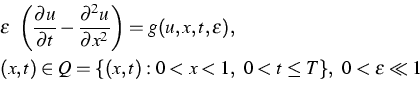
|
|
|
[Contents] | [Index] |
Collaborator: K.R. Schneider , E.V. Shchetinina
Cooperation with: V.F. Butuzov, N.N. Nefedov (Moscow State University, Russia)
Supported by: DFG: Cooperation Project ``Singulär gestörte Systeme und Stabilitätswechsel'' (Singularly perturbed systems and exchange of stability) of German and Russian scientists in the framework of the Memorandum of Understanding between DFG and RFFI
Description:
The problem of delayed exchange of stabilities for a scalar non-autonomous ordinary differential equation has been treated some time ago ([3]). Very recently, the same problem for the scalar singularly perturbed parabolic differential equation
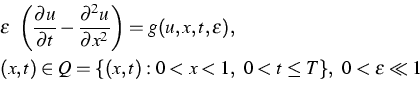 |
(1) |
has been solved successfully by means of the method of asymptotic lower and upper solutions [2]. This result provides a first proof for the existence of canard solutions for partial differential equations.
Under the assumption that the degenerate equation
g(u,x,t,0) =0
has exactly two roots ![]() and
and ![]() intersecting in some smooth curve
intersecting in some smooth curve ![]() with the representation
t=tc (x),
with the representation
t=tc (x), ![]() and that
and that ![]() for
all
for
all ![]() under consideration, we derive conditions on
g
and on u0
such that the initial-boundary value problem to (1)
under consideration, we derive conditions on
g
and on u0
such that the initial-boundary value problem to (1)
![\begin{eqnarray*}
u(x,0,\varepsilon) & = & u^0 (x) \qquad \qquad \ \mbox{ for } ...
...{\partial x} (1,t,\varepsilon) = 0 \ \ \mbox{ for } \ t \in [0,T]\end{eqnarray*}](img209.gif)
has for sufficiently small ![]() a unique
solution satisfying
a unique
solution satisfying
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\lim_{\varepsilon \rightarrow 0} \ u(x,t,\varepsilon) & = & 0 ...
... (x,t) \ \ \mbox{ for } \ (x,t) \in [0,1] \times (t_{\max} , T], \end{eqnarray*}](img210.gif)
that is, ![]() and
and ![]() are lower and upper bounds for the
delay of exchange of stabilities.
are lower and upper bounds for the
delay of exchange of stabilities.
The results of the research cooperation between WIAS and the Department of Mathematics of the Faculty of Physics of the Moscow State University in the field of exchange of stabilities in multiscale systems over the last five years have been represented as a report [1] which will appear as a research monography in Russia and in the USA.
References:
Cooperation with: B. Lani-Wayda (Justus-Liebig-Universität Giessen)
Description:
Dynamical systems as mathematical models of real-life processes depend on
several parameters which are assumed to be fixed within
some time period. The influence
of parameters on the behavior of a dynamical system is
studied within the framework of bifurcation theory.
This project aims to study the influence of some relevant system
parameter ![]() changing
slowly in time (for example,
because of an aging process).
For ordinary
differential equations it is well known that a slowly changing
parameter can lead to a special phenomenon known as
delayed loss of stability [2].
Such phenomenon manifests in a
jumping behavior of some state variables which can imply dramatic
consequences (e.g., thermal explosion).
The main goal of this project is to describe a similar effect for
nonlinear differential-delay equations of the type
changing
slowly in time (for example,
because of an aging process).
For ordinary
differential equations it is well known that a slowly changing
parameter can lead to a special phenomenon known as
delayed loss of stability [2].
Such phenomenon manifests in a
jumping behavior of some state variables which can imply dramatic
consequences (e.g., thermal explosion).
The main goal of this project is to describe a similar effect for
nonlinear differential-delay equations of the type
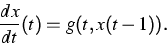 |
(2) |
For this purpose, we study the linear inhomogeneous equation
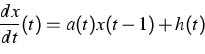 |
(3) |
assuming that the function a takes values in ![]() and changes slowly. It is well known that for constant a and h =
0, the zero solution of the linear equation (3)
is stable for
and changes slowly. It is well known that for constant a and h =
0, the zero solution of the linear equation (3)
is stable for
![]() ,and unstable for
,and unstable for ![]() . Contrary to the ODE case, the
exponential
rate of growth or decay is not directly given by a, but has to be
estimated. We provide such estimates and derive
a variation-of-constants formula for the case of nonconstant a
and
. Contrary to the ODE case, the
exponential
rate of growth or decay is not directly given by a, but has to be
estimated. We provide such estimates and derive
a variation-of-constants formula for the case of nonconstant a
and ![]() . This formula will be used to express solutions of
(2) on successive time
intervals Ii by solutions of the equation
. This formula will be used to express solutions of
(2) on successive time
intervals Ii by solutions of the equation
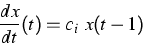
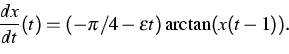
Complementary to the results on delayed loss of stability, which express similar behavior of delay equations and ordinary differential equations (ODEs), we exhibit a substantial difference between both types of equations. Namely, the additive term h(t) in the equation
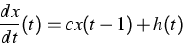
References:
Cooperation with: V.A. Sobolev, E.A. Shchepakina (Samara State University, Russia)
Description: Slow-fast systems have been considered which can be transformed into the form
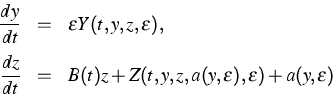 |
(4) |
with ![]() ,
,![]() is a small positive parameter,
a is a 2-dimensional vector function, and B(t) is the matrix
is a small positive parameter,
a is a 2-dimensional vector function, and B(t) is the matrix
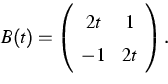
The aim of this project is to
establish an integral manifold of the form
![]() to reduce the order of
system (4) under non-hyperbolicity conditions.
