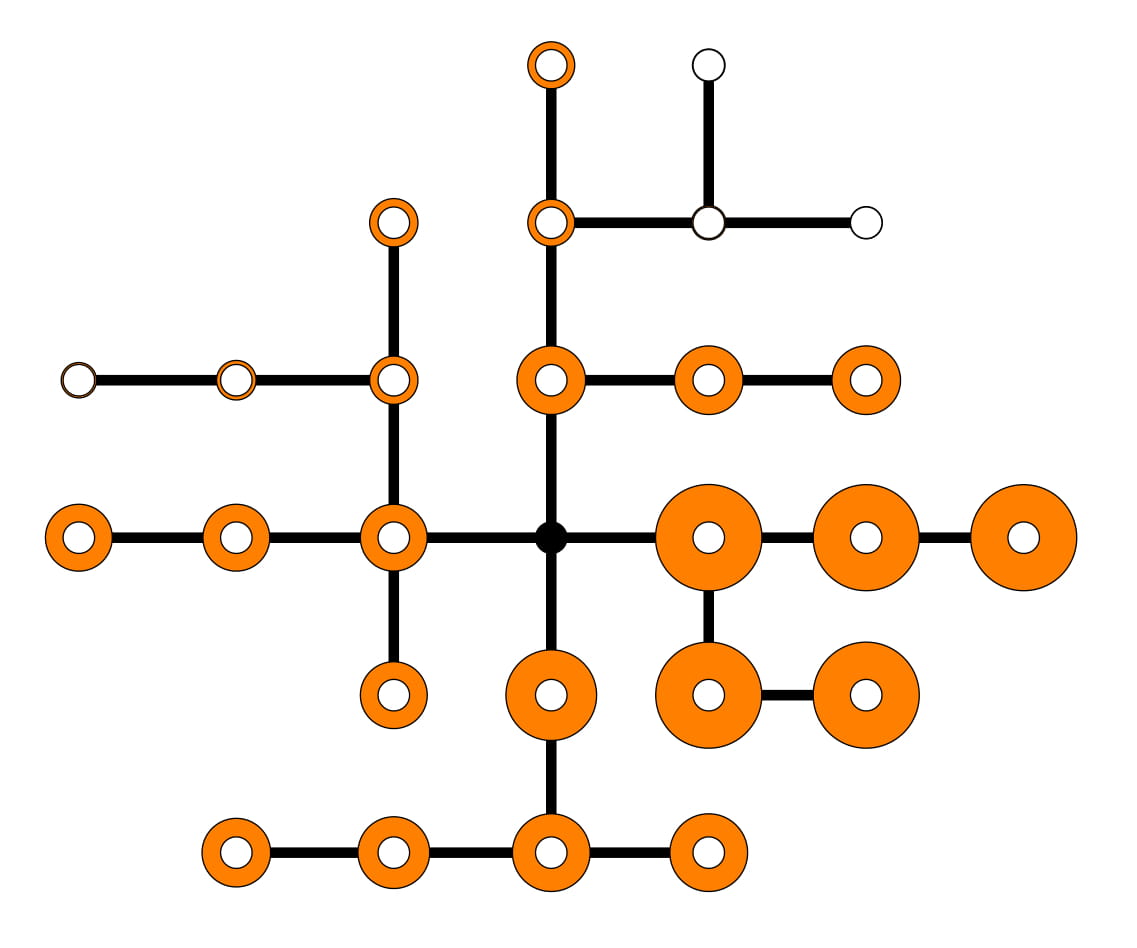
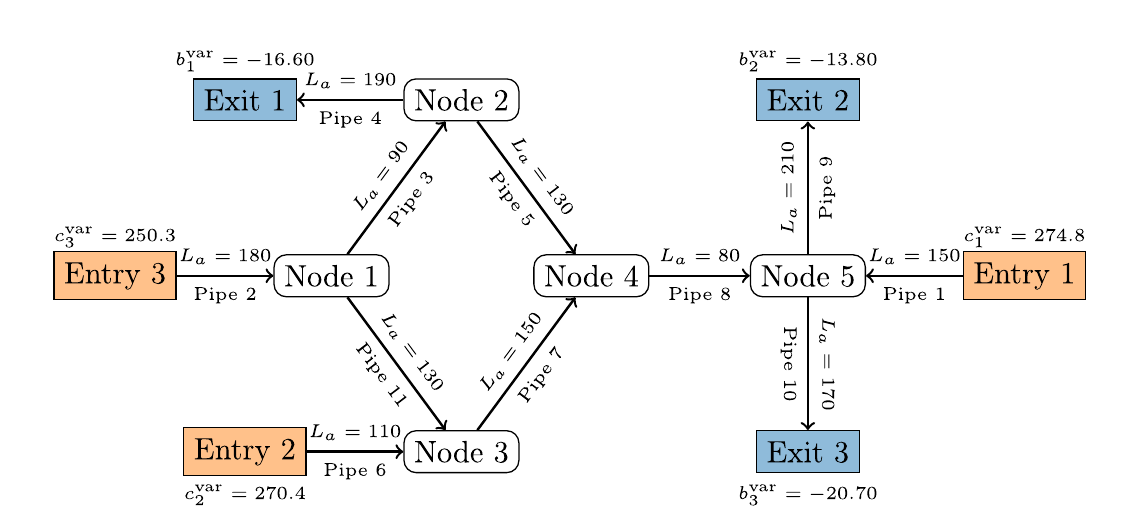
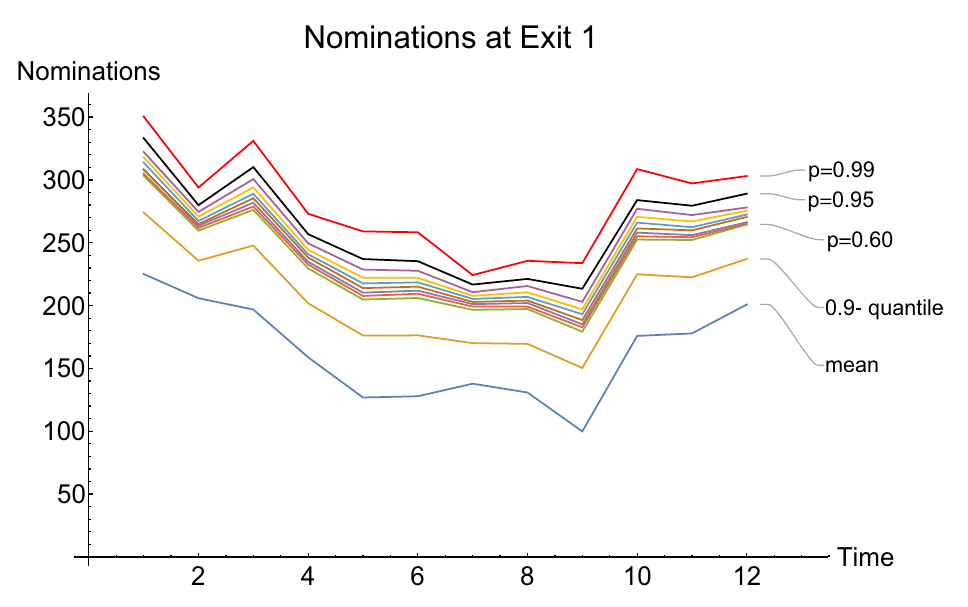
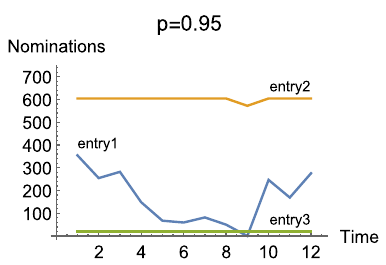
Modeling gas markets leads to hierarchic optimization problems such as coupled bilevel problems. Gas producers inject gas into so-called entries of the gas network, while it is withdrawn by retailers at exits of the network, where customer loads have to be satisfied. The left figure below illustrates a little 'entry-exit-network'. Both, producers and retailers nominate gas within certain booking limits sold by the network owner. The latter is obliged to ensure arbitrary technical gas transport from entries to exits according to balanced nominations within the booking limits. Retailers nominate gas on a day-ahead-market in order to satisfy the real load on the next day. Producers and retailers maximize their profit under the given constraints at the lower level of an hierachical game in which the network owner maximizes total welfare on the upper level. This deterministic model can be reasonably extended by taking into account the stochastic load at the exits which might deviate more or less from the estimate made the day ahead. In order to avoid significant discrepancies and the posterior regulating measures needed for balancing them, one may impose an additional constraint on the retailers forcing them to nominate in a way that the real loads are covered with a minimum probability (e.g., 0.95). This creates a coupled system of bilevel problems with probabilistic constraints. It is of much interest to identify the equilibria in these problem since they define, for instance, the market clearing price. The figure in the middle below shows retailer nominations under increaing probability required for load coverage. The figure on the right presents an analogous diagram for nominations of different producers at the given probability.
