|
|
|
[Contents] | [Index] |
Cooperation with: U. Bayer (GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam)
Description:
We regard the following model of thermal convection:
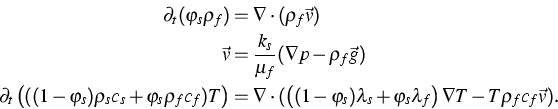
These equations describe fluid flow in a saturated porous medium, and energy transport driven by thermal diffusion in both the solid matrix and the fluid, and by convection based on the fluid flux.
The basic variables are the pressure p and the temperature
T. ![]() , cs,cf,
, cs,cf, ![]() are the
densities, heat capacities and heat transfer coefficients for solid
matrix and fluid, respectively.
are the
densities, heat capacities and heat transfer coefficients for solid
matrix and fluid, respectively. ![]() are the porosity and the hydraulic
permeability of the solid. The remaining data are fluid viscosity
are the porosity and the hydraulic
permeability of the solid. The remaining data are fluid viscosity
![]() , acceleration of gravity
, acceleration of gravity ![]() and volumetric flux of
water
and volumetric flux of
water ![]() . The system is closed by standard boundary
conditions. When applied to sedimental basins heated from below by the
Earth core, heterogeneity is introduced by the strong variation of the
solid matrix parameters between the sedimental layers.
. The system is closed by standard boundary
conditions. When applied to sedimental basins heated from below by the
Earth core, heterogeneity is introduced by the strong variation of the
solid matrix parameters between the sedimental layers.
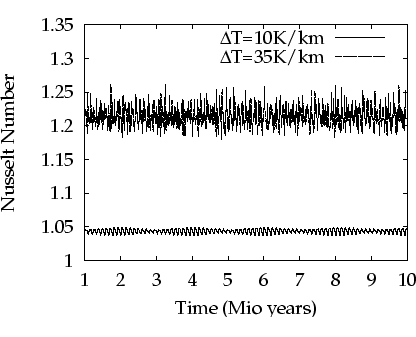
Using a time implicit, Voronoi box based finite volume method, simulations for two-dimensional slices of the North-East German basin have been carried out. These suggest that a quasi-periodic, if not chaotic flow regime might be present in the basin region.
|
From the viewpoint of the geosciences, the implications of a non-stationary flow behavior would be quite severe. Further investigation of this question, a more realistic model ansatz including the dissolved salt, and the development of three-dimensional simulation tools are subject of further research.
References:
|
|
|
[Contents] | [Index] |