodynamically consistent PDE system for phase transitions and damage, Symposium on Trends in Application of Mathematics to Mechanics (STAMM), September 8 - 11, 2014, International Society for the Interaction of Mechanics and Mathematics (ISIMM), Poitiers, France, September 9, 2014.
-
CH. Heinemann, Analysis of degenerating Cahn--Hilliard systems coupled with complete damage processes, 2013 CNA Summer School, Center for Nonlinear Analysis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, USA, May 30 - June 7, 2013.
-
CH. Heinemann, Degenerating Cahn--Hilliard systems coupled with complete damage processes, DIMO2013 -- Diffuse Interface Models, Levico Terme, Italy, September 10 - 13, 2013.
-
CH. Heinemann, Degenerating Cahn--Hilliard systems coupled with mechanical effects and complete damage processes, Equadiff13, MS27 -- Recent Results in Continuum and Fracture Mechanics, August 26 - 30, 2013, Prague, Czech Republic, August 27, 2013.
-
CH. Heinemann, On a PDE system describing damage processes and phase separation, Oberseminar Analysis, Universität Augsburg, July 11, 2013.
-
H. Abels, J. Daube, Ch. Kraus, D. Kröner, Sharp interface limit for the Navier--Stokes--Korteweg model, DIMO2013 -- Diffuse Interface Models, Levico Terme, Italy, September 10 - 13, 2013.
-
CH. Kraus, Damage and phase separation processes: Modeling and analysis of nonlinear PDE systems, DIMO2013 -- Diffuse Interface Models, September 10 - 13, 2013, Levico Terme, Italy, September 11, 2013.
-
CH. Kraus, Modeling and analysis of a nonlinear PDE system for phase separation and damage, Università di Pavia, Dipartimento di Matematica, Italy, January 22, 2013.
-
A. Mielke, On the geometry of reaction-diffusion systems: Optimal transport versus reaction, Recent Trends in Differential Equations: Analysis and Discretisation Methods, November 7 - 9, 2013, Technische Universität Berlin, Institut für Mathematik, November 9, 2013.
-
J. Sprekels, Optimal control of Allen--Cahn equations with singular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions, DIMO2013 -- Diffuse Interface Models, September 10 - 13, 2013, Levico Terme, Italy, September 11, 2013.
-
J. Sprekels, Optimal control of the Allen--Cahn equation with dynamic boundary condition and double obstacle potentials: A ``deep quench'' approach, Applied Mathematics Seminar, Università di Pavia, Dipartimento di Matematica ``F. Casorati'', Italy, September 17, 2013.
-
J. Sprekels, Prandtl--Ishlinskii operators and elastoplasticity, Spring School on ``Rate-independent Evolutions and Hysteresis Modelling'', May 27 - 31, 2013, Politecnico di Milano, Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy.
-
CH. Heinemann, Complete damage in linear elastic materials, Variational Models and Methods for Evolution, Levico, Italy, September 10 - 12, 2012.
-
CH. Heinemann, Damage processes coupled with phase separation in elastically stressed alloys, GAMM Jahrestagung 2012 (83rd Annual Meeting), March 26 - 30, 2012, Technische Universität Darmstadt, March 27, 2012.
-
CH. Heinemann, Existence of weak solutions for rate-dependent complete damage processes, Materialmodellierungsseminar, WIAS, Berlin, October 31, 2012.
-
CH. Heinemann, Kopplung von Phasenseparation und Schädigung in elastischen Materialien, Leibniz-Doktoranden-Forum der Sektion D, Berlin, June 7 - 8, 2012.
-
CH. Kraus, A nonlinear PDE system for phase separation and damage, Universität Freiburg, Abteilung Angewandte Mathematik, November 13, 2012.
-
CH. Kraus, Cahn--Larché systems coupled with damage, Università degli Studi di Milano, Dipartimento di Matematica, Italy, November 28, 2012.
-
CH. Kraus, Phase field systems for phase separation and damage processes, 12th International Conference on Free Boundary Problems: Theory and Applications, June 11 - 15, 2012, Frauenchiemsee, June 12, 2012.
-
CH. Kraus, Phasenfeldsysteme für Entmischungs- und Schädigungsprozesse, Mathematisches Kolloquium, Universität Stuttgart, Fachbereich Mathematik, May 15, 2012.
-
J. Sprekels, A time discretization for a nonstandard viscous Cahn--Hilliard system, INDAM Workshop PDEs for Multiphase Advanced Materials (ADMAT2012), September 17 - 21, 2012, Cortona, Italy, September 19, 2012.
-
J.A. Griepentrog, On nonlocal phase separation processes in multicomponent systems, 10th GAMM Seminar on Microstructures, January 20 - 22, 2011, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Fachbereich Mathematik, January 22, 2011.
-
J.A. Griepentrog, The role of nonsmooth regularity theory in the analysis of phase separation processes, Ehrenkolloquium anlässlich des 60. Geburtstages von PD Dr. habil. Lutz Recke, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institut für Mathematik, November 21, 2011.
-
CH. Heinemann, Existence results for Cahn-Hilliard equations coupled with elasticity and damage, Workshop on Phase Separation, Damage and Fracture, September 21 - 23, 2011, WIAS, September 23, 2011.
-
CH. Kraus, Diffuse interface systems for phase separation and damage, Seminar on Partial Differential Equations, Institute of Mathematics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague, May 3, 2011.
-
CH. Kraus, Phase separation systems coupled with elasticity and damage, ICIAM 2011, July 18 - 22, 2011, Vancouver, Canada, July 18, 2011.