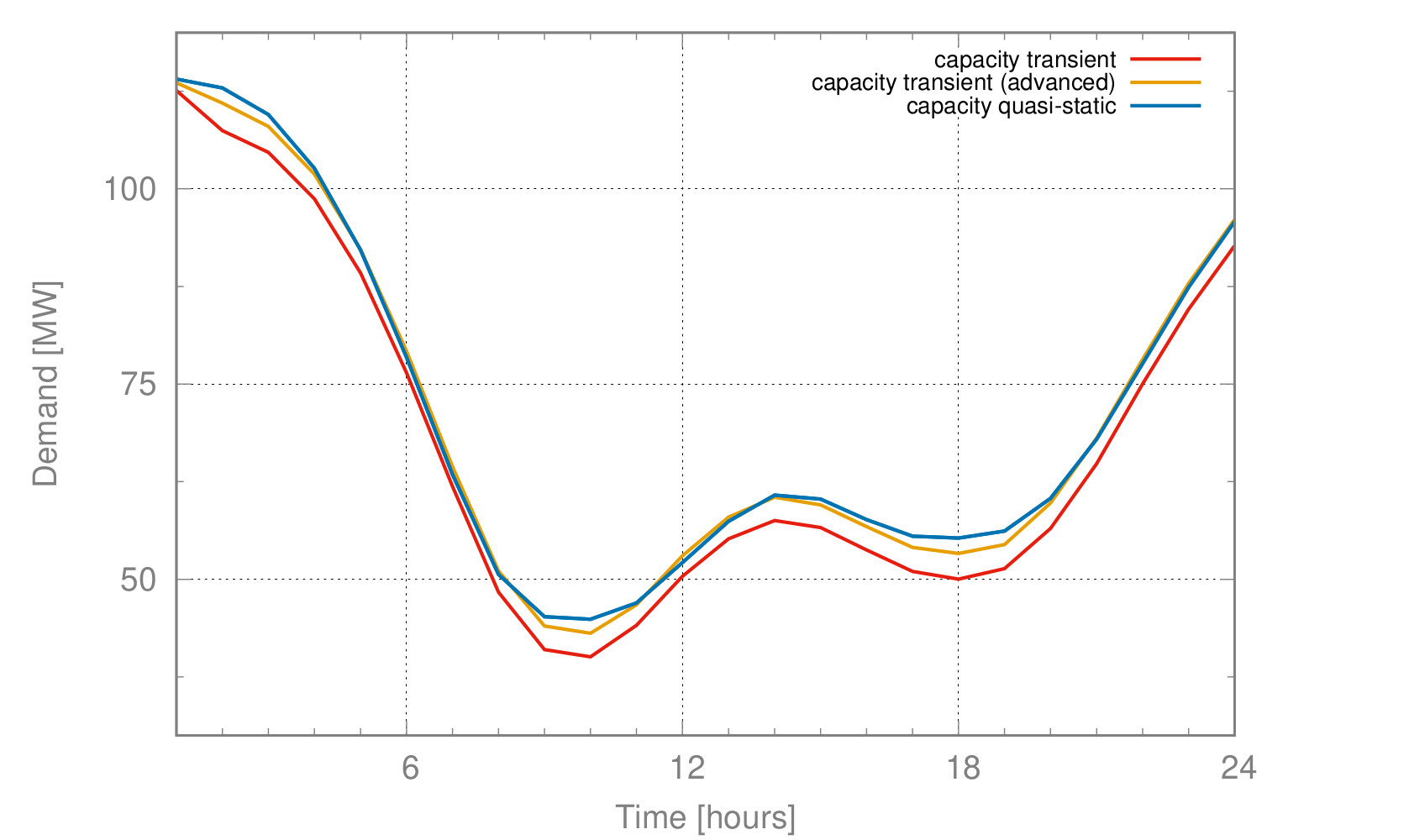
Of further interest are also dynamic models where the physics of gas transport play a role. Market players can only make decisions that collectively lead to feasible loads on the underlying network. Mathematically, the problems involve solving equilibrium problems subject to uncertainty.
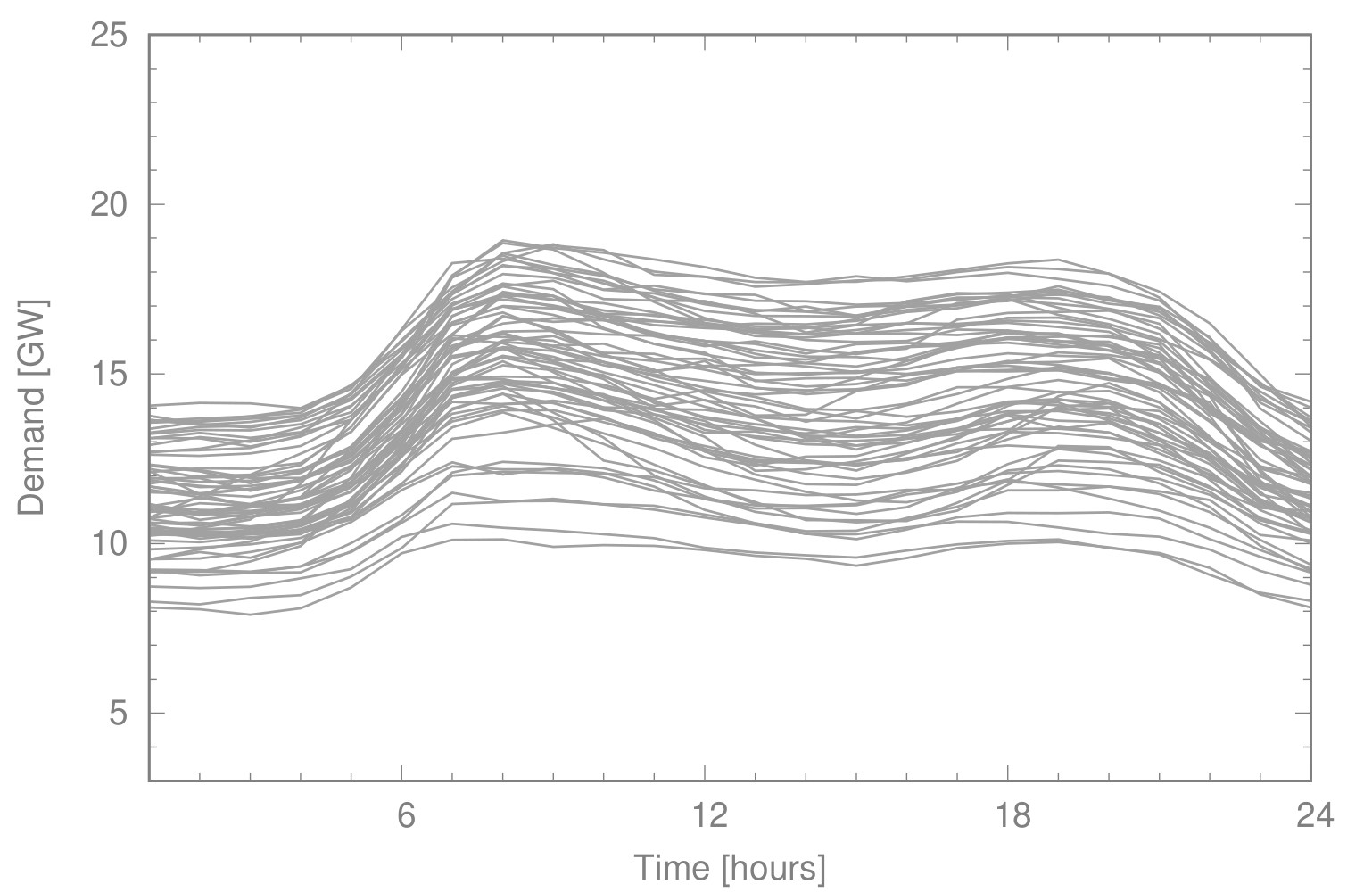
Another application concerns the optimal dispatch of weakly connected minigrids as they are typical for rural areas in Africa. Such minigrids consist of renewable energies (solar, wind), of batteries for storing energy, of a connection (import and export) to a main grid and possibly of a backupby Diesel generators. A major problem arises with relative frequent outages of the main grid. Therefore, it is reasonable to keep certain reserves for battery storage and Diesel employment in order to guarantee with high probability (with respect to uncertainties in renewables and demand) that the local load can be covered by autonomous means for the duration of an outage with unknown time of occurence ('probability of successful islanding').
