Collaborator: J. Elschner
(FG 4),
J. Rehberg
(FG 1),
G. Schmidt
(FG 4)
Cooperation with: V. Maz'ya (Linköping University, Sweden)
Description:
The reported work continues efforts to prove existence, uniqueness, and
regularity results for elliptic and parabolic equations and systems
which describe phenomena in physics, chemistry, and biology (see Annual
Research Reports 2000 p. 19 et sqq. and 2002 p. 39 et sqq.). In particular,
we are interested in quasilinear systems
of the form
uk' - 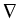 . ( . (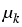 Jk(u) Jk(u)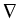 uk) = Rk(u, uk) = Rk(u,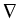 u) , u(T0) = u0 ; u = (u1,..., um) u) , u(T0) = u0 ; u = (u1,..., um)
|
(1) |
which comprise--among others--reaction-diffusion systems and heat
conduction, see [1] or
[4] and the references cited therein. The focus is on
the case of spatially three-dimensional nonsmooth domains and
discontinuous coefficients 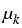 , which occur in modeling
heterogeneous media.
Over the past years various tools
for the study of such equations have been developed at the
Weierstrass Institute, see [13,
14, 15, 19].
In particular, the result of
Gröger [15] is of great use in many applications, see
[2, 4, 7,
11, 18] to name only a
few. Gröger's result states that
, which occur in modeling
heterogeneous media.
Over the past years various tools
for the study of such equations have been developed at the
Weierstrass Institute, see [13,
14, 15, 19].
In particular, the result of
Gröger [15] is of great use in many applications, see
[2, 4, 7,
11, 18] to name only a
few. Gröger's result states that
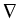 . . 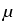 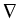 : H : H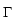 1, q( 1, q(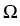 ) ) 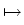 (H (H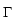 1, q'( 1, q'(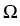 ))' ))'
|
(2) |
is a topological isomorphism for
q 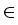 ]2, q0[ in case of Lipschitz
domains, (elliptic) L
]2, q0[ in case of Lipschitz
domains, (elliptic) L coefficient functions, and mixed
boundary conditions. Unfortunately, it is well known that
in
general q0 exceeds 2 only slightly.
Thus, in view of
embedding theorems generically only the case of two space dimensions
is covered. However,
for many applications it is not sufficient to study only equations
in two space dimensions, that means physical systems which are--in
one space direction--translational or circular invariant, see, e.g.,
[2] or [9].
The increasing structural complexity
of technical devices requires to perform
simulations and the corresponding mathematical analysis on
three-dimensional domains, see
[10, 16].
coefficient functions, and mixed
boundary conditions. Unfortunately, it is well known that
in
general q0 exceeds 2 only slightly.
Thus, in view of
embedding theorems generically only the case of two space dimensions
is covered. However,
for many applications it is not sufficient to study only equations
in two space dimensions, that means physical systems which are--in
one space direction--translational or circular invariant, see, e.g.,
[2] or [9].
The increasing structural complexity
of technical devices requires to perform
simulations and the corresponding mathematical analysis on
three-dimensional domains, see
[10, 16].
In our recent paper [22] we
study the Dirichlet problem for (1)
with
piecewise constant coefficients 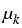 in a
polyhedral domain
in a
polyhedral domain
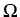
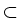
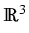 .
We
give conditions
under which the problem
admits a unique solution from a space
.
We
give conditions
under which the problem
admits a unique solution from a space
C([
T0,
T],
Lp(
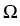
;
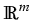
))
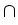 C1
C1((
T0,
T],
Lp(
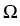
;
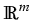
)).
The Dirichlet boundary data may depend on time,
and 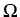 is a Lipschitz
polyhedron, that means
is a Lipschitz
polyhedron, that means 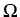 is a bounded Lipschitz domain with
piecewise plane boundary. Furthermore, we assume that
is a bounded Lipschitz domain with
piecewise plane boundary. Furthermore, we assume that 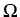 is the
union of a finite number of Lipschitz polyhedra
is the
union of a finite number of Lipschitz polyhedra 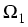 , ...,
, ...,
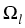 such that the
(3 x 3) matrix functions
such that the
(3 x 3) matrix functions 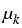 are
constant on these subdomains. The dependence of the functions Rk
on
are
constant on these subdomains. The dependence of the functions Rk
on
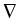 u is not stronger than quadratic.
