Collaborator: J. Fuhrmann
,
H. Langmach
,
K. Gärtner
,
Th. Koprucki
Description:
The aim of this project is the maintenance and further development of
pdelib, a toolbox of software components for the numerical
solution of partial differential equations.
Recent tasks within this project can be grouped into three main parts:
Maintenance. The code has now been successfully
ported to all actual Unix systems (Linux/Intel, Compaq Tru64 Unix, IBM
AIX, HP UX, Sun Solaris, SGI Irix). This took considerable effort
mainly for the installation system. A CVS release policy has been
formulated. New revisions of integrated software have been
added. Noteably, version 4.0 of the extension language Lua with more
convenient scripting possibilities is available for the pdelib
users.
New Features. Newly added features have been influenced
mainly by application projects. The main effort here
went into the multiphysics capabilities of the pdelib/sysconlaw
code for the solution of systems of viscous nonlinear conservation
laws. For a system of partial differential equations it is possible
to allow a particular variable to exist only in a subdomain. This
takes into account the situation in fuel cells where one has to be able
to couple different physical processes in the diffusion layer, the
reaction zones, and the membrane.
A similar aim is followed in the development of the 3-d
version of WIAS-TeSCA .
Here, a flexible material management scheme is tested, which
will enable the user to describe complex heterogeneous physical
models.
For Lua input scripts, a library of all SI Units has been developed.
Thus, in applications, scaling of physical units can be managed in a
safe way.
Projects. Within the research group, a considerable
effort went into the simulation of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells and the
simulation of thermal convection in sedimental layers.
Collaboration with the Research Group Partial Differential Equations
and Variational Equations (see page
![[*]](http://www.wias-berlin.de/misc/icons/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) has been established. Here, the
support of existing projects concerning the three-dimensional simulation
of semiconductor devices, the numerical handling of
) has been established. Here, the
support of existing projects concerning the three-dimensional simulation
of semiconductor devices, the numerical handling of 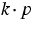 Schrödinger
operators, the simulation of resistance welding and crystal growth have
been continued. Recent new projects are the simulation bending of
gallium arsenide plates, and the GUI-based laser treatment simulator.
Future Directions.
Discussions and draft code studies have been started in order to
develop the successor of pdelib, pdelib2. Aims of this
effort are:
Schrödinger
operators, the simulation of resistance welding and crystal growth have
been continued. Recent new projects are the simulation bending of
gallium arsenide plates, and the GUI-based laser treatment simulator.
Future Directions.
Discussions and draft code studies have been started in order to
develop the successor of pdelib, pdelib2. Aims of this
effort are:
- increased efficiency, parallelization in order to be able to
treat large three-dimensional problems,
- flexible management of degrees of freedom at nodes, edges, faces of a discretization,
higher-order finite elements,
- adaptivity and geometry evolution based on Delaunay
meshing/refinement techniques,
- easy-to-understand API for the implementation of new problems,
- improved user interface.
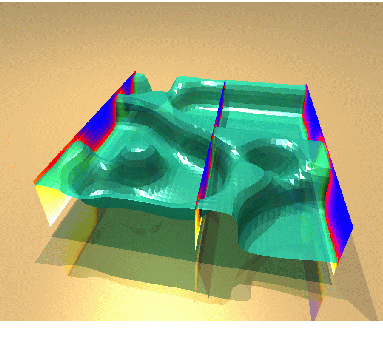
Fig. 1:
Thermal convection in a
three-dimensional porous layer. Ray-traced scene generated with
gltools and povray.
|
LaTeX typesetting by I. Bremer
9/9/2002