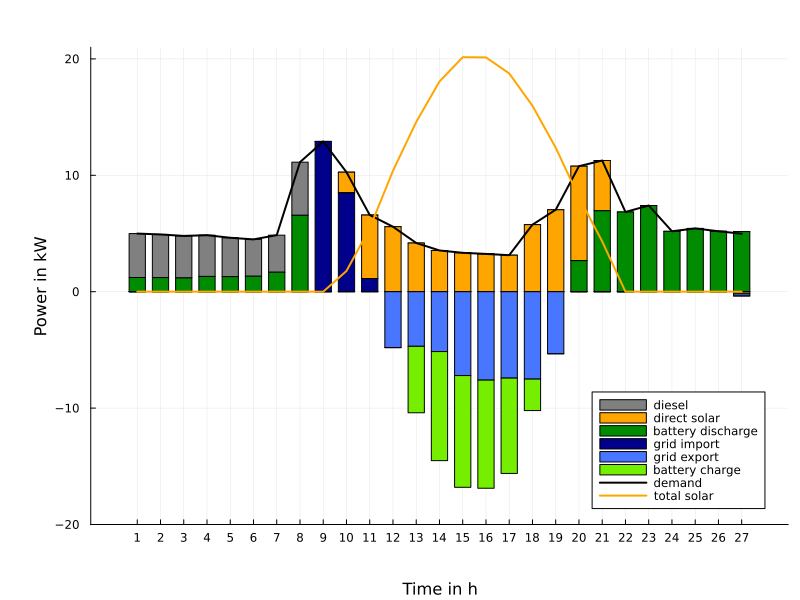
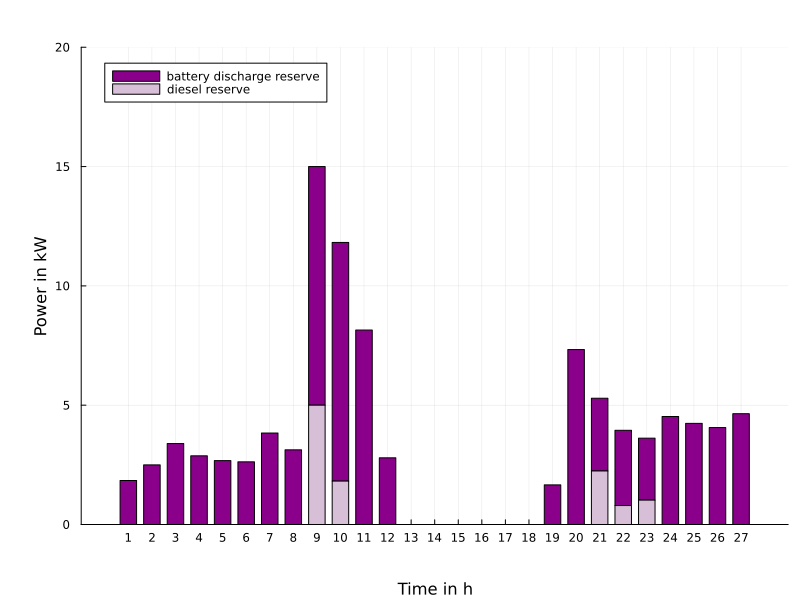
The figure on the left shows the optimal daily dispatch for a 'survival probability' of 90% with an arbitrary begin and a duration of 3 hours of the outage. The right figure illustrates the reserves taken into account for battery and Diesel which would be additionally employed in case of an outage in order to cover the local demand.
Highlights
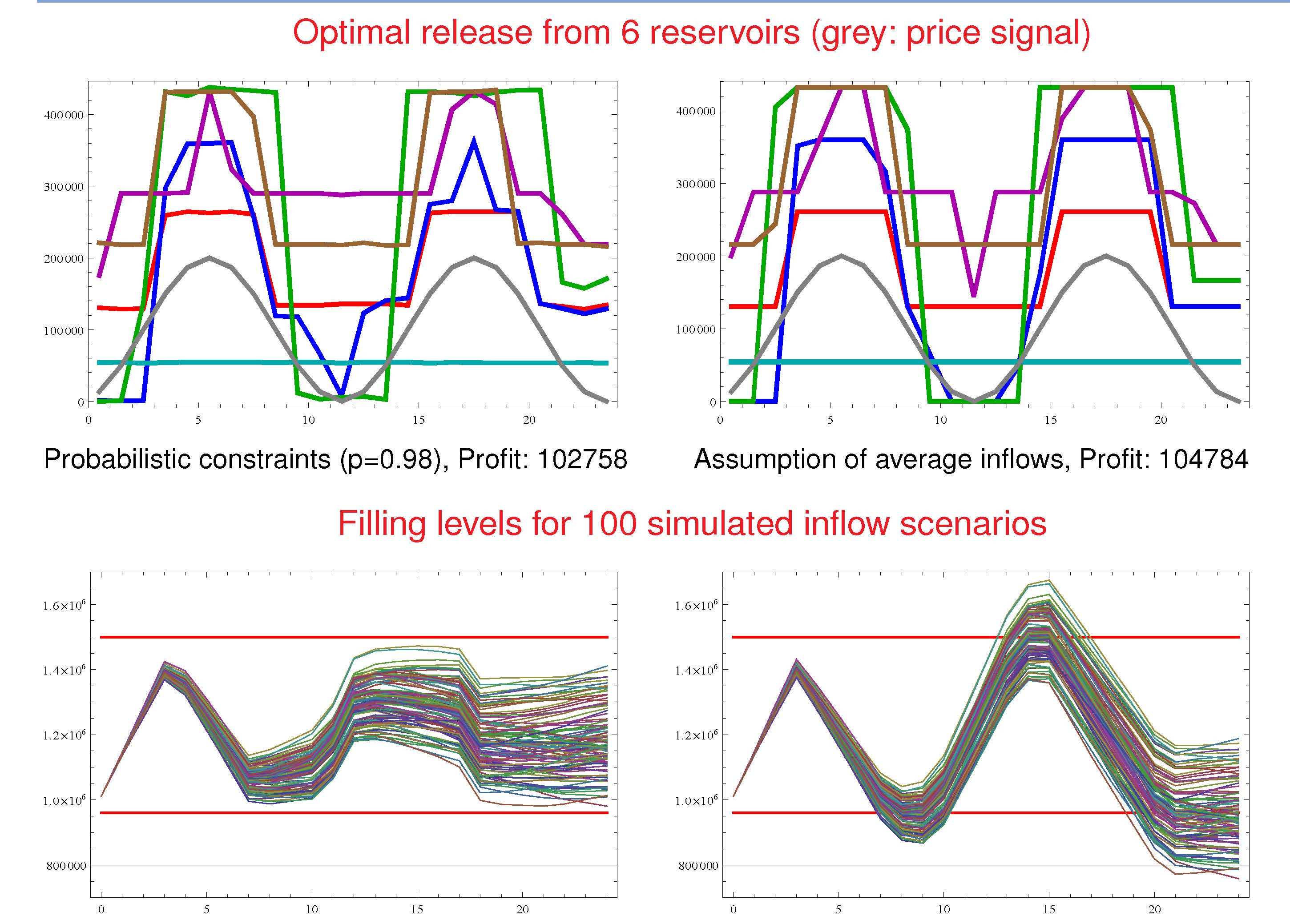
The research on optimization problems under probabilistic constraints led to an intensive cooperation with EDF (Electricité de France) and resulted in particular in a reasearch project continuously funded by the Fondation Mathématique Jacques Hadamard since 2014. Here, the management of water reservoirs with random filling level and/or demand constraints is in the focus. Furthermore, suitable models for optimal gas transport are considered in several research projects subordinate to the DFG-funded Collaborative Research Centre Transregio TRR154 (funding period: 2014-2026). In connection with this research, the monograph 'Evaluating Gas Network Capacities' published at SIAM has been co-authored. This monograph has been awarded the 'Euro Excellence in Practice Award 2016'.Publications
 Monographs
Monographs
-
M. Hintermüller, T. Keil, Chapter 3: Optimal Control of Geometric Partial Differential Equations, in: Geometric Partial Differential Equations: Part 2, A. Bonito, R.H. Nochetto, eds., 22 of Handbook of Numerical Analysis, Elsevier, 2021, pp. 213--270, (Chapter Published), DOI 10.1016/bs.hna.2020.10.003 .
-
M. Hintermüller, M. Hinze, J. Sokołowski, S. Ulbrich, eds., Special issue to honour Guenter Leugering on his 65th birthday, 1 of Control & Cybernetics, Systems Research Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, 2019, (Collection Published).