The main advantage of our approach in comparison to the concept of
weak solutions is the strong differentiability of the solution
with
respect to time and that the divergence of the corresponding currents
jk =
u is not stronger than quadratic.
The main advantage of our approach in comparison to the concept of
weak solutions is the strong differentiability of the solution
with
respect to time and that the divergence of the corresponding currents
jk = 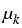 Jk(t,u)
Jk(t,u)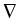 uk are functions, not only
distributions. In a strict sense, only this justifies the application
of Gauss' theorem to calculate the normal components of the currents
over boundaries of (suitable) subdomains.
Our main result, [22, Theorem 6.10], ensures the
continuity of the normal fluxes across interfaces.
This property is also very important
in the numerical analysis of finite volume
methods for heterostructures.
uk are functions, not only
distributions. In a strict sense, only this justifies the application
of Gauss' theorem to calculate the normal components of the currents
over boundaries of (suitable) subdomains.
Our main result, [22, Theorem 6.10], ensures the
continuity of the normal fluxes across interfaces.
This property is also very important
in the numerical analysis of finite volume
methods for heterostructures.
The local existence result for (1) rests upon the classical
theorem of Sobolevskii on abstract quasilinear parabolic equations in
Banach spaces and estimates for elliptic transmission problems.
The problem is to find an adequate function space with respect to which the
hypotheses of Sobolevskii's theorem can be verified.
In the three-dimensional case one has to ensure
that the linear operators in (2)
are topological isomorphisms for some q > 3, if the matrices
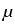 =
= 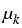 in (1) are piecewise constant. The operator
(2) corresponds to an interface (or transmission) problem
for the Laplacian,
with different anisotropic materials given on the
polyhedral subdomains
in (1) are piecewise constant. The operator
(2) corresponds to an interface (or transmission) problem
for the Laplacian,
with different anisotropic materials given on the
polyhedral subdomains 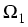 , ...,
, ..., 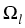 of
of 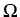 , with
Dirichlet conditions given on
, with
Dirichlet conditions given on
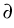
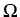 .
.
In contrast to the pure Laplacian on a Lipschitz
domain, see [17, Theorem 0.5], the gradients of
solutions to the transmission problems only belong to
L2+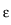 for some
for some
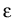 > 0. In the vicinity of
vertices and edges,
> 0. In the vicinity of
vertices and edges,
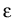 may be arbitrarily small, even for
polygonal interface problems with only four isotropic
materials meeting in a vertex, see [20].
In the case of complex material coefficients,
which corresponds to some special anisotropy, even two materials
can produce strong singularities near vertices (see
[5, 6], where similar problems are studied for
Helmholtz equations).
Therefore, a
large part of our investigation, [22], is devoted to
the optimal regularity for (2). This result inherently
applies to elliptic systems describing heterostructures on
three-dimensional domains.
may be arbitrarily small, even for
polygonal interface problems with only four isotropic
materials meeting in a vertex, see [20].
In the case of complex material coefficients,
which corresponds to some special anisotropy, even two materials
can produce strong singularities near vertices (see
[5, 6], where similar problems are studied for
Helmholtz equations).
Therefore, a
large part of our investigation, [22], is devoted to
the optimal regularity for (2). This result inherently
applies to elliptic systems describing heterostructures on
three-dimensional domains.
It is well known that the singularities of solutions to elliptic
boundary value problems near vertices and edges can be characterized
in terms of the eigenvalues of certain polynomial operator pencils on
domains of the unit sphere or the unit circle. We refer to
[21] for the case of the Dirichlet and Neumann problem
and to [12] for the polyhedral Laplace interface problem
with two isotropic materials. The corresponding analysis for several
anisotropic materials has not been performed so far and is the subject of our
investigation in [22].
To avoid the cumbersome analysis of optimal regularity near vertices,
see [3], we use the somewhat surprising fact that if
the solution of the interface problem belongs to Lq for some q > 3
near each interior point of the interface and boundary edges, then the
operator (2) is an isomorphism. Thus, the regularity
result for (2) can be reduced to that for an interface
problem on dihedral angles with one common edge. The proof relies
essentially on sharp pointwise estimates of Green's function, which we
perform in [22].
