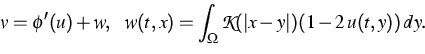Collaborator: H. Gajewski
(FG 1),
K. Gärtner
(FG 3)
Description:
Understanding an image as binary grey ``alloy'' of a black and a white
component, we
use a nonlocal phase separation model [1], [3], [4]
to describe image segmentation
and noise reduction.
The model consists in a
degenerate nonlinear parabolic equation with a nonlocal drift term additionally
to the familiar Perona-Malik model:
![\begin{displaymath}
\frac{\partial u}{\partial t} -
\nabla \cdot [f(\vert\nabla ...
...abla w}{\phi ''(u)})]
+ \beta (u-g)=0, ~~
u(0,\cdot)= g(\cdot),\end{displaymath}](img517.gif)
where
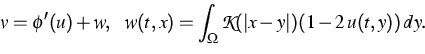
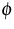 is a convex function, the kernel
is a convex function, the kernel 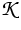 represents nonlocal
attracting forces, and v may be interpreted as chemical potential.
represents nonlocal
attracting forces, and v may be interpreted as chemical potential.
u has the meaning of a concentration/modified image, and g is the initial
value/noisy image, respectively.
Relevant examples for 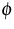 and
and 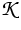 are given by
are given by
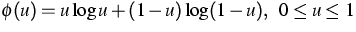 ,
, 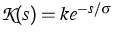 .
.
The model parameters (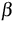 , k,
, k, 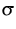 in the example) can be
adjusted by minimizing a functional evaluating smoothness and entropy
of u and the distance between u and g.
in the example) can be
adjusted by minimizing a functional evaluating smoothness and entropy
of u and the distance between u and g.
We formulate conditions for the model parameters to guarantee
global existence of a unique solution that tends exponentially
in time to a unique steady state.
This steady state is solution of a nonlocal
nonlinear elliptic boundary value problem and allows a variational
characterization.
The application of the model to noise reduction is related to model
parameters guaranteeing a unique steady state.
Image segmentation is related to parameters where a unique steady state
may not exist.
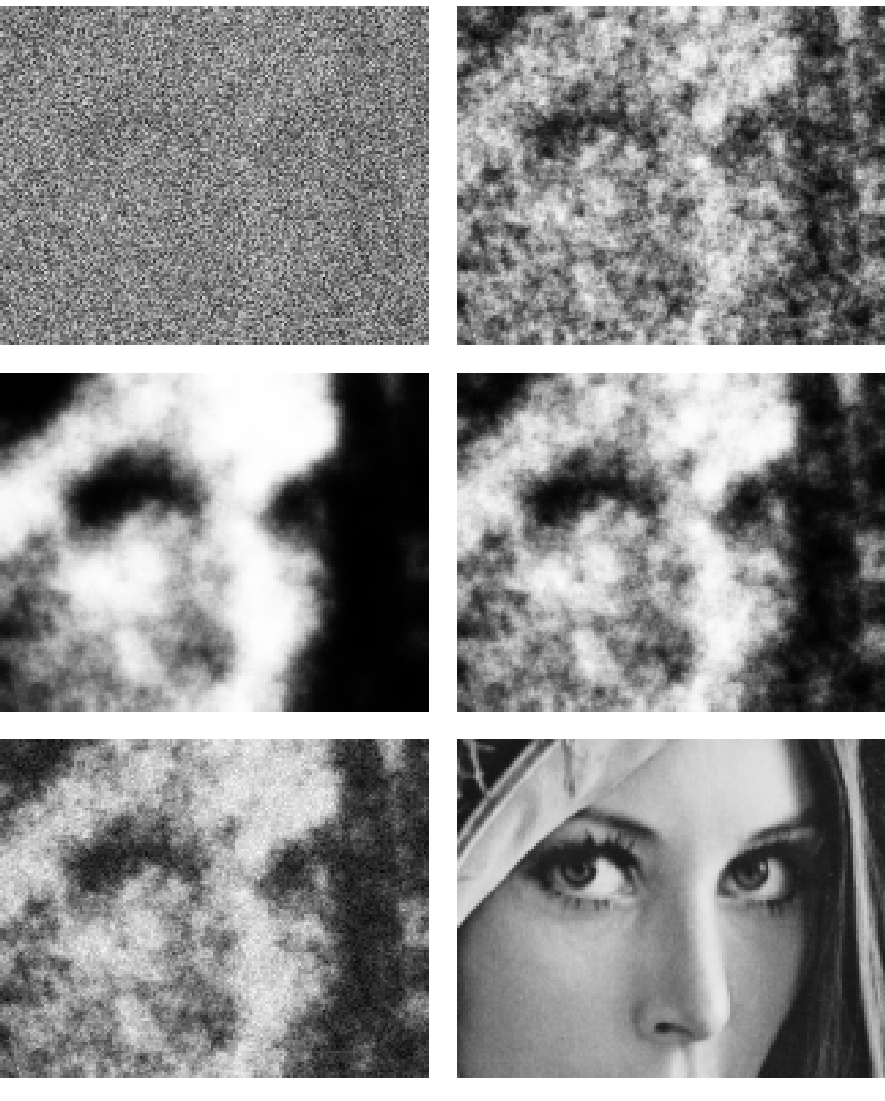
Figure 1 demonstrates some properties of the model
applied to the noise reduction problem.
References:
- H. GAJEWSKI,
On a nonlocal model of non-isothermal phase separation,
WIAS Preprint no. 671
, 2001, to appear in: Adv. Math. Sci. Appl.
- H. GAJEWSKI, K. GÄRTNER,
On a nonlocal model of image segmentation,
WIAS Preprint no. 762
, 2002.
- H. GAJEWSKI, K. ZACHARIAS,
On a nonlocal phase separation model,
WIAS Preprint no. 656
, 2001, to appear in: J. Math. Anal. Appl.
- G. GIACOMIN, J.L. LEBOWITZ,
Phase segregation dynamics in particle systems with long
range interactions I. Macroscopic limits,
J. Statist. Phys., 87 (1997), pp. 37-61.
Fig. 1:
Noisy
picture (157 by 124 pixel section, UL),
first optimization step (UR),
intermediate optimization step (ML), final optimization result (MR),
steady state (LL), original image (LR)
|
LaTeX typesetting by I. Bremer
5/16/2003
![\begin{displaymath}
\frac{\partial u}{\partial t} -
\nabla \cdot [f(\vert\nabla ...
...abla w}{\phi ''(u)})]
+ \beta (u-g)=0, ~~
u(0,\cdot)= g(\cdot),\end{displaymath}](img517.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
\frac{\partial u}{\partial t} -
\nabla \cdot [f(\vert\nabla ...
...abla w}{\phi ''(u)})]
+ \beta (u-g)=0, ~~
u(0,\cdot)= g(\cdot),\end{displaymath}](img517.gif)