-
M. Hintermüller, D. Wegner, Distributed and Boundary Control Problems for the Semidiscrete Cahn--Hilliard/Navier--Stokes System with Nonsmooth Ginzburg--Landau Energies, in: Topological Optimization and Optimal Transport in the Applied Sciences, M. Bergounioux, E. Oudet, M. Rumpf, G. Carlier, Th. Champion, F. Santambrogio, eds., 17 of Radon Series on Computational and Applied Mathematics, De Gruyter, Berlin, 2017, pp. 40--63, (Chapter Published).
-
L. Ghezzi, D. Hömberg, Ch. Landry, eds., Math for the Digital Factory, 27 of Mathematics in Industry / The European Consortium for Mathematics in Industry, Springer International Publishing AG, Cham, 2017, x+348 pages, (Collection Published), DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-63957-4 .
-
H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, H. Leövey, R. Mirkov, A. Möller, W. Römisch, I. Wegner-Specht, Chapter 13: Empirical Observations and Statistical Analysis of Gas Demand Data, in: Evaluating Gas Network Capacities, Th. Koch, B. Hiller, M.E. Pfetsch, L. Schewe, eds., MOS-SIAM Series on Optimization, SIAM, Philadelphia, 2015, pp. 273--290, (Chapter Published).
-
B. Hiller, Ch. Hayn, H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, H. Leövey, A. Möller, W. Römisch, Chapter 14: Methods for Verifying Booked Capacities, in: Evaluating Gas Network Capacities, Th. Koch, B. Hiller, M.E. Pfetsch, L. Schewe, eds., MOS-SIAM Series on Optimization, SIAM, Philadelphia, 2015, pp. 291--315, (Chapter Published).
-
P. Deuflhard, M. Grötschel, D. Hömberg, U. Horst, J. Kramer, V. Mehrmann, K. Polthier, F. Schmidt, Ch. Schütte, M. Skutella, J. Sprekels, eds., MATHEON -- Mathematics for Key Technologies, 1 of EMS Series in Industrial and Applied Mathematics, European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Zurich, 2014, 453 pages, (Collection Published).
 Articles in Refereed Journals
Articles in Refereed Journals
-
R. Henrion, D. Hömberg, N. Kliche, Modeling and simulation of an isolated mini-grid including battery operation strategies under uncertainty using chance constraints, Energy Systems, published online on 19.09.2025, DOI 10.1007/s12667-025-00764-1 .
Abstract
This paper addresses the challenge of handling uncertainties in mini-grid operation, crucial for achieving universal access to reliable and sustainable energy, especially in regions lacking access to a national grid. Mini-grids, consisting of small-scale power generation systems and distribution infrastructure, offer a cost-effective solution. However, the intermittency and uncertainty of renewable energy sources poses challenges, mitigated by employing batteries for energy storage. Optimizing the lifespan of the battery energy storage system is critical, requiring a balance between degradation and operational expenses, with battery operation strategies playing a key role in achieving this balance. Accounting for uncertainties in renewable energy sources, demand, and ambient temperature is essential for reliable energy management strategies. By formulating a probabilistic optimal control problem for minimizing the daily operational costs of stand-alone mini-grids under uncertainty, and exploiting the concept of joint chance constraints, we address the uncertainties inherent in battery dynamics and the associated operational constraints. -
M. Gugat, J. Habermann, M. Hintermüller, O. Huber, Constrained exact boundary controllability of a semilinear model for pipeline gas flow, European Journal of Applied Mathematics, 34 (2023), pp. 532--553, DOI 10.1017/S0956792522000389 .
Abstract
While the quasilinear isothermal Euler equations are an excellent model for gas pipeline flow, the operation of the pipeline flow with high pressure and small Mach numbers allows us to obtain approximate solutions by a simpler semilinear model. We provide a derivation of the semilinear model that shows that the semilinear model is valid for sufficiently low Mach numbers and sufficiently high pressures. We prove an existence result for continuous solutions of the semilinear model that takes into account lower and upper bounds for the pressure and an upper bound for the magnitude of the Mach number of the gas flow. These state constraints are important both in the operation of gas pipelines and to guarantee that the solution remains in the set where the model is physically valid. We show the constrained exact boundary controllability of the system with the same pressure and Mach number constraints. -
H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, Th. Kleinert, M. Schmidt, On convex lower-level black-box constraints in bilevel optimization with an application to gas market models with chance constraints, Journal of Global Optimization. An International Journal Dealing with Theoretical and Computational Aspects of Seeking Global Optima and Their Applications in Science, Management and Engineering, 84 (2022), pp. 651--685, DOI 10.1007/s10898-022-01161-z .
Abstract
Bilevel optimization is an increasingly important tool to model hierarchical decision making. However, the ability of modeling such settings makes bilevel problems hard to solve in theory and practice. In this paper, we add on the general difficulty of this class of problems by further incorporating convex black-box constraints in the lower level. For this setup, we develop a cutting-plane algorithm that computes approximate bilevel-feasible points. We apply this method to a bilevel model of the European gas market in which we use a joint chance constraint to model uncertain loads. Since the chance constraint is not available in closed form, this fits into the black-box setting studied before. For the applied model, we use further problem-specific insights to derive bounds on the objective value of the bilevel problem. By doing so, we are able to show that we solve the application problem to approximate global optimality. In our numerical case study we are thus able to evaluate the welfare sensitivity in dependence of the achieved safety level of uncertain load coverage. -
M. Branda, R. Henrion, M. Pištěk, Value at risk approach to producer's best response in electricity market with uncertain demand, Optimization. A Journal of Mathematical Programming and Operations Research, 72 (2023), pp. 2745--2767 (published online on 15.05.2022), DOI 10.1080/02331934.2022.2076232 .
Abstract
We deal with several sources of uncertainty in electricity markets. The independent system operator (ISO) maximizes the social welfare using chance constraints to hedge against discrepancies between the estimated and real electricity demand. We find an explicit solution of the ISO problem, and use it to tackle the problem of a producer. In our model, production as well as income of a producer are determined based on the estimated electricity demand predicted by the ISO, that is unknown to producers. Thus, each producer is hedging against the uncertainty of prediction of the demand using the value-at-risk approach. To illustrate our results, a numerical study of a producer's best response given a historical distribution of both estimated and real electricity demand is provided. -
F. Stonyakin, A. Gasnikov, P. Dvurechensky, A. Titov, M. Alkousa, Generalized mirror prox algorithm for monotone variational inequalities: Universality and inexact oracle, Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 194 (2022), pp. 988--1013, DOI 10.1007/s10957-022-02062-7 .
-
H. Berthold, H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, J. Schwientek, On the algorithmic solution of optimization problems subject to probabilistic/robust (probust) constraints, Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 96 (2022), pp. 1--37 (published online on 14.12.2021), DOI 10.1007/s00186-021-00764-8 .
Abstract
We present an adaptive grid refinement algorithm to solve probabilistic optimization problems with infinitely many random constraints. Using a bilevel approach, we iteratively aggregate inequalities that provide most information not in a geometric but in a probabilistic sense. This conceptual idea, for which a convergence proof is provided, is then adapted to an implementable algorithm. The efficiency of our approach when compared to naive methods based on uniform grid refinement is illustrated for a numerical test example as well as for a water reservoir problem with joint probabilistic filling level constraints. -
T. González Grandón, R. Henrion, P. Pérez-Aros, Dynamic probabilistic constraints under continuous random distributions, Mathematical Programming. A Publication of the Mathematical Programming Society, 196 (2022), pp. 1065--1096 (published online on 13.11.2020), DOI 10.1007/s10107-020-01593-z .
Abstract
The paper investigates analytical properties of dynamic probabilistic constraints (chance constraints). The underlying random distribution is supposed to be continuous. In the first part, a general multistage model with decision rules depending on past observations of the random process is analyzed. Basic properties like (weak sequential) (semi-) continuity of the probability function or existence of solutions are studied. It turns out that the results differ significantly according to whether decision rules are embedded into Lebesgue or Sobolev spaces. In the second part, the simplest meaningful two-stage model with decision rules from L 2 is investigated. More specific properties like Lipschitz continuity and differentiability of the probability function are considered. Explicitly verifiable conditions for these properties are provided along with explicit gradient formulae in the Gaussian case. The application of such formulae in the context of necessary optimality conditions is discussed and a concrete identification of solutions presented. -
L. Blank, E. Meneses Rioseco, U. Wilbrandt, A. Caiazzo, Modeling, simulation, and optimization of geothermal energy production from hot sedimentary aquifers, Computer & Geosciences, 25 (2021), pp. 67--104 (published online on 02.09.2020), DOI 10.1007/s10596-020-09989-8 .