In the hyperbolic case the existence of such integral manifolds
has been known for a long time (see, e.g., [3]).
to reduce the order of
system (4) under non-hyperbolicity conditions.
In the hyperbolic case the existence of such integral manifolds
has been known for a long time (see, e.g., [3]).
As a result we derived conditions on
Y and Z guaranteeing the existence of a function
![]() such that (4) has an integral manifold of the form
such that (4) has an integral manifold of the form
![]() where h is uniformly bounded,
||h|| and ||a|| tend to zero as
where h is uniformly bounded,
||h|| and ||a|| tend to zero as
![]() .Moreover, we derived an algorithm to determine the coefficients in
the asymptotic representation of the functions
.Moreover, we derived an algorithm to determine the coefficients in
the asymptotic representation of the functions ![]() and
and
![]() as
as
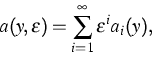
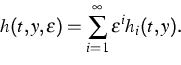
The established manifold ![]() is of canard type,
that is, it is attracting for t<0
and repelling for t>0.
is of canard type,
that is, it is attracting for t<0
and repelling for t>0.
References:
Cooperation with: V.A. Sobolev, E.A. Shchepakina (Samara State University, Russia)
Description:
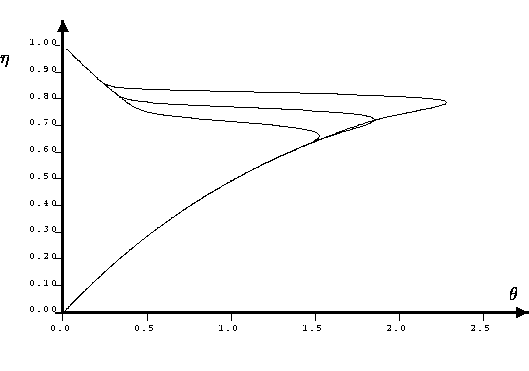
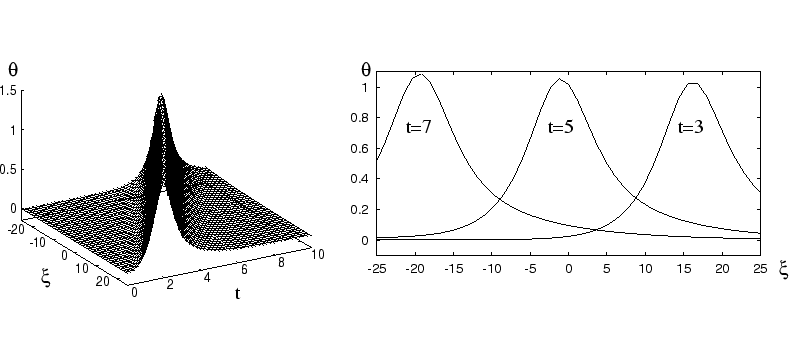
We consider the problem of thermal explosion in case of an autocatalytic combustion reaction. The goal of the project is to establish the existence of traveling wave solutions of the system
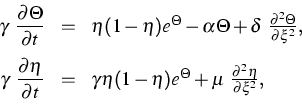 |
(5) |
where ![]() is the temperature,
is the temperature, ![]() the depth of conversion of
the gas mixture,
the depth of conversion of
the gas mixture, ![]() is a small parameter (case of highly
exothermic reaction). The existence of a traveling wave
is a small parameter (case of highly
exothermic reaction). The existence of a traveling wave
![]() ,
, ![]() to (5) is equivalent to the existence of a heteroclinic orbit of the
system (
to (5) is equivalent to the existence of a heteroclinic orbit of the
system (![]() )
)
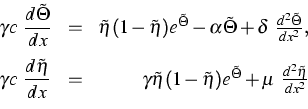 |
(6) |
connecting two equilibria of the reaction system.
Basing on the fact that the reaction system has
canard solutions separating the slow combustion regime from the
explosive one [2], we prove by applying the geometric theory of singularly
perturbed differential equations the existence of a new type of
traveling wave solutions, the so-called canard traveling waves.
|
|
References:
|
|
|
[Contents] | [Index] |