The main result of our linear regularity theory is that the operator
(2) is an isomorphism for some q > 3 provided that
a parameter
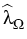 , which depends on
the decomposition of
, which depends on
the decomposition of 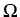 into the subdomains
into the subdomains 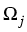 ,
satisfies the inequality
,
satisfies the inequality
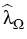 > > 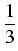 . .
|
(3) |
This number is the minimum over all edges
of spectral parameters, which
can be expressed in terms of the
eigenvalues of certain transmission problems on the unit circle.
These problems
are obtained applying the partial Fourier transform along an edge and
the Mellin transform with respect to the radial direction. The regularity
result is sufficient for the treatment of the quadratic gradient terms
in (1), if the Banach space is the space Lp with p = q/2.
However, condition (3) imposes a rather strong
assumption on the geometry of the subdomains 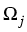 and the coefficient
and the coefficient 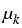 , or equivalently, on the
eigenvalues of certain pencils of ordinary differential operators.
These conditions can be checked for many heterostructures of practical
interest. Though at this point our results are restricted to
Dirichlet boundary conditions, it should be possible to extend the
result to mixed boundary conditions, which occur, e.g., in modeling
semiconductor devices ([8]). This problem will be
investigated in 2004.
, or equivalently, on the
eigenvalues of certain pencils of ordinary differential operators.
These conditions can be checked for many heterostructures of practical
interest. Though at this point our results are restricted to
Dirichlet boundary conditions, it should be possible to extend the
result to mixed boundary conditions, which occur, e.g., in modeling
semiconductor devices ([8]). This problem will be
investigated in 2004.
References:
- H. AMANN, Nonhomogeneous linear and quasilinear elliptic and
parabolic boundary value problems, in: Function Spaces, Differential
Operators and Nonlinear Analysis. Survey articles and communications of the
international conference held in Friedrichsroda, Germany, September 20-26,
1992, H.J. Schmeisser, H. Triebel, eds., vol. 133 of
Teubner-Texte Math., Teubner, Stuttgart, Leipzig, 1993, pp. 9-126.
- L. CONSIGLIERI, M.M.C. MUNIZ, Existence of solutions
for a free boundary problem in the thermoelectrical modelling of an aluminium
electrolytic cell, Eur. J. Appl. Math., 14 (2003), pp. 201-216.
- M. DAUGE, Neumann and mixed problems on curvilinear polyhedra,
Integral Equations Oper. Theory, 15 (1992), pp. 227-261.
- P. DEGOND, S. GÉNIEYS, A. JÜNGEL,
A steady-state system in non-equilibrium thermodynamics including
thermal and electrical effects, Math. Methods Appl. Sci., 21 (1998),
pp. 1399-1413.
- J. ELSCHNER, G. SCHMIDT,
Diffraction in periodic structures and optimal design of binary
gratings. I. Direct problems and gradient formulas,
Math. Methods Appl. Sci., 21 (1998), pp. 1297-1342.
- J. ELSCHNER, R. HINDER, F. PENZEL, G. SCHMIDT,
Existence, uniqueness and regularity for solutions of the conical
diffraction problem, Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci.
10, (2000), pp. 317-341.
- P. FABRIE, T. GALLOU╦T, Modeling wells in porous media
flow, Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci., 10 (2000), pp. 673-709.
- H. GAJEWSKI, Analysis und Numerik von Ladungstransport in
Halbleitern (Analysis and numerics of carrier transport in
semiconductors), Mitt. Ges. Angew. Math. Mech., 16 (1993), pp. 35-57.
- H. GAJEWSKI, K. GRÖGER, Initial boundary value problems
modelling heterogeneous semiconductor devices, in: Surveys on Analysis,
Geometry and Math. Phys., vol. 117 of Teubner-Texte Math.,
Teubner, Leipzig, 1990, pp. 4-53.
- H. GAJEWSKI, H.-CHR. KAISER, H. LANGMACH, R. NÜRNBERG, R.H.
RICHTER, Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation of
semiconductor detectors, in: Mathematics -- Key Technology for the Future.
Joint Projects Between Universities and Industry, W. Jäger,
H.J. Krebs, eds., Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2003, pp. 355-364.
- A. GLITZKY, R. HÜNLICH, Global estimates and
asymptotics for electro-reaction-diffusion systems in heterostructures,
Appl. Anal., 66 (1997), pp. 205-226.