Abstract
Geothermal district heating development has been gaining momentum in Europe with numerous deep geothermal installations and projects currently under development. With the increasing density of geothermal wells, questions related to the optimal and sustainable reservoir exploitation become more and more important. A quantitative understanding of the complex thermo-hydraulic interaction between tightly deployed geothermal wells in heterogeneous temperature and permeability fields is key for a maximum sustainable use of geothermal resources. Motivated by the geological settings of the Upper Jurassic aquifer in the Greater Munich region, we develop a computational model based on finite element analysis and gradient-free optimization to simulate groundwater flow and heat transport in hot sedimentary aquifers, and investigate numerically the optimal positioning and spacing of multi-well systems. Based on our numerical simulations, net energy production from deep geothermal reservoirs in sedimentary basins by smart geothermal multi-well arrangements provides significant amounts of energy to meet heat demand in highly urbanized regions. Our results show that taking into account heterogeneous permeability structures and variable reservoir temperature may drastically affect the results in the optimal configuration. We demonstrate that the proposed numerical framework is able to efficiently handle generic geometrical and geologocal configurations, and can be thus flexibly used in the context of multi-variable optimization problems. Hence, this numerical framework can be used to assess the extractable geothermal energy from heterogeneous deep geothermal reservoirs by the optimized deployment of smart multi-well systems. -
M. Hintermüller, N. Strogies, Identification of the friction function in a semilinear system for gas transport through a network, Optimization Methods & Software, 35 (2020), pp. 576--617 (published online on 10.12.2019), DOI 10.1080/10556788.2019.1692206 .
-
M. Eigel, J. Neumann, R. Schneider, S. Wolf, Risk averse stochastic structural topology optimization, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 334 (2018), pp. 470--482, DOI 10.1016/j.cma.2018.02.003 .
Abstract
A novel approach for risk-averse structural topology optimization under uncertainties is presented which takes into account random material properties and random forces. For the distribution of material, a phase field approach is employed which allows for arbitrary topological changes during optimization. The state equation is assumed to be a high-dimensional PDE parametrized in a (finite) set of random variables. For the examined case, linearized elasticity with a parametric elasticity tensor is used. Instead of an optimization with respect to the expectation of the involved random fields, for practical purposes it is important to design structures which are also robust in case of events that are not the most frequent. As a common risk-aware measure, the Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR) is used in the cost functional during the minimization procedure. Since the treatment of such high-dimensional problems is a numerically challenging task, a representation in the modern hierarchical tensor train format is proposed. In order to obtain this highly efficient representation of the solution of the random state equation, a tensor completion algorithm is employed which only required the pointwise evaluation of solution realizations. The new method is illustrated with numerical examples and compared with a classical Monte Carlo sampling approach. -
L. Adam, M. Branda, H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, Solving joint chance constrained problems using regularization and Benders' decomposition, Annals of Operations Research, 292 (2020), pp. 683--709 (published online on 08.11.2018), DOI 10.1007/s10479-018-3091-9 .
Abstract
In this paper we investigate stochastic programms with joint chance constraints. We consider discrete scenario set and reformulate the problem by adding auxiliary variables. Since the resulting problem has a difficult feasible set, we regularize it. To decrease the dependence on the scenario number, we propose a numerical method by iteratively solving a master problem while adding Benders cuts. We find the solution of the slave problem (generating the Benders cuts) in a closed form and propose a heuristic method to decrease the number of cuts. We perform a numerical study by increasing the number of scenarios and compare our solution with a solution obtained by solving the same problem with continuous distribution. -
T. González Grandón, H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, A joint model of probabilistic/robust constraints for gas transport management in stationary networks, Computational Management Science, 14 (2017), pp. 443--460, DOI 10.1007/s10287-017-0284-7 .
Abstract
We present a novel mathematical algorithm to assist gas network operators in managing uncertainty, while increasing reliability of transmission and supply. As a result, we solve an optimization problem with a joint probabilistic constraint over an infinite system of random inequalities. Such models arise in the presence of uncertain parameters having partially stochastic and partially non-stochastic character. The application that drives this new approach is a stationary network with uncertain demand (which are stochastic due to the possibility of fitting statistical distributions based on historical measurements) and with uncertain roughness coefficients in the pipes (which are uncertain but non-stochastic due to a lack of attainable measurements). We study the sensitivity of local uncertainties in the roughness coefficients and their impact on a highly reliable network operation. In particular, we are going to answer the question, what is the maximum uncertainty that is allowed (shaping a 'maximal' uncertainty set) around nominal roughness coefficients, such that random demands in a stationary gas network can be satisfied at given high probability level for no matter which realization of true roughness coefficients within the uncertainty set. One ends up with a constraint, which is probabilistic with respect to the load of gas and robust with respect to the roughness coefficients. We demonstrate how such constraints can be dealt with in the framework of the so-called spheric-radial decomposition of multivariate Gaussian distributions. The numerical solution of a corresponding optimization problem is illustrated. The results might assist the network operator with the implementation of cost-intensive roughness measurements. -
H. Egger, Th. Kugler, N. Strogies, Parameter identification in a semilinear hyperbolic system, Inverse Problems. An International Journal on the Theory and Practice of Inverse Problems, Inverse Methods and Computerized Inversion of Data, 33 (2017), pp. 055022/1--055022/25, DOI 10.1088/1361-6420/aa648c .
Abstract
We consider the identification of a nonlinear friction law in a one-dimensional damped wave equation from additional boundary measurements. Well-posedness of the governing semilinear hyperbolic system is established via semigroup theory and contraction arguments. We then investigate the inverse problem of recovering the unknown nonlinear damping law from additional boundary measurements of the pressure drop along the pipe. This coefficient inverse problem is shown to be ill-posed and a variational regularization method is considered for its stable solution. We prove existence of minimizers for the Tikhonov functional and discuss the convergence of the regularized solutions under an approximate source condition. The meaning of this condition and some arguments for its validity are discussed in detail and numerical results are presented for illustration of the theoretical findings. -
S. Hajian, M. Hintermüller, S. Ulbrich, Total variation diminishing schemes in optimal control of scalar conservation laws, IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 39 (2019), pp. 105--140 (published online on 14.12.2017), DOI 10.1093/imanum/drx073 .
Abstract
In this paper, optimal control problems subject to a nonlinear scalar conservation law are studied. Such optimal control problems are challenging both at the continuous and at the discrete level since the control-to-state operator poses difficulties as it is, e.g., not differentiable. Therefore discretization of the underlying optimal control problem should be designed with care. Here the discretize-then-optimize approach is employed where first the full discretization of the objective function as well as the underlying PDE is considered. Then, the derivative of the reduced objective is obtained by using an adjoint calculus. In this paper total variation diminishing Runge-Kutta (TVD-RK) methods for the time discretization of such problems are studied. TVD-RK methods, also called strong stability preserving (SSP), are originally designed to preserve total variation of the discrete solution. It is proven in this paper that providing an SSP state scheme, is enough to ensure stability of the discrete adjoint. However requiring SSP for both discrete state and adjoint is too strong. Also approximation properties that the discrete adjoint inherits from the discretization of the state equation are studied. Moreover order conditions are derived. In addition, optimal choices with respect to CFL constant are discussed and numerical experiments are presented. -
M. Hintermüller, C.N. Rautenberg, M. Mohammadi, M. Kanitsar, Optimal sensor placement: A robust approach, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 55 (2017), pp. 3609--3639.
Abstract
We address the problem of optimally placing sensor networks for convection-diffusion processes where the convective part is perturbed. The problem is formulated as an optimal control problem where the integral Riccati equation is a constraint and the design variables are sensor locations. The objective functional involves a term associated to the trace of the solution to the Riccati equation and a term given by a constrained optimization problem for the directional derivative of the previous quantity over a set of admissible perturbations. The paper addresses the existence of the derivative with respect to the convective part of the solution to the Riccati equation, the well-posedness of the optimization problem and finalizes with a range of numerical tests. -
H. Heitsch, H. Leövey, W. Römisch, Are quasi-Monte Carlo algorithms efficient for two-stage stochastic programs?, Computational Optimization and Applications. An International Journal, 65 (2016), pp. 567--603.
