|
Modelling and simulation
of power devices for
high-voltage integrated circuits
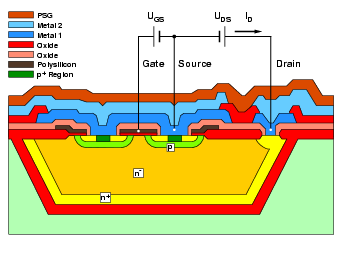
<-- Scheme of a High Voltage MOS Transistor (alpha microelectronics gmbh Frankfurt (Oder)) |

|
|
| Head: | R. Hünlich |
| Team: | G. Albinus, H. Gajewski, A. Glitzky, J. A. Griepentrog, W. Röpke |
| Cooperation: |
W. Pfau, J. Knopke, R. Rothe
(alpha microelectronics gmbh Frankfurt (Oder)) B. Heinemann (Institut für Halbleiterphysik Frankfurt (Oder)) K. Gröger W. Merz (Institut für Angewandte Mathematik Universität Erlangen) |
| Term: | July 1997 - June 2000 |
| Support: | BMBF Mathematikprogramm 1997 - 2000 Grant 03HU7FV1/0 |