- N. GRACHEV, V. MAZ'YA, On a contact problem for the
Laplace operator in the exterior of the boundary of a dihedral angle,
Math. Nachr., 151 (1991), pp. 207-231.
- J.A. GRIEPENTROG, K. GRÖGER, H.-CHR. KAISER, J. REHBERG,
Interpolation for function
spaces related to mixed boundary value problems, Math. Nachr.,
241 (2002), pp. 110-120.
- J.A. GRIEPENTROG, H.-CHR. KAISER, J. REHBERG,
Heat kernel and resolvent properties for second order elliptic
differential operators with general boundary conditions on Lp,
Adv. Math. Sci. Appl., 11 (2001), pp. 87-112.
- K. GRÖGER, A W1, p-estimate for solutions to mixed boundary
value problems for second order elliptic differential equations, Math. Ann.,
283 (1989), pp. 679-687.
- D. HÖMBERG, A mathematical model for induction hardening
including mechanical effects, Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl.,
5 (2004), pp. 55-90.
- D. JERISON, C.E. KENIG, The inhomogeneous Dirichlet
problem in Lipschitz domains, J. Funct. Anal., 130 (1995),
pp. 161-219.
- A. JÜNGEL, Regularity and uniqueness of solutions to a
parabolic system in nonequilibrium thermodynamics, Nonlinear Anal.,
Theory, Methods, Appl., 41 (2000), pp. 669-688.
- H.-CHR. KAISER, H. NEIDHARDT, J. REHBERG,
Classical solutions of quasilinear parabolic systems on two
dimensional domains, Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl., in press.
- R.B. KELLOG, On the Poisson equation with intersecting interfaces,
Appl. Anal., 4 (1975), pp. 101-129.
- V. KOZLOV, V. MAZ'YA, J. ROSSMANN,
Spectral Problems Associated with Corner Singularities of Solutions to
Elliptic Equations, vol. 85 of Math. Surv. Monogr.,
American Mathematical Society (AMS), Providence, RI, 2001.
- V. MAZ'YA, J. ELSCHNER, J. REHBERG, G. SCHMIDT,
Solutions for quasilinear
nonsmooth evolution systems in Lp, Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal., in press.
LaTeX typesetting by I. Bremer
2004-08-13
![]() in a
polyhedral domain
in a
polyhedral domain
![]()
![]()
![]() .
We
give conditions
under which the problem
admits a unique solution from a space
.
We
give conditions
under which the problem
admits a unique solution from a space
![]() =
= ![]() in (1) are piecewise constant. The operator
(2) corresponds to an interface (or transmission) problem
for the Laplacian,
with different anisotropic materials given on the
polyhedral subdomains
in (1) are piecewise constant. The operator
(2) corresponds to an interface (or transmission) problem
for the Laplacian,
with different anisotropic materials given on the
polyhedral subdomains ![]() , ...,
, ..., ![]() of
of ![]() , with
Dirichlet conditions given on
, with
Dirichlet conditions given on
![]()
![]() .
.
![]() for some
for some
![]() > 0. In the vicinity of
vertices and edges,
> 0. In the vicinity of
vertices and edges,
![]() may be arbitrarily small, even for
polygonal interface problems with only four isotropic
materials meeting in a vertex, see [20].
In the case of complex material coefficients,
which corresponds to some special anisotropy, even two materials
can produce strong singularities near vertices (see
[5, 6], where similar problems are studied for
Helmholtz equations).
Therefore, a
large part of our investigation, [22], is devoted to
the optimal regularity for (2). This result inherently
applies to elliptic systems describing heterostructures on
three-dimensional domains.
may be arbitrarily small, even for
polygonal interface problems with only four isotropic
materials meeting in a vertex, see [20].
In the case of complex material coefficients,
which corresponds to some special anisotropy, even two materials
can produce strong singularities near vertices (see
[5, 6], where similar problems are studied for
Helmholtz equations).
Therefore, a
large part of our investigation, [22], is devoted to
the optimal regularity for (2). This result inherently
applies to elliptic systems describing heterostructures on
three-dimensional domains.
![]() , which depends on
the decomposition of
, which depends on
the decomposition of ![]() into the subdomains
into the subdomains ![]() ,
satisfies the inequality
,
satisfies the inequality