Abstract
Quasi-Monte Carlo algorithms are studied for designing discrete approximations of two-stage linear stochastic programs with random right-hand side and continuous probability distribution. The latter should allow for a transformation to a distribution with independent marginals. The two-stage integrands are piecewise linear, but neither smooth nor lie in the function spaces considered for QMC error analysis. We show that under some weak geometric condition on the two-stage model all terms of their ANOVA decomposition, except the one of highest order, are continuously differentiable and that first and second order ANOVA terms have mixed first order partial derivatives. Hence, randomly shifted lattice rules (SLR) may achieve the optimal rate of convergence not depending on the dimension if the effective superposition dimension is at most two. We discuss effective dimensions and dimension reduction for two-stage integrands. The geometric condition is shown to be satisfied almost everywhere if the underlying probability distribution is normal and principal component analysis (PCA) is used for transforming the covariance matrix. Numerical experiments for a large scale two-stage stochastic production planning model with normal demand show that indeed convergence rates close to the optimal are achieved when using SLR and randomly scrambled Sobol' point sets accompanied with PCA for dimension reduction. -
C. Gotzes, H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, R. Schultz, On the quantification of nomination feasibility in stationary gas networks with random load, Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 84 (2016), pp. 427--457.
Abstract
The paper considers the computation of the probability of feasible load constellations in a stationary gas network with uncertain demand. More precisely, a network with a single entry and several exits with uncertain loads is studied. Feasibility of a load constellation is understood in the sense of an existing flow meeting these loads along with given pressure bounds in the pipes. In a first step, feasibility of deterministic exit loads is characterized algebraically and these general conditions are specified to networks involving at most one cycle. This prerequisite is essential for determining probabilities in a stochastic setting when exit loads are assumed to follow some (joint) Gaussian distribution when modeling uncertain customer demand. The key of our approach is the application of the spheric-radial decomposition of Gaussian random vectors coupled with Quasi Monte-Carlo sampling. This approach requires an efficient algorithmic treatment of the mentioned algebraic relations moreover depending on a scalar parameter. Numerical results are illustrated for different network examples and demonstrate a clear superiority in terms of precision over simple generic Monte-Carlo sampling. They lead to fairly accurate probability values even for moderate sample size. -
M. Hintermüller, Th. Surowiec, A bundle-free implicit programming approach for a class of elliptic MPECs in function space, Mathematical Programming Series A, 160 (2016), pp. 271--305.
-
I. Bremer, R. Henrion, A. Möller, Probabilistic constraints via SQP solver: Application to a renewable energy management problem, Computational Management Science, 12 (2015), pp. 435--459.
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to illustrate the efficient solution of nonlinear optimization problems with joint probabilistic constraints by means of an SQP method. Here, the random vector is assumed to obey some multivariate Gaussian distribution. The numerical solution approach is applied to a renewable energy management problem. We consider a coupled system of hydro and wind power production used in order to satisfy some local demand of energy and to sell/buy excessive or missing energy on a day-ahead and intraday market, respectively. A short term planning horizon of 2 days is considered and only wind power is assumed to be random. In the first part of the paper, we develop an appropriate optimization problem involving a probabilistic constraint reflecting demand satisfaction. Major attention will be payed to formulate this probabilistic constraint not directly in terms of random wind energy produced but rather in terms of random wind speed, in order to benefit from a large data base for identifying an appropriate distribution of the random parameter. The second part presents some details on integrating Genz' code for Gaussian probabilities of rectangles into the environment of the SQP solver SNOPT. The procedure is validated by means of a simplified optimization problem which by its convex structure allows to estimate the gap between the numerical and theoretical optimal values, respectively. In the last part, numerical results are presented and discussed for the original (nonconvex) optimization problem. -
A. Fügenschuh, B. Geissler, Ch. Hayn, R. Henrion, B. Hiller, J. Humpola, Th. Koch ET AL., Mathematical optimization for challenging network planning problems in unbundled liberalized gas markets, Energy Systems, 5 (2014), pp. 449--473.
-
W. VAN Ackooij, R. Zorgati, R. Henrion, A. Möller, Joint chance constrained programming for hydro reservoir management, Optimization and Engineering. International Multidisciplinary Journal to Promote Optimization Theory & Applications in Engineering Sciences, 15 (2014), pp. 509--531.
-
L. Andrieu, R. Henrion, W. Römisch, A model for dynamic chance constraints in hydro power reservoir management, European Journal of Operational Research, 207 (2010), pp. 579--589.
-
W. VAN Ackooij, R. Henrion, A. Möller, R. Zorgati, On probabilistic constraints induced by rectangular sets and multivariate normal distributions, Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 71 (2010), pp. 535--549.
-
R. Henrion, W. Römisch, On M-stationary points for a stochastic equilibrium problem under equilibrium constraints in electricity spot market modeling, Applications of Mathematics, 522 (2007), pp. 473--494.
Abstract
Modeling several competitive leaders and followers acting in an electricity market leads to coupled systems of mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints, called equilibrium problems with equilibrium constraints (EPECs). We consider a simplified model for competition in electricity markets under uncertainty of demand in an electricity network as a (stochastic) multi-leader-follower game. First order necessary conditions are developed for the corresponding stochastic EPEC based on a result of Outrata [17]. For applying the general result an explicit representation of the co-derivative of the normal cone mapping to a polyhedron is derived (Proposition 3.2). Later the co-derivative formula is used for verifying constraint qualifications and for identifying M-stationary solutions of the stochastic EPEC if the demand is represented by a finite number of scenarios.
 Contributions to Collected Editions
Contributions to Collected Editions
-
D. Pasechnyuk, P. Dvurechensky, S. Omelchenko, A. Gasnikov, Stochastic optimization for dynamic pricing, in: Advances in Optimization and Applications, N.N. Olenev, Y.G. Evtushenko, M. Jaćimović, M. Khachay, eds., 1514 of Communications in Computer and Information Science, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham, 2021, pp. 82--94, DOI 10.1007/978-3-030-92711-0 .
-
K. Safin, P. Dvurechensky, A. Gasnikov, Adaptive gradient-free method for stochastic optimization, in: Advances in Optimization and Applications, N.N. Olenev, Y.G. Evtushenko, M. Jaćimović, M. Khachay, eds., 1514 of Communications in Computer and Information Science, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham, 2021, pp. 95--108, DOI 10.1007/978-3-030-92711-0_7 .
-
H. Heitsch, N. Strogies, Consequences of uncertain friction for the transport of natural gas through passive networks of pipelines, in: Topics in Applied Analysis and Optimisation, M. Hintermüller, J.F. Rodrigues, eds., CIM Series in Mathematical Sciences, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham, 2019, pp. 211--238.
-
TH. Arnold, R. Henrion, M. Grötschel, W. Römisch ET AL., B4 -- A Jack of all trades? Solving stochastic mixed-integer nonlinear constraint programs, in: MATHEON -- Mathematics for Key Technologies, M. Grötschel, D. Hömberg, J. Sprekels, V. Mehrmann ET AL., eds., 1 of EMS Series in Industrial and Applied Mathematics, European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Zurich, 2014, pp. 135--146.
-
H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, Ch. Küchler, W. Römisch, Generierung von Szenariobäumen und Szenarioreduktion für stochastische Optimierungsprobleme in der Energiewirtschaft, in: Dezentrale regenerative Energieversorgung: Innovative Modellierung und Optimierung, R. Schultz, H.-J. Wagner, eds., LIT Verlag, Münster, 2009, pp. 227--254.
 Preprints, Reports, Technical Reports
Preprints, Reports, Technical Reports
-
D. Bernhard, H. Heitsch, R. Henrion, F. Liers, M. Stingl, A. Uihlein, V. Zipf, Continuous stochastic gradient and spherical radial decomposition, Preprint no. 3245, WIAS, Berlin, 2025, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3245 .
Abstract, PDF (634 kByte)
In this paper, a new method is presented for solving chance-constrained optimization problems. The method combines the well-established Spherical-Radial Decomposition approach with the Continuous Stochastic Gradient method. While the Continuous Stochastic Gradient method has been successfully applied to chance-constrained problems in the past, only the combination with the Spherical-Radial Decomposition allows to avoid smoothing of the integrand. In this chapter, we prove this fact for a relevant class of chance-constrained problems and apply the resulting method to the capacity maximization problem for gas networks. -
R. Henrion, D. Hömberg, N. Kliche, Modeling and simulation of an isolated mini-grid including battery operation strategies under uncertainty using chance constraints, Preprint no. 3125, WIAS, Berlin, 2024, DOI 10.20347/WIAS.PREPRINT.3125 .