-
J. Sprekels, A non-standard phase-field system of Cahn--Hilliard type for diffusive phase segregation, Schwerpunktkolloquium``Analysis und Numerik'', Universität Konstanz, Fachbereich Mathematik und Statistik, July 14, 2011.
-
J. Sprekels, A nonstandard phase field system of Cahn--Hilliard type for diffusive phase segregation, Seminario Matematico e Fisico di Milano, Università degli Studi di Milano, Dipartimento di Matematica, Italy, September 21, 2011.
-
J. Sprekels, Phase field models and hysteresis operators, Trends in Thermodynamics and Materials Theory 2011, December 15 - 17, 2011, Technische Universität Berlin, December 16, 2011.
-
J. Sprekels, Well-posedness, asymptotic behavior and optimal control of a nonstandard phase field model for diffusive phase segregation, Workshop on Optimal Control of Partial Differential Equations, November 28 - December 1, 2011, Wasserschloss Klaffenbach, Chemnitz, November 30, 2011.
-
J. Sprekels, Models of phase transitions and hysteresis operators, Joint International Meeting UMI-DMV 2007, Minisymposium ``Phase Transitions and Hysteresis in Free Boundary Problems'', June 18 - 22, 2007, Università degli Studi di Perugia, Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica, Italy, June 21, 2007.
-
J. Sprekels, Nonlocal phase-field models for nonisothermal phase transitions, International Conference ``Free Boundary Problems: Theory and Applications'', June 7 - 12, 2005, Coimbra, Portugal, June 8, 2005.
-
O. Klein, Asymptotic behaviour for a phase-field model with hysteresis in thermo-visco-plasticity, INdAM Workshop ``Dissipative Models in Phase Transitions'', September 5 - 11, 2004, Cortona, Italy, September 9, 2004.
-
O. Klein, Long-time behaviour of solutions to equations involving outwards pointing hysteresis operators, International Workshop on Hysteresis & Multi-Scale Asymptotics (HAMSA 2004), March 17 - 21, 2004, University College Cork, Ireland, March 19, 2004.
-
J. Sprekels, On nonlocal phase-field models, Workshop ``Thermodynamische Materialtheorien'', December 12 - 15, 2004, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, December 14, 2004.
-
O. Klein, Asymptotic behaviour of evolution equations involving outwards pointing hysteresis operators, 4th International Symposium on Hysteresis and Micromagnetic Modeling (HMM-2003), May 28 - 30, 2003, Universidad de Salamanca, Departamento de Física Aplicada, Spain, May 30, 2003.
-
J. Sprekels, On nonlocal models for non-isothermal phase transitions, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Institute of Mathematics, Prague, February 19, 2002.
-
J. Sprekels, On nonlocal phase transition models for non-conserved order parameters, Università degli Studi di Firenze, Dipartimento di Matematica ``U. Dini'', Italy, October 14, 2002.
-
J. Sprekels, Hysteresis operators in phase-field modelling, Workshop ``Phasenübergänge'', April 29 - May 4, 2001, Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, May 1, 2001.
-
J. Sprekels, Hysteresis operators in phase-field systems, University of Warsaw, Interdisciplinary Centre for Mathematics and Computer Modelling, Poland, January 5, 2001.
-
J. Sprekels, On nonlocal phase transition models for non-conserved order parameters, Università di Pavia, Dipartimento di Matematica, Italy, September 19, 2001.
-
J. Sprekels, Phase-field systems and vector hysteresis operators, Workshop "`Phase Transitions and Interfaces in Evolution Equations: Analysis, Control and Approximation"', February 8 - 12, 2000, Santa Margherita Ligure, Italy, February 11, 2000.
-
J. Sprekels, Phase-field systems with hysteresis, Konferenz "`Evolution Equations 2000: Applications to Physics, Industry, Life Sciences and Economics"', October 30 - 31, 2000, Levico, Italy, October 30, 2000.
 External Preprints
External Preprints
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, A temperature-dependent phase segregation problem of the Allen--Cahn type, Preprint no. arXiv:1005.0911, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2010.
-
S. Bartels, R. Müller, Error controlled local resolution of evolving interfaces for generalized Cahn-Hilliard equations, Preprint no. 09--02, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institut für Mathematik, 2009.
-
P. Colli, G. Gilardi, P. Podio-Guidugli, J. Sprekels, Global solution and long-time behavior for a problem of phase segregation of the Allen--Cahn type (electronic only), Preprint no. arXiv:0902.4741, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2009.
Abstract
In this paper we study a model for phase segregation consisting in a sistem of a partial and an ordinary differential equation. By a careful definition of maximal solution to the latter equation, this system reduces to an Allen-Cahn equation with a memory term. Global existence and uniqueness of a smooth solution are proven and a characterization of the omega-limit set is given. -
F. Klopp, B. Metzger, The Gross--Pitaevskii functional with a random background potential and condensation in the single particle ground state, Preprint no. arXiv:0910.2896, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2009.
Abstract
For discrete and continuous Gross-Pitaevskii energy functionals with a random background potential, we study the Gross-Pitaevskii ground state. We characterize a regime of interaction coupling when the Gross-Pitaevskii ground state and the ground state of the random background Hamiltonian asymptotically coincide. -
F. Lanzara, V. Maz'ya, G. Schmidt, On the fast computation of high dimensional volume potentials (electronic only), Preprint no. arXiv:0911.0443, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2009.
-
P. Krejčí, E. Rocca, J. Sprekels, Phase separation in a gravity field (electronic only), Preprint no. arXiv:0905.2131, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2009.