Abstract, PDF (932 kByte)
This paper addresses the challenge of handling uncertainties in mini-grid operation, crucial for achieving universal access to reliable and sustainable energy, especially in regions lacking access to a national grid. Mini-grids, consisting of small-scale power generation systems and distribution infrastructure, offer a cost-effective solution. However, the intermittency and uncertainty of renewable energy sources poses challenges, mitigated by employing batteries for energy storage. Optimizing the lifespan of the battery energy storage system is critical, requiring a balance between degradation and operational expenses, with battery operation strategies playing a key role in achieving this balance. Accounting for uncertainties in renewable energy sources, demand, and ambient temperature is essential for reliable energy management strategies. By formulating a probabilistic optimal control problem for minimizing the daily operational costs of stand-alone mini-grids under uncertainty, and exploiting the concept of joint chance constraints, we address the uncertainties inherent in battery dynamics and the associated operational constraints.
 Talks, Poster
Talks, Poster
-
F. Sauer, Equilibria for distributed multi--modal energy systems under uncertainty, MATH+ Day, Urania Berlin, November 17, 2025.
-
F. Sauer, On solving generalized Nash equilibrium problems constrained by PDEs on networks under uncertainty, Mathematics for Smart Energy, November 4 - 6, 2025, WIAS Berlin, November 5, 2025.
-
R. Henrion, Chance constraints in optimal control, Lothar-Collatz-Kolloquium für Angewandte Mathematik, Universität Hamburg, Fachbereich Mathematik, April 17, 2025.
-
M. Hintermüller, A descent algorithm for the optimal control of ReLU neural network informed PDEs based on approximate directional derivatives, 30th Biennial Conference on Numerical Analysis, Minisymposium M22 ``Advancements and applications of solvers for PDE systems with nonsmooth structures", June 24 - 27, 2025, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, June 26, 2025.
-
F. Sauer, Equilibria for distributed multi-modal energy systems under uncertainty, MATH+ Day, Urania Berlin, October 18, 2024.
-
CH. Bayer, W. Kenmoe Nzali, D. Kreher, M. Landstorfer, Volatile electricity markets and battery storage: A model-based approach for optimal control, MATH+ Day, Urania Berlin, October 18, 2024.
-
M. Hintermüller, Quasi-variational inequalities: Semismooth Newton methods, optimal control, and uncertainties, Workshop on One World Optimization Seminar in Vienna, June 3 - 7, 2024, Erwin Schrödinger International Institute for Mathematics and Physics and University of Vienna, Austria, June 4, 2024.
-
M. Bongarti, Network boundary control of the semilinear isothermal Euler equation modeling gas transport on a network of pipelines, 93rd Annual Meeting of the International Association of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (GAMM 2023), Session S19 ``Optimization of Differential Equations'', May 30 - June 2, 2023, Technische Universität Dresden, June 2, 2023.
-
A. Alphonse, Risk-averse optimal control of elliptic random variational inequalities, SPP 1962 Annual Meeting 2022, October 24 - 26, 2022, Novotel Berlin Mitte, October 25, 2022.
-
H. Heitsch, An algorithmic approach for solving optimization problems with probabilistic/robust (probust) constraints (online talk), TRR154 Summer School on Modelling, Simulation and Optimization for Energy Networks (Online Event), June 8 - 9, 2022, June 8, 2022.
-
C. Geiersbach, Game-theoretical modeling for green hydrogen markets, Future WiNS: New Energies for a Sustainable World, December 7 - 9, 2022, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, December 9, 2022.
-
R. Henrion, A turnpike property for a discrete-time linear optimal control problem with probabilistic constraints, Workshop on Optimal Control Theory, June 22 - 24, 2022, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées Rouen Normandie, France, June 24, 2022.
-
H. Heitsch, An algorithmic approach for solving optimization problems with probabilistic/robust (probust) constraints, Workshop ``Applications of Semi-Infinite Optimization'' (Online Event), May 20 - 21, 2021, Fraunhofer-Institut für Techno- und Wirtschaftsmathematik ITWM, Kaiserslautern, May 21, 2021.
-
D. Sommer, Robust nonlinear model predictive control using tensor networks (online talk), European Conference on Mathematics for Industry (ECMI2021), MS23: ``Data-Driven Optimization'' (Online Event), April 13 - 15, 2021, Bergische Universität Wuppertal, April 14, 2021.
-
R. Henrion, Contraintes en probabilité au-delà de la recherche opérationnelle (online talk), 13e Journée Normandie-Mathématique (Hybrid Event), Rouen, France, June 24, 2021.
-
R. Henrion, Dealing with probust constraints in stochastic optimization, Workshop ``Applications of Semi-Infinite Optimization'' (Online Event), May 20 - 21, 2021, Fraunhofer-Institut für Techno- und Wirtschaftsmathematik ITWM, Kaiserslautern, May 21, 2021.
-
A. Caiazzo, Geothermal reservoir: Modeling, simulation and optimization for district heating in hot sedimentary acquires, Leibniz MMS Days 2019, March 20 - 22, 2019, Universität Rostock , Leibniz-Institut für Atmosphärenphysik, Kühlungsborn, March 22, 2019.
-
M. Hintermüller, Generalized Nash equilibrium problems with PDEs connected to spot markets with (gas) transport, 9th International Congress on Industrial and Applied Mathematics (ICIAM 2019), Session MS ME-1-4 1 ``Recent Advances in PDE-constrained Optimization'', July 15 - 19, 2019, Valencia, Spain, July 15, 2019.
-
M. Hintermüller, Generalized Nash equilibrium problems with application to spot markets with gas transport, Workshop ``Electricity Systems of the Future: Incentives, Regulation and Analysis for Efficient Investment'', March 18 - 22, 2019, Isaac Newton Institute, Cambridge, UK, March 21, 2019.
-
M. Hintermüller, Generalized Nash games with PDEs and applications in energy markets, French-German-Swiss Conference on Optimization (FGS'2019), September 17 - 20, 2019, Nice, France, September 20, 2019.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of multiphase fluids and droplets, Colloquium of the Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, UK, June 7, 2019.
-
I. Bremer, Using an SQP-solver for nonlinear optimization under probabilistic constraints, 100th Meeting of the GOR Working Group ``Real World Mathematical Optimization'', April 12 - 13, 2018, Regenstauf, April 12, 2018.
-
A. Caiazzo, Mathematical modeling and simulations of geothermal reservoirs, Leibniz-Institut für Angewandte Geophysik, Hannover, November 7, 2018.
-
R. Henrion, Maximization of free capacities in gas networks with random load, Conference ``Variational Analysis -- Challenges in Energy'', June 4 - 6, 2018, Castro Urdiales, Spain, June 4, 2018.
-
M. Hintermüller, Generalised Nash equilibrium problems with partial differential equations, Search Based Model Engineering Workshop, August 7 - 9, 2018, King's College London, UK, August 7, 2018.
-
M. Hintermüller, Multiobjective optimization with PDE constraints, International Workshop on PDE-Constrained Optimization, Optimal Controls and Applications, December 10 - 14, 2018, Sanya, China, December 13, 2018.
-
M. Hintermüller, Multiobjective optimization with PDE constraints, 23rd International Symposium on Mathematical Programming (ISMP2018), July 1 - 6, 2018, Bordeaux, France, July 2, 2018.
-
M. Hintermüller, Nonsmooth structures in PDE constrained optimization, Mathematisches Kolloquium, Universität Bielefeld, Fakultät für Mathematik, June 7, 2018.
-
H. Heitsch, A probabilistic approach to optimization problems in gas transport networks, SESO 2017 International Thematic Week ``Smart Energy and Stochastic Optimization'', May 30 - June 1, 2017, ENSTA ParisTech and École des Ponts ParisTech, Paris, France, June 1, 2017.
-
H. Heitsch, A probabilistic approach to optimization problems in gas transport networks, CIM-WIAS Workshop ``Topics in Applied Analysis and Optimisation'', December 6 - 8, 2017, International Center for Mathematics, University of Lisbon, Portugal, December 6, 2017.
-
R. Henrion, On M-stationary condition for a simple electricity spot market model, Workshop ``Variational Analysis and Applications for Modelling of Energy Exchange'', May 4 - 5, 2017, Université Perpignan, France, May 4, 2017.
-
R. Henrion, Probabilistic constraints in infinite dimensions, Universität Wien, Institut für Statistik und Operations Research, Austria, November 6, 2017.
-
R. Henrion, Probabilistic programming: Structural properties and applications, Control and Optimization Conference on the occasion of Frédéric Bonnans 60th birthday, November 15 - 17, 2017, Electricité de France, Palaiseau, France, November 17, 2017.
-
R. Henrion, Subdifferential characterization of Gaussian probability functions, SESO 2017 International Thematic Week ``Smart Energy and Stochastic Optimization'', May 30 - June 1, 2017, ENSTA ParisTech and École des Ponts ParisTech, Paris, France, June 1, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Generalized Nash equilibrium problems in Banach spaces: Theory, Nikaido--Isoda-based path-following methods, and applications, The Third International Conference on Engineering and Computational Mathematics (ECM2017), Stream 3 ``Computational Optimization'', May 31 - June 2, 2017, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China, June 2, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Generalized Nash games with partial differential equations, Kolloquium Arbeitsgruppe Modellierung, Numerik, Differentialgleichungen, Technische Universität Berlin, June 20, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Nonsmooth structures in PDE constrained optimization, Optimization Seminar, Chinese Academy of Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Scientific and Engineering Computing, Beijing, China, June 6, 2017.
-
M. Hintermüller, Total variation diminishing Runge--Kutta methods for the optimal control of conservation laws: Stability and order-conditions, SIAM Conference on Optimization, Minisymposium MS111 ``Optimization with Balance Laws on Graphs'', May 22 - 25, 2017, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, May 25, 2017.
-
H. Heitsch, Nonlinear probabilistic constraints in gas transportation problems, WIAS-PGMO Workshop on Nonsmooth and Stochastic Optimization with Applications to Energy Management, May 10 - 12, 2016, WIAS Berlin, Australia, May 11, 2016.
-
H. Heitsch, Optimization in gas transport networks using nonlinear probabilistic constraints, XIV International Conference on Stochastic Programming (ICSP 2016), Thematic Session: Probabilistic Constraints: Applications and Theory, June 25 - July 1, 2016, Búzios, Brazil, June 28, 2016.
-
J. Neumann, The phase field approach for topology optimization under uncertainties, ZIB Computational Medicine and Numerical Mathematics Seminar, Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin, August 25, 2016.
-
I. Bremer, Dealing with probabilistic constraints under multivariate normal distribution in a standard SQP solver by using Genz' method, WIAS-PGMO Workshop on Nonsmooth and Stochastic Optimization with Applications to Energy Management, May 10 - 12, 2016, WIAS Berlin, May 11, 2016.
-
R. Henrion, Formules du gradient pour des fonctions probabilistes Gaussiennes, Workshop on Offshore Wind Generation, September 9, 2016, Electricité de France R&D, Paris, France, September 9, 2016.
-
R. Henrion, Optimisation sous contraintes en probabilité, Séminaire du Groupe de Travail ``Modèles Stochastiques en Finance'', Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Techniques Avancées (ENSTA) ParisTech, Palaiseau, France, November 28, 2016.
-
R. Henrion, Robust-stochastic optimization problems in stationary gas networks, Conference ``Mathematics of Gas Transport'', October 6 - 7, 2016, Zuse Institut Berlin, October 6, 2016.
-
M. Hintermüller, S. Hajian, N. Strogies, Subproject B02 -- Parameter id., sensor localization and quantification of uncertainties in switched PDE systems, Annual Meeting of the Collaborative Research Center/Transregio (TRR) 154 ``Mathematical Modeling, Simulation and Optimization Using the Example of Gas Networks'', Technische Universität Berlin, October 4 - 5, 2016.
-
M. Hintermüller, S. Hajian, N. Strogies, Subproject B02 -- Parameter id., sensor localization and quantification of uncertainties in switched PDE systems, Conference ``Mathematics of Gas Transport'', Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin, October 6 - 7, 2016.
-
M. Hintermüller, Optimal control of multiphase fluids and droplets, The Fifth International Conference on Continuous Optimization, Session: ``Recent Developments in PDE-constrained Optimization I'', August 6 - 11, 2016, Tokyo, Japan, August 10, 2016.
-
M. Hintermüller, Recent trends in optimal control problems with nonsmooth structures, Computational Methods for Control of Infinite-dimensional Systems, March 14 - 18, 2016, Institute for Mathematics and its Applications, Minneapolis, USA, March 14, 2016.
-
M. Hintermüller, Towards sharp stationarity conditions for classes of optimal control problems for variational inequalities of the second kind, International INdAM Conference ``Optimal Control for Evolutionary PDEs and Related Topics (OCERTO 2016)'', June 20 - 24, 2016, Cortona, Italy, June 20, 2016.
-
H. Heitsch, Optimization of booked capacity in gas transport networks using nonlinear probabilistic constraints, 2nd International Symposium on Mathematical Programming (ISMP 2015), Cluster ``Optimization in Energy Systems'', July 13 - 17, 2015, Pittsburgh, USA, July 17, 2015.
-
R. Henrion, (Sub-)Gradient formulae for probability functions with applications to power management, Universidad de Chile, Centro de Modelamiento Matemático, Santiago de Chile, Chile, November 25, 2015.
-
R. Henrion, Application of chance constraints in a coupled model of hydro-wind energy production, Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Czech Republic, March 6, 2014.
-
R. Henrion, Application of probabilistic constraints to problems of energy management under uncertainty, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich, Power Systems Laboratory, Switzerland, September 30, 2014.
-
R. Henrion, Nonlinear programming for solving chance constrained optimization problems: Application to renewable energies, Winter School on Stochastic Programming with Applications in Energy, Finance and Insurance, March 23 - 28, 2014, Bad Hofgastein, Austria, March 25, 2014.
-
R. Henrion, Probabilistic constraints in hydro reservoir management, XIII Symposium of Specialists in Electric Operational and Expansion Planning (SEPOPE), May 18 - 21, 2014, Foz do Iguassu, Brazil, May 19, 2014.
-
R. Henrion, Probabilistic constraints via nonlinear programming: Application to energy management problems, Euro Mini Conference on Stochastic Programming and Energy Applications (EuroCSP2014), September 24 - 26, 2014, Institut Henri Poincaré, Paris, France, September 25, 2014.
-
A. Möller, Probabilistic programming in hydro power management, International Conference Operations Research ``Mastering Complexity'', September 1 - 3, 2010, München, September 1, 2010.
-
R. Henrion, A model for dynamic chance constraints in water reservoir management, 23rd European Conference on Operational Research (EURO23), July 6 - 8, 2009, Bonn, July 7, 2009.
-
R. Henrion, Characterization of M-stationary points for an equilibrium problem in an electricity spot market model, 16th International Conference on Mathematical Methods in Economics and Industry, June 15 - 18, 2009, České Budějovice, Czech Republic, June 17, 2009.
-
R. Henrion, On stationarity conditions for an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints from an electricity spot market model, 23rd European Conference on Operational Research (EURO23), July 6 - 8, 2009, Bonn, July 7, 2009.
-
R. Henrion, On a dynamical model for chance constrained programming, Conference on Optimization & Practices in Industry (COPI08), November 26 - 28, 2008, Clamart, France, November 28, 2008.
-
R. Henrion, Contraintes en probabilité: synthèse bibliographique et approche à la situation dynamique, Electricité de France R&D, Clamart, France, November 28, 2007.
 External Preprints
External Preprints
-
V. Grimm, M. Hintermüller, O. Huber, L. Schewe, M. Schmidt, G. Zöttl, A PDE-constrained generalized Nash equilibrium approach for modeling gas markets with transport, Preprint no. 458, Dokumentserver des Sonderforschungsbereichs Transregio 154, urlhttps://opus4.kobv.de/opus4-trr154/home, 2021.
-
D. Pasechnyuk, P. Dvurechensky, S. Omelchenko, A. Gasnikov, Stochastic optimization for dynamic pricing, Preprint no. arXiv:2106.14090, Cornell University Library, arXiv.org, 2021.
Abstract
We consider the problem of supply and demand balancing that is stated as a minimization problem for the total expected revenue function describing the behavior of both consumers and suppliers. In the considered market model we assume that consumers follow the discrete choice demand model, while suppliers are equipped with some quantity adjustment costs. The resulting optimization problem is smooth and convex making it amenable for application of efficient optimization algorithms with the aim of automatically setting prices for online marketplaces. We propose to use stochastic gradient methods to solve the above problem. We interpret the stochastic oracle as a response to the behavior of a random market participant, consumer or supplier. This allows us to interpret the considered algorithms and describe a suitable behavior of consumers and suppliers that leads to fast convergence to the equilibrium in a close to the real marketplace environment. -
M. Hintermüller, N. Strogies, On the identification of the friction coefficient in a semilinear system for gas transport through a network, Preprint, DFG SFB Transregio 154 ``Mathematical Modelling, Simulation and Optimization using the Example of Gas Networks'', 2017.
Contact
Projects/Grants
- Multicriteria optimization subject to equilibrium constraints using the example of gas markets
- Probabilistic constraints in gas market models
- Probabilistic least squares and applications
- Probabilistic optimal control of PDEs with feedback on unfolding randomness
- Stochastic gradient methods for almost sure state constraints for optimal control of gas flow under